1. Abstract
(1)基于会话的推荐问题旨在基于匿名会话来预测用户的行为。
The problem of session-based recommendation aims to predict user actions based on anonymous sessions.
(2) 以前的方法存在的不足:不足以在会话中获得准确的用户向量,并且忽略了项目的复杂转换。
Previous methods model a session as a sequence and estimate user representations besides item representations to make recommendations. Though achieved promising results, they are insuffificient to obtain accurate user vectors in sessions and neglect complex transitions of items.
(3)为了获得准确的项目嵌入并考虑到项目的复杂转换,论文提出了一种新的方法,即基于图神经网络的会话推荐(SR-GNN)。
To obtain accurate item embedding and take complex transitions of items into account, we propose a novel method, i.e. Session-based Recommendation with Graph Neural Networks, SR-GNN for brevity.
2. Introduction
2.1 常用的会话推荐方式存在的缺点
(1)当一个会话中用户的行为序列较少时,较难捕获用户的行为表示;
without adequate user behavior in one session, these methods have diffificulty in estimating user representations.
(2)只构建了单项的转移向量,忽略了一个会话中用户的其他行为,对信息的表达能力不够强。
complex transitions among distant items are often overlooked by these methods.
注意:这里的常用的会话推荐包括:循环神经网络、马尔科夫链
2.2 论文工作的主要贡献
(1)会话序列——>图形结构——>图神经网络(GNN)来捕获复杂的项目转换
We model separated session sequences into graphstructured data and use graph neural networks to capture complex item transitions. To best of our knowledge, it presents a novel perspective on modeling in the session-based recommendation scenario.
(2)使用会话嵌入
To generate session-based recommendations, we do not rely on user representations, but use the session embedding, which can be obtained merely based on latent vectors of items involved in each single session.
3. Related Work
回顾一些基于会话的推荐系统方法,包括:传统方法、基于马尔可夫链的顺序方法和基于RNN的方法。
3.1 Conventional recommendation methods
3.1.1 Matrix factorization(MF)
(1)方法:将一个用户-项目评级矩阵分解为两个低秩矩阵进行内积
(2)缺点:用户偏好只通过一些积极的点击提供
3.1.2 The item-based neighborhood methods
(1)方法:计算同一会话中的项目相似度
(2)缺点:很难考虑项目的顺序,并且仅基于最后一次点击就能产生预测
3.1.3 sequential methods based on Markov chains
(1)方法:将推荐生成作为一个顺序优化问题
(2)缺点:独立性假设太强,限制了预测的精度
3.2 Deep-learning-based methods.
(1)RNN
(2)基于RNN衍生增强
3.3 Neural network on graphs
(1)基于无监督的网络嵌入算法LINE
(2)基于RNN和CNN的一种图数据结构上的卷积神经网络
(3)GNN
4. The Proposed Method
4.1 论文模型结构图
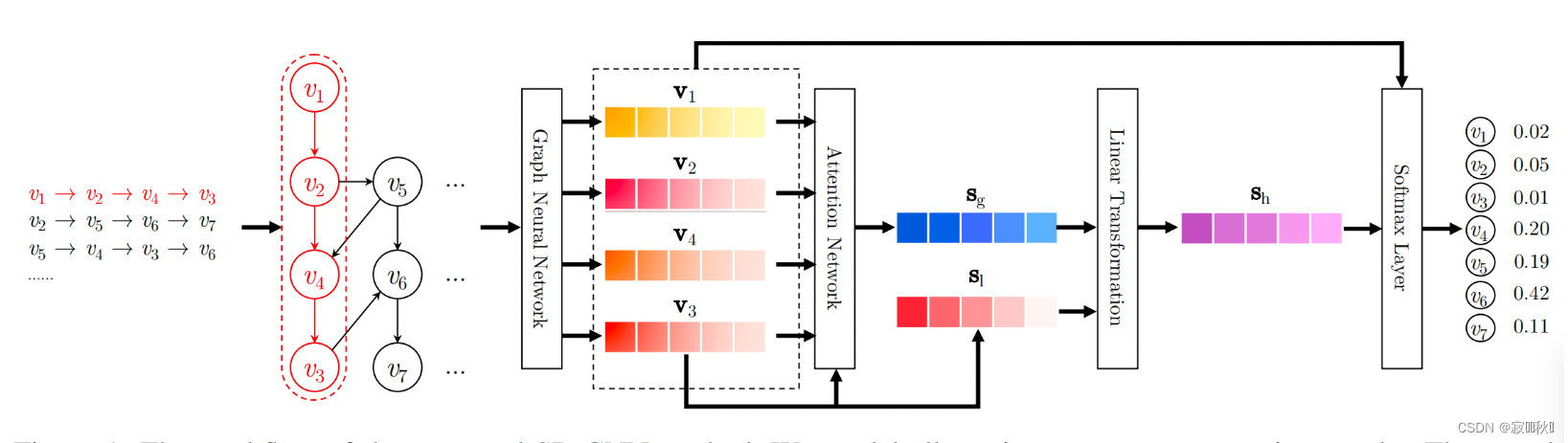
(1)输入:用户的行为序列(用户交互过的item id的列表);
(2)将用户的行为序列构造成 Session Graph;
(3)通过GNN来对所得的 Session Graph进行特征提取,得到每一个Item的向量表征;
(4)经过GNN提取Session Graph之后,通过attention机制和线性层对所有的Item的向量表征进行融合,得到User的向量表征;
(5)经过softmax函数得到用户下一个时刻可能点击的top-k个item
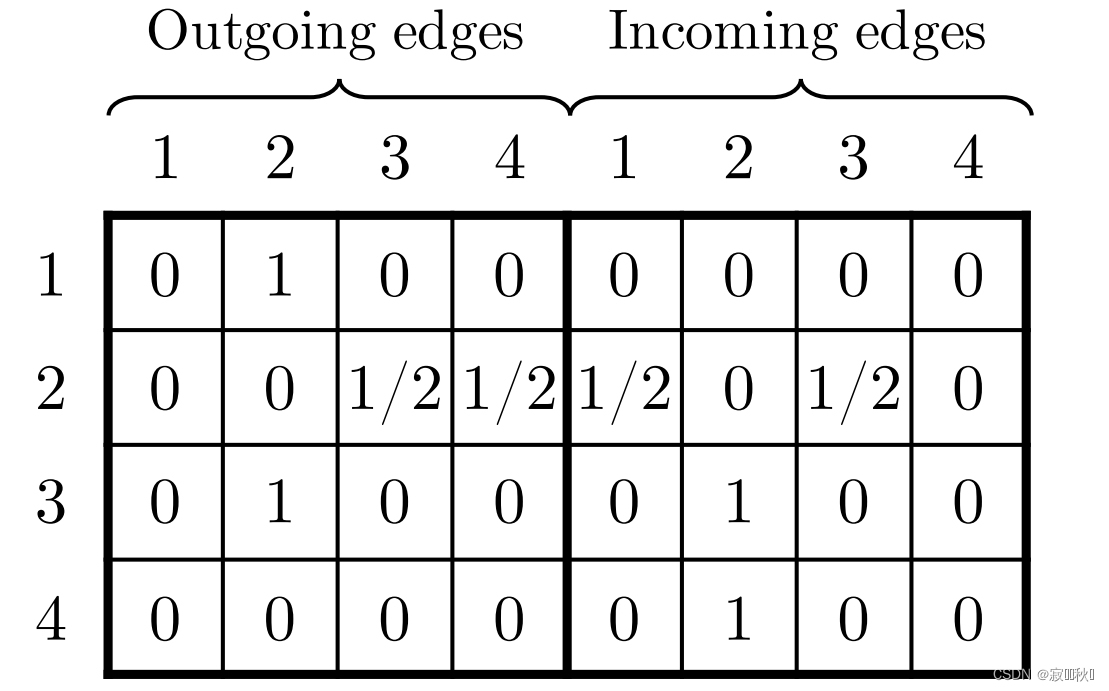
4.2 Constructing Session Graphs
(1) A example of a session graph

(2)the connection matrix As
4.3 Learning Item Embeddings on Session Graphs实现中
长期偏好 + 当前的会话兴趣 = 会话嵌入
会话嵌入公式推导:
注意:第一个公式在使用代码实现矩阵相乘的时候不能直接乘,因为这里输入是两个矩阵,导致维度对不上,在实际代码中是将outing和incoming分开进行矩阵乘积,然后进行conca。
4.4 Generating Session Embedding
(1)用attention机制来获取序列中每一个item对于序列中最后一个item的attention score,然后加权求和。
(2)将Sg与序列中的最后一个item信息相结合,得到最后的嵌入表征。
4.5 Making Recommendation and Model Training
(1)公式推导


(2)损失函数:交叉熵损失函数
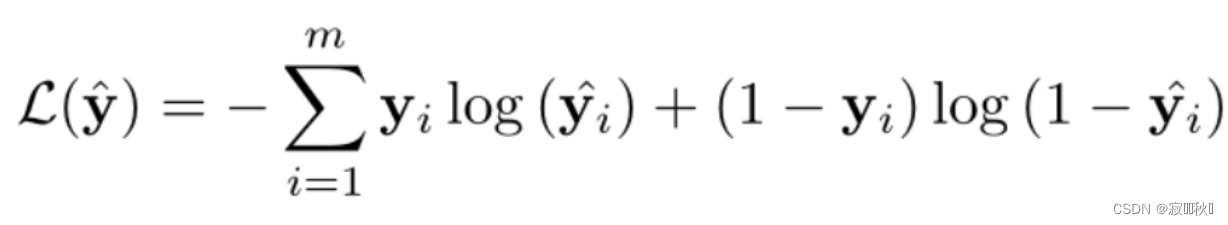
5. 模型代码实践
基于paddle的SR-GNN模型定义:
class GNN(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, embedding_size, step=1):
super(GNN, self).__init__()
self.step = step
self.embedding_size = embedding_size
self.input_size = embedding_size * 2
self.gate_size = embedding_size * 3
self.w_ih = self.create_parameter(shape=[self.input_size, self.gate_size])
self.w_hh = self.create_parameter(shape=[self.embedding_size, self.gate_size])
self.b_ih = self.create_parameter(shape=[self.gate_size])
self.b_hh = self.create_parameter(shape=[self.gate_size])
self.b_iah = self.create_parameter(shape=[self.embedding_size])
self.b_ioh = self.create_parameter(shape=[self.embedding_size])
self.linear_edge_in = nn.Linear(self.embedding_size, self.embedding_size)
self.linear_edge_out = nn.Linear(self.embedding_size, self.embedding_size)
def GNNCell(self, A, hidden):
input_in = paddle.matmul(A[:, :, :A.shape[1]], self.linear_edge_in(hidden)) + self.b_iah
input_out = paddle.matmul(A[:, :, A.shape[1]:], self.linear_edge_out(hidden)) + self.b_ioh
# [batch_size, max_session_len, embedding_size * 2]
inputs = paddle.concat([input_in, input_out], 2)
# gi.size equals to gh.size, shape of [batch_size, max_session_len, embedding_size * 3]
gi = paddle.matmul(inputs, self.w_ih) + self.b_ih
gh = paddle.matmul(hidden, self.w_hh) + self.b_hh
# (batch_size, max_session_len, embedding_size)
i_r, i_i, i_n = gi.chunk(3, 2)
h_r, h_i, h_n = gh.chunk(3, 2)
reset_gate = F.sigmoid(i_r + h_r)
input_gate = F.sigmoid(i_i + h_i)
new_gate = paddle.tanh(i_n + reset_gate * h_n)
hy = (1 - input_gate) * hidden + input_gate * new_gate
return hy
def forward(self, A, hidden):
for i in range(self.step):
hidden = self.GNNCell(A, hidden)
return hidden
class SRGNN(nn.Layer):
def __init__(self, config):
super(SRGNN, self).__init__()
# load parameters info
self.config = config
self.embedding_size = config['embedding_dim']
self.step = config['step']
self.n_items = self.config['n_items']
# define layers and loss
# item embedding
self.item_emb = nn.Embedding(self.n_items, self.embedding_size, padding_idx=0)
# define layers and loss
self.gnn = GNN(self.embedding_size, self.step)
self.linear_one = nn.Linear(self.embedding_size, self.embedding_size)
self.linear_two = nn.Linear(self.embedding_size, self.embedding_size)
self.linear_three = nn.Linear(self.embedding_size, 1, bias_attr=False)
self.linear_transform = nn.Linear(self.embedding_size * 2, self.embedding_size)
self.loss_fun = nn.CrossEntropyLoss()
# parameters initialization
self.reset_parameters()
def gather_indexes(self, output, gather_index):
"""Gathers the vectors at the specific positions over a minibatch"""
# gather_index = gather_index.view(-1, 1, 1).expand(-1, -1, output.shape[-1])
gather_index = gather_index.reshape([-1, 1, 1])
gather_index = paddle.repeat_interleave(gather_index,output.shape[-1],2)
output_tensor = paddle.take_along_axis(output, gather_index, 1)
return output_tensor.squeeze(1)
def calculate_loss(self,user_emb,pos_item):
all_items = self.item_emb.weight
scores = paddle.matmul(user_emb, all_items.transpose([1, 0]))
return self.loss_fun(scores,pos_item)
def output_items(self):
return self.item_emb.weight
def reset_parameters(self, initializer=None):
for weight in self.parameters():
paddle.nn.initializer.KaimingNormal(weight)
def _get_slice(self, item_seq):
# Mask matrix, shape of [batch_size, max_session_len]
mask = (item_seq>0).astype('int32')
items, n_node, A, alias_inputs = [], [], [], []
max_n_node = item_seq.shape[1]
item_seq = item_seq.cpu().numpy()
for u_input in item_seq:
node = np.unique(u_input)
items.append(node.tolist() + (max_n_node - len(node)) * [0])
u_A = np.zeros((max_n_node, max_n_node))
for i in np.arange(len(u_input) - 1):
if u_input[i + 1] == 0:
break
u = np.where(node == u_input[i])[0][0]
v = np.where(node == u_input[i + 1])[0][0]
u_A[u][v] = 1
u_sum_in = np.sum(u_A, 0)
u_sum_in[np.where(u_sum_in == 0)] = 1
u_A_in = np.divide(u_A, u_sum_in)
u_sum_out = np.sum(u_A, 1)
u_sum_out[np.where(u_sum_out == 0)] = 1
u_A_out = np.divide(u_A.transpose(), u_sum_out)
u_A = np.concatenate([u_A_in, u_A_out]).transpose()
A.append(u_A)
alias_inputs.append([np.where(node == i)[0][0] for i in u_input])
# The relative coordinates of the item node, shape of [batch_size, max_session_len]
alias_inputs = paddle.to_tensor(alias_inputs)
# The connecting matrix, shape of [batch_size, max_session_len, 2 * max_session_len]
A = paddle.to_tensor(A)
# The unique item nodes, shape of [batch_size, max_session_len]
items = paddle.to_tensor(items)
return alias_inputs, A, items, mask
def forward(self, item_seq, mask, item, train=True):
if train:
alias_inputs, A, items, mask = self._get_slice(item_seq)
hidden = self.item_emb(items)
hidden = self.gnn(A, hidden)
alias_inputs = alias_inputs.reshape([-1, alias_inputs.shape[1],1])
alias_inputs = paddle.repeat_interleave(alias_inputs, self.embedding_size, 2)
seq_hidden = paddle.take_along_axis(hidden,alias_inputs,1)
# fetch the last hidden state of last timestamp
item_seq_len = paddle.sum(mask,axis=1)
ht = self.gather_indexes(seq_hidden, item_seq_len - 1)
q1 = self.linear_one(ht).reshape([ht.shape[0], 1, ht.shape[1]])
q2 = self.linear_two(seq_hidden)
alpha = self.linear_three(F.sigmoid(q1 + q2))
a = paddle.sum(alpha * seq_hidden * mask.reshape([mask.shape[0], -1, 1]), 1)
user_emb = self.linear_transform(paddle.concat([a, ht], axis=1))
loss = self.calculate_loss(user_emb,item)
output_dict = {
'user_emb': user_emb,
'loss': loss
}
else:
alias_inputs, A, items, mask = self._get_slice(item_seq)
hidden = self.item_emb(items)
hidden = self.gnn(A, hidden)
alias_inputs = alias_inputs.reshape([-1, alias_inputs.shape[1],1])
alias_inputs = paddle.repeat_interleave(alias_inputs, self.embedding_size, 2)
seq_hidden = paddle.take_along_axis(hidden, alias_inputs,1)
# fetch the last hidden state of last timestamp
item_seq_len = paddle.sum(mask, axis=1)
ht = self.gather_indexes(seq_hidden, item_seq_len - 1)
q1 = self.linear_one(ht).reshape([ht.shape[0], 1, ht.shape[1]])
q2 = self.linear_two(seq_hidden)
alpha = self.linear_three(F.sigmoid(q1 + q2))
a = paddle.sum(alpha * seq_hidden * mask.reshape([mask.shape[0], -1, 1]), 1)
user_emb = self.linear_transform(paddle.concat([a, ht], axis=1))
output_dict = {
'user_emb': user_emb,
}
return output_dict
参考内容及代码来自:手把手教你实现序列召回推荐模型






















 375
375











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








