文章目录
1. 面试题目
设计一个类,我们只能生成该类的一个实例(一个对象)
代码示例
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
static A&& GetA()//右值引用返回
{
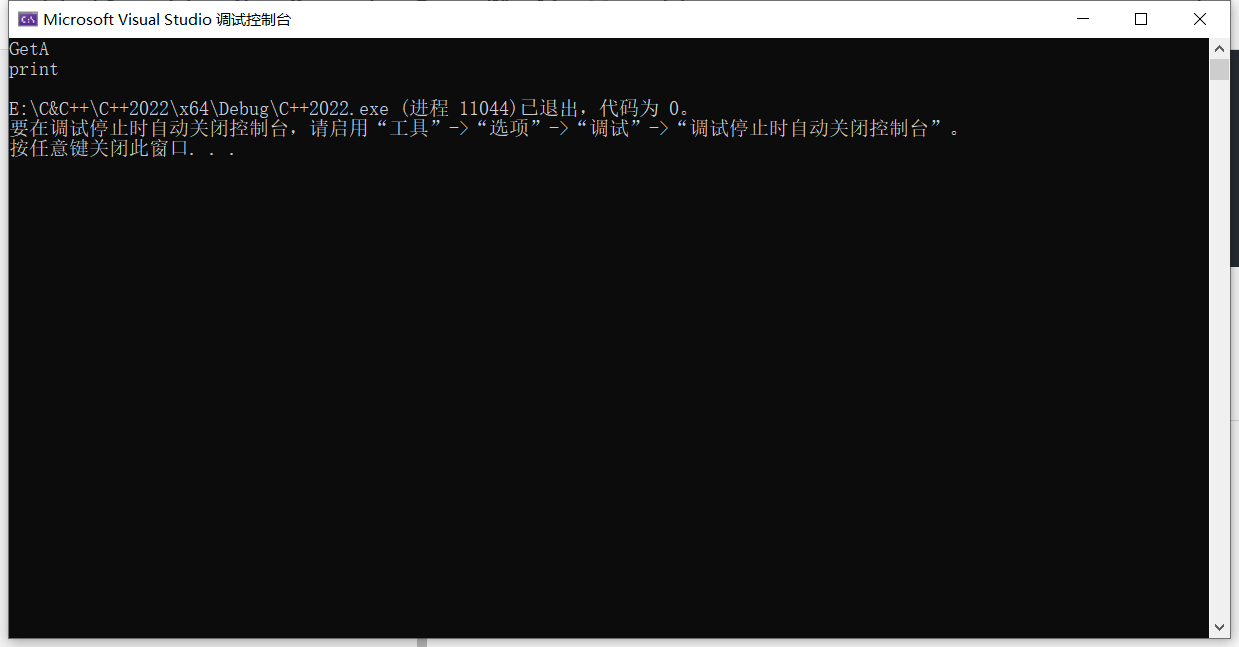
cout << "GetA" << endl;
return A();
}
A(const A& a) = delete;
void Print()
{
cout << "print" << endl;
}
private:
A() {}
};
int main()
{
A::GetA().Print();
return 0;
}
运行结果
2. 继承构造对象顺序问题
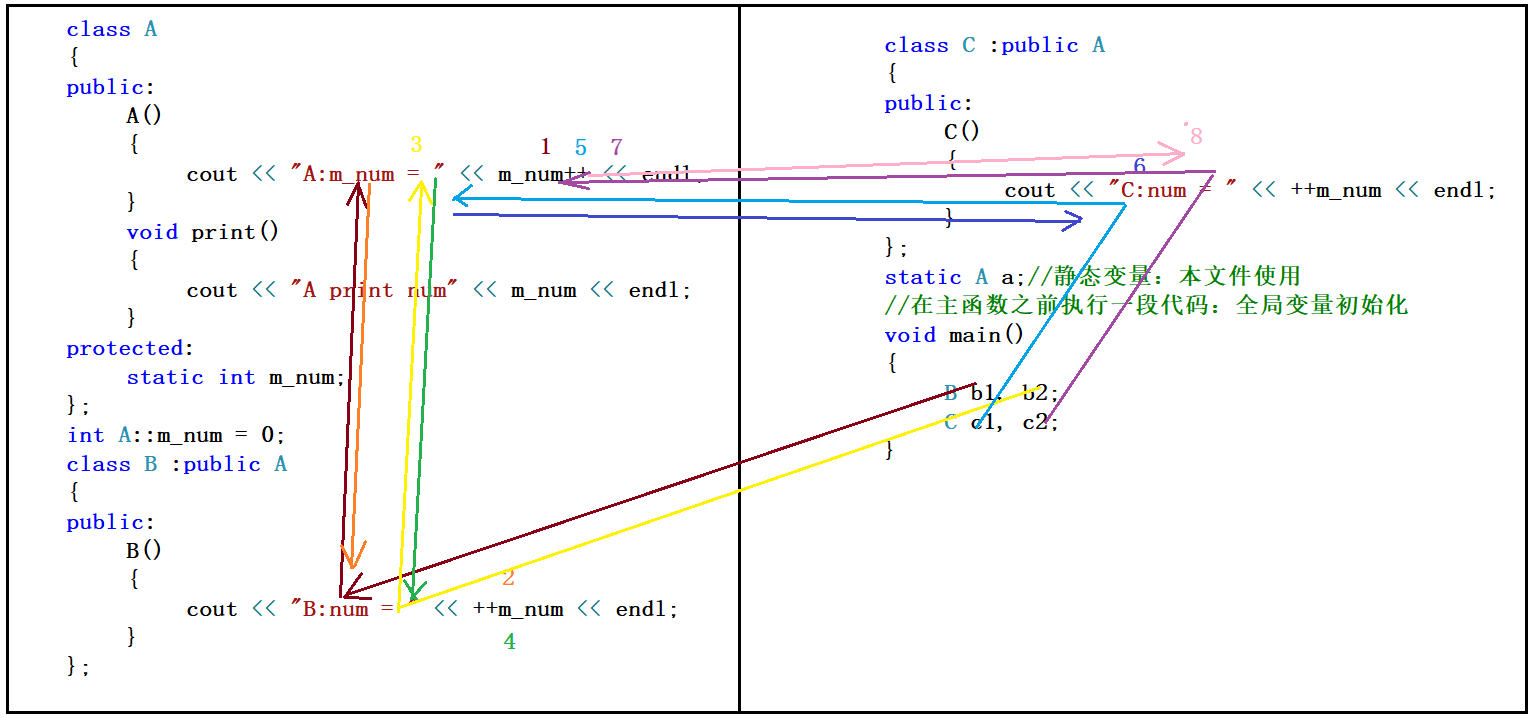
子类和基类共用静态成员
显式调用基类拷贝构造
继承构造对象调用顺序问题
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
A()
{
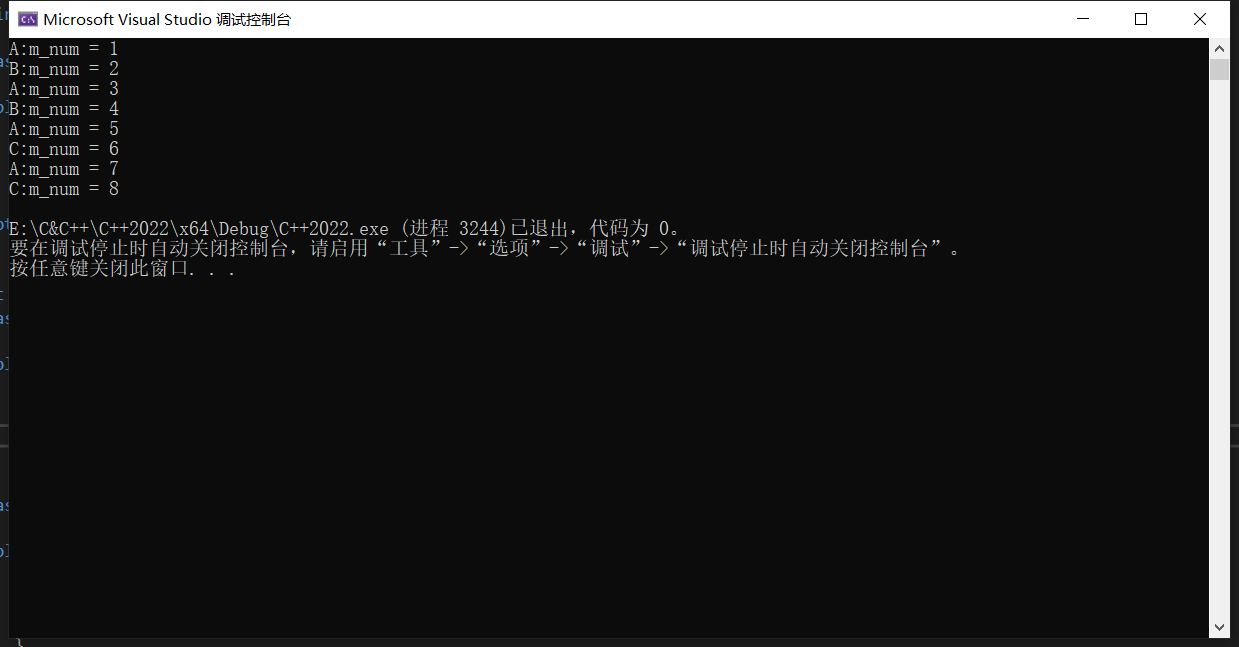
cout << "A:m_num = " << ++m_num << endl;
}
protected:
static int m_num;
};
int A::m_num = 0;
class B :public A
{
public:
B()
{
cout << "B:m_num = " << ++m_num << endl;
}
};
class C :public A
{
public:
C()
{
cout << "C:m_num = " << ++m_num << endl;
}
};
void main()
{
B b1, b2;
C c1, c2;
}
运行结果
代码图解
3. struct和class有什么区别?
3.1 在C++里面
struct默认为公有,class 默认为私有
3.2 在C语言里面
struct空结构为0,C++里面为1(有占位符)
struct不能封装函数,class可以
4. C++继承全局变量问题
代码示例
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
A()
{
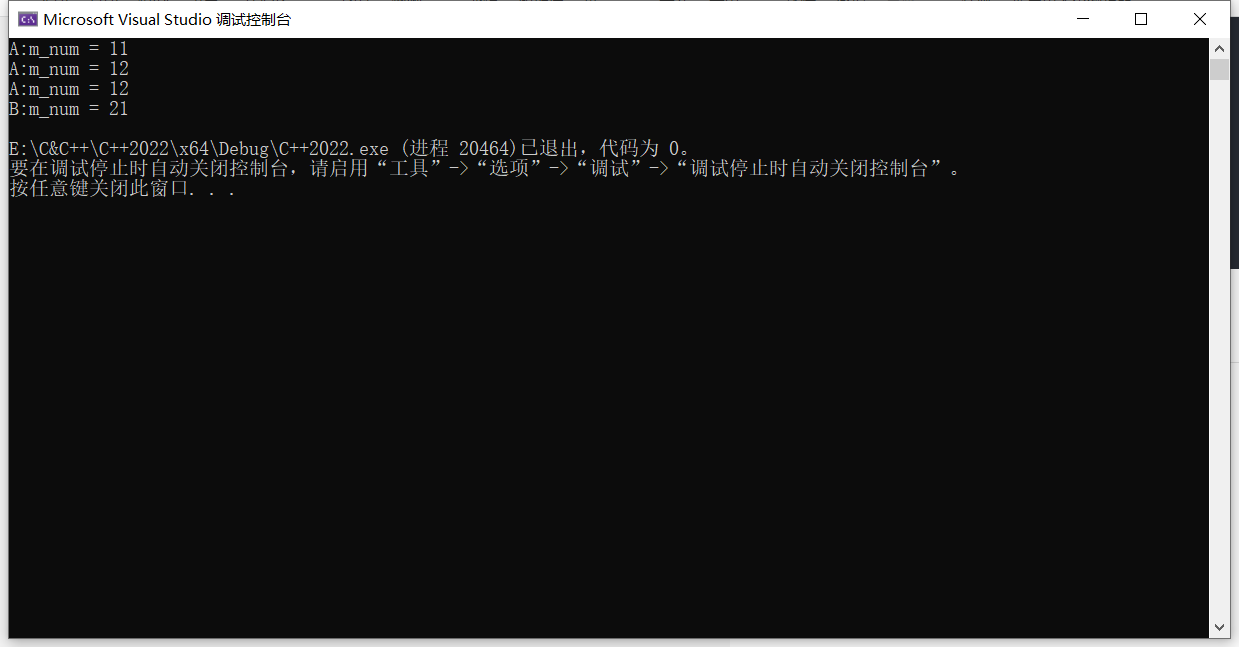
cout << "A:m_num = " << ++m_num << endl;
}
void Print()
{
cout << "A:m_num = " << m_num << endl;
}
protected:
static int m_num;
};
int A::m_num = 10;
class B :public A
{
public:
B()
{
m_num++;
}
void print()
{
cout << "B:m_num = " << m_num << endl;
}
protected:
static int m_num;
};
int B::m_num = 20;
void main()
{
A a;
B b;
a.Print();
b.print();
}
运行结果
5. 静态成员
静态成员不能访问非静态数据,如果想要访问,就必须调用对象作为参数传递给静态函数。
代码示例
class Object
{
int value;
static int num;
public:
Object(int x=0) :value(x) {}
static void Show(Object&obj)
{
obj.value += 10;
cout << obj.value << endl;
cout << num << endl;
}
};
int Object::num = 10;
int main()
{
Object obja(10);
Object objb(20);
obja.Show(obja);//参数调用
Object::Show(objb);//通过访问类名来调用
return 0;
}
6. 继承
接上一篇博客,详情查看上一篇博客:C++ 13:面向对象,继承,1-100相加
6.1 继承定义
继承(inheritance)机制是面向对象程序设计使代码可以复用的最重要的手段,它允许程序员在保持原有类特性的基础上进行扩展,增加功能。这样产生新的类,称派生类。继承呈现了面向对象程序设计的层次结构。体现了由简单到复杂的认识过程。
6.2 继承函数的调用顺序
先构建基类对象,在构建派生类对象。
代码示例
class Object
{
public:
int value;
int num;
public:
Object(int x = 0, int y = 0) :value(x), num(y)
{
cout << "create Object: " << this << endl;
}
};
class Base :public Object
{
public:
int sum;
int fib;
public:
Base(int a = 0, int b = 0) :sum(a), fib(b)
{
cout << "Create Base: " << this << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Base base;
}
代码图解

6.3 继承属性
1. 保护属性在继承关系中可以看作公有继承来使用。无论任何继承关系,派生类对象的方法可以访问隐藏基对象的公有和保护。
2. 具名对象,只有访问公有对象;继承关系,可以访问公有和保护
3. 外部函数只能访问公有成员和公有函数
6.3.1 例1:公有继承
代码示例
class A
{
private:
int ax;
protected:
int ay;
public:
int az;
public:
A()
{
ax = ay = az = 0;
}
};
class B :public A
{
private:
int bx;
protected:
int by;
public:
int bz;
public:
B()
{
bx = by = bz = 0;
}
void fun()
{
ax = 10;
ay = 20;
az = 30;
};
代码图解

6.3.2 例2:私有继承
对于c对象,ax,ay,az不能访问,bx不能访问
代码示例
class A
{
private:
int ax;
protected:
int ay;
public:
int az;
};
class B :private A
{
private:
int bx;
protected:
int by;
public:
int bz;
};
class C :public B
{
private:
int cx;
protected:
int cy;
public:
int cz;
void fun()
{
cx = cy = cz = 10;
by = bz = 20;
ay = az = 30;
}
};
内存结构

代码图解
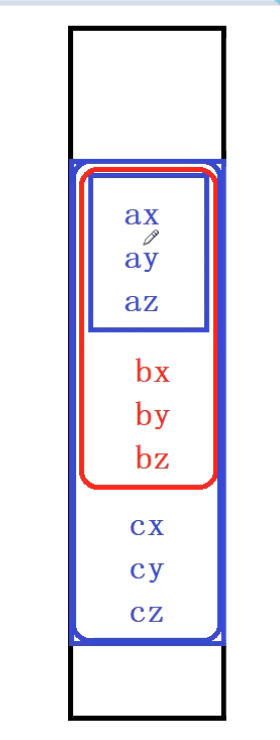
6.3.3 例3:隐藏基类同名成员
优先访问派生类中的成员方法
隐藏成员
class A
{
protected:
int ax;
public:
A() :ax(0) {}
};
class B :private A
{
private:
int ax;//命名冲突
public:
B() :ax(10) {}
void fun()
{
ax = 100;
}
};
int main()
{
B b;
b.fun();
}
隐藏方法
class A
{
protected:
int ax;
public:
A() :ax(0) {}
void fun()
{
ax = 100;
}
};
class B :public A
{
private:
int ax;//命名冲突
public:
B() :ax(10) {}
void fun()
{
ax = 100;
}
};
int main()
{
B b;
b.fun();//调用B里面的函数
b.A::fun();//调用A里面的函数
}
6.4 派生类与基类
在任何需要基类对象的地方都可以用公有派生类的对象来代替,这条规则称赋值兼容规则。它包括以下情况:C++面向对象编程中一条重要的规则是:公有继承意味着“是一个”。一定要牢牢记住这条规则。
- 派生类的对象可以赋值给基类的对象,这时是把派生类对象中从对应基类中继承来的隐藏对象赋值给基类对象。反过来不行,因为派生类的新成员无值可赋。
- 可以将一个派生类的对象的地址赋给其基类的指针变量,但只能通过这个指针访问派生类中由基类继承来的隐藏对象,不能访问派生类中的新成员。同样也不能反过来做。
- 派生类对象可以初始化基类的引用。引用是别名,但这个别名只能包含派生类对象中的由基类继承来的隐藏对象。
6.4.1 构建顺序
先构造隐藏父对象,再构建成员(切片现象)
列表方式存在构造,拷贝构造函数
}
Object(const Object& obj) :value(obj.value)
{
cout << "Copy Create Object: " << this << endl;
}
};
class Base :public Object
{
private:
int num;
public:
Base(int x) :num(x), Object(x + 10)
{
cout << "Create Base: " << this << endl;
}
~Base()
{
cout << "Destroy Base: " << this << endl;
}
Base(const Base& base) :num(base.num), Object(base)
{
cout << "Copy Creater Base: " << this << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
Base base(10);
return 0;
}
7. 同名隐藏
编译时候发生同名隐藏
“重定义”也称隐藏
-
派生类函数名与子类相同,但参数列表不同。此时不管有无virtual,基类函数都被隐藏
-
派生类函数名和参数列表都与基类相同,但基类函数没有virtual,此时基类函数被隐藏(若有virtual则属于覆盖)
Object* op = new Object(10);
Object* op = new Object[10];//连续创建10个对象
7.1 属性隐藏
代码示例
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class A
{
public:
A()
{
cout << "A:m_num = " << ++m_num << endl;
}
void Print()
{
cout << "A:m_num = " << m_num << endl;
}
protected:
static int m_num;
};
int A::m_num = 10;
class B :public A
{
public:
B()
{
m_num++;
}
void print()
{
cout << "B:m_num = " << m_num << endl;
}
protected:
static int m_num;
};
int B::m_num = 20;
void main()
{
A a;
B b;
a.Print();
b.print();
}
运行结果
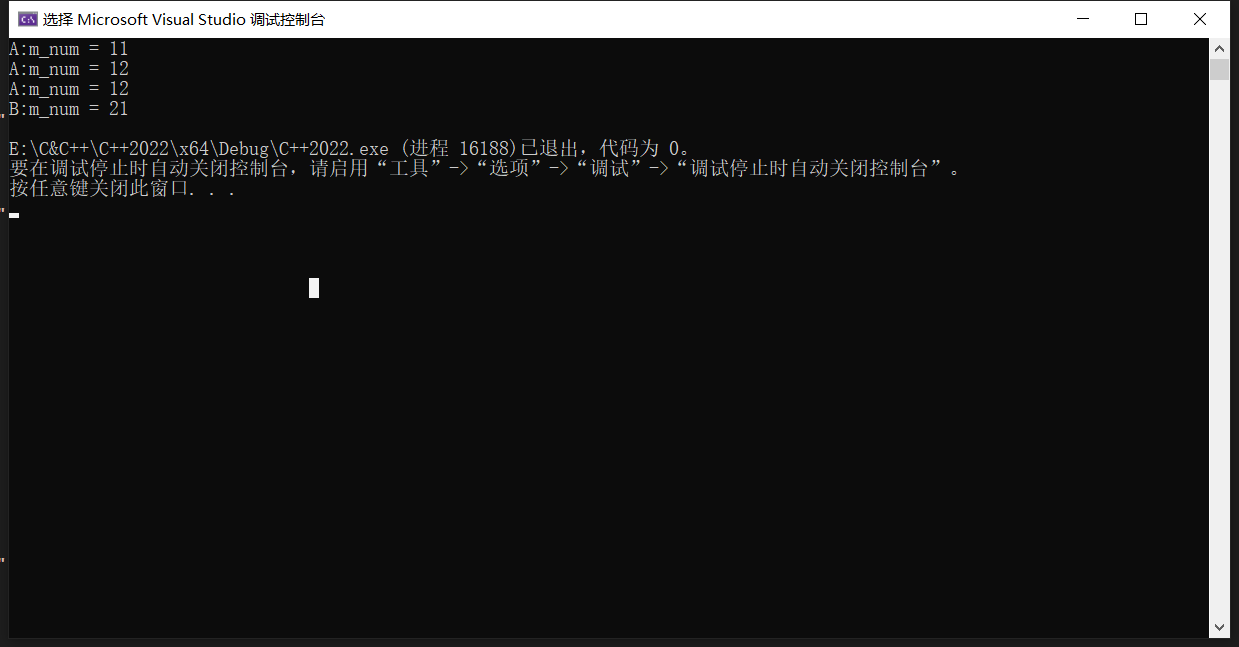
代码图解
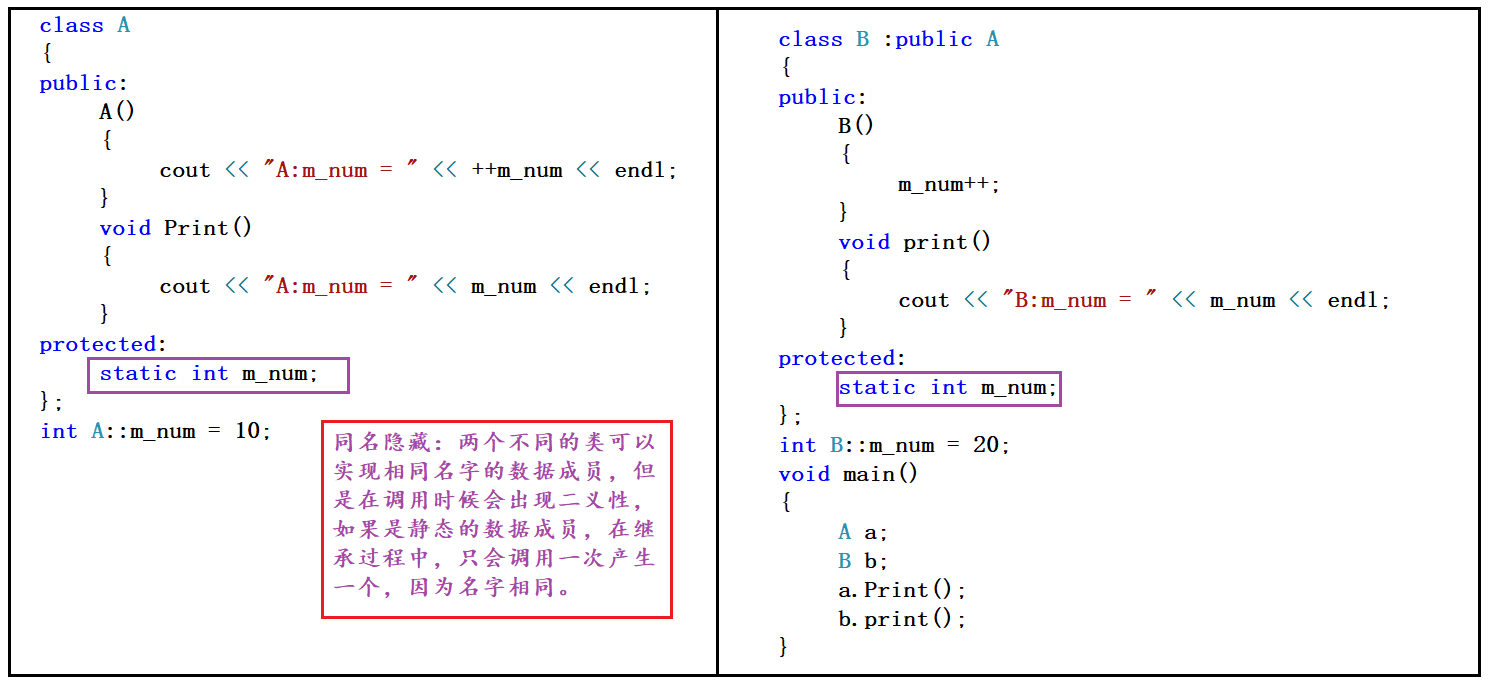
7.2 方法隐藏
问题提出:A和B里面都有fn函数,而且B继承了A里面的fn函数,所以A里面的fn函数是否存在?
答:fn都存在,只是被隐藏了,不可见了
class A
{
public:
A(int i = 0) :m_i(i) {}
void fn()
{
cout << "A:fn" << endl;
}
private:
int m_i;
};
class B :public A
{
public:
B(int i = 0, int j = 0) :A(i), m_j(j) {} //显示构造
void fn()
{
cout << "B:fn" << endl;
}
private:
int m_j;
};
显式调用
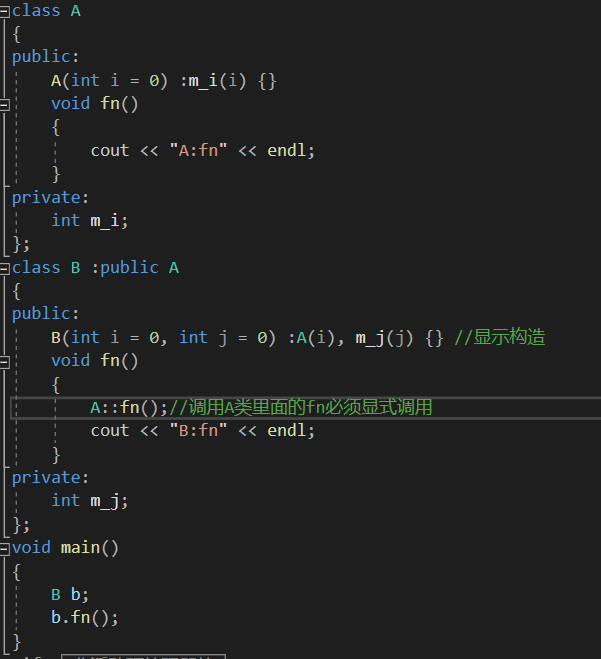
同名隐藏:如果是非虚函数,函数名相同,无论参数是否相同都是同名隐藏。如果是虚函数,函数同名,参数不同。
虚继承——>普通继承——>普通组合
8. final最终的关键字
问题提出:设计一个不能被继承的类?
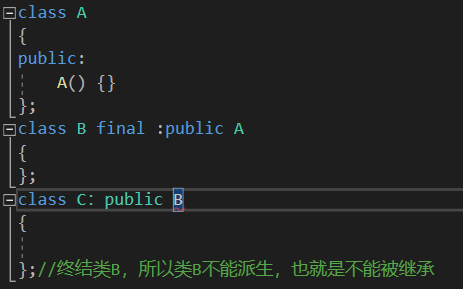
虽然不能创建对象,但是B类可以创建对象
9. 菱形继承
菱形继承是多继承一种特殊的情况
图示例
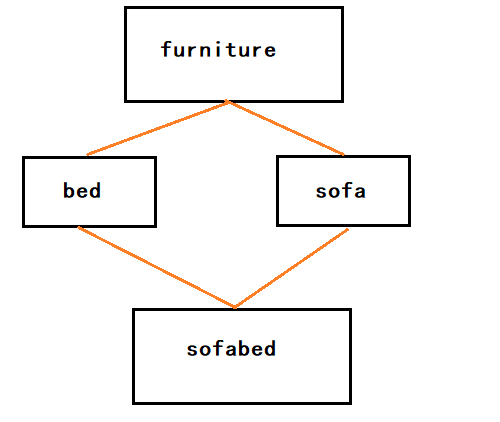
9.1 如果两个类拥有相同的属性,则派生类就会产生二义性,如何解决?
如上图所示,可以把共同基类设置为虚基类(furniture类),这样从不同路径继承来的同名数据成员在内存中就只有一个拷贝,同名函数也只有一种映射。
9.2 虚基类定义方式
class 派生类名:virtual 访问限定符 基类类名{...};
class 派生类名:访问限定符 virtual 基类类名{...}
virtual关键字只对紧随其后的基类名起作用
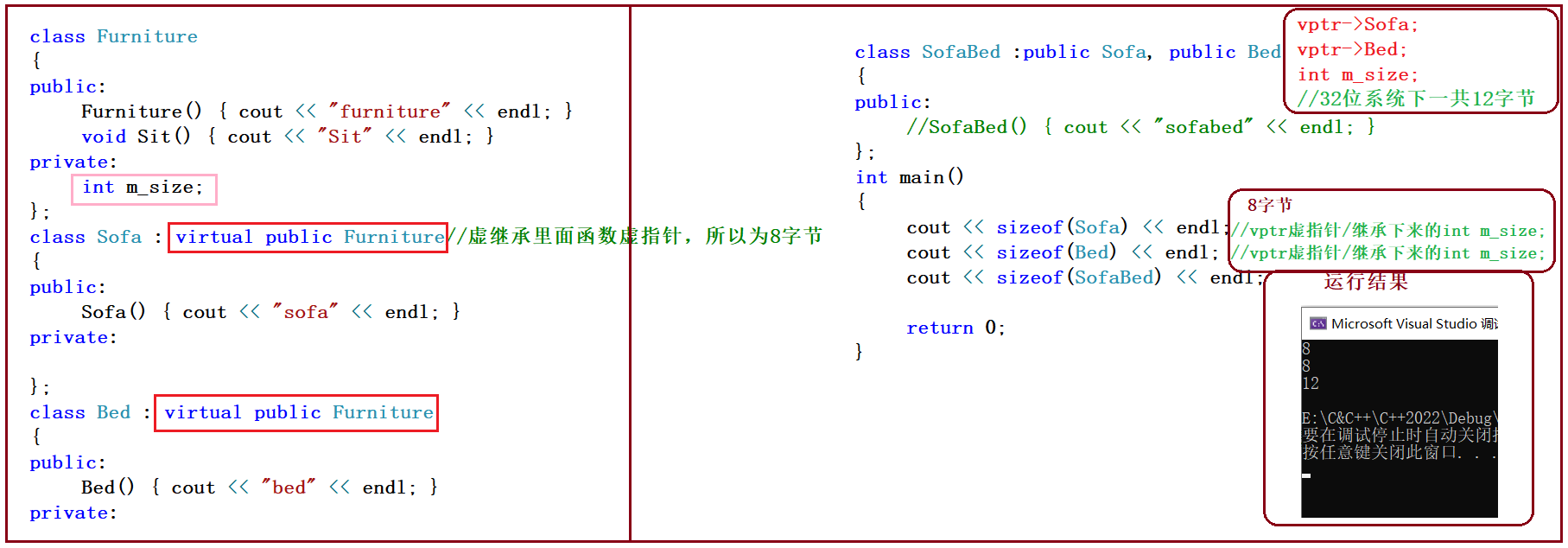
代码示例
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
class Furniture
{
public:
Furniture() { cout << "furniture" << endl; }
void Sit() { cout << "Sit" << endl; }
private:
int m_size;
};
class Sofa : virtual public Furniture//虚继承里面函数虚指针,所以为8字节
{
public:
Sofa() { cout << "sofa" << endl; }
private:
};
class Bed : virtual public Furniture
{
public:
Bed() { cout << "bed" << endl; }
private:
};
class SofaBed :public Sofa, public Bed
{
public:
//SofaBed() { cout << "sofabed" << endl; }
};
int main()
{
cout << sizeof(Sofa) << endl;
cout << sizeof(Bed) << endl;
cout << sizeof(SofaBed) << endl;
return 0;
}
运行结果
代码图解






















 405
405











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








