491.递增子序列

class Solution {
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
//与前几题相比:
//仍然是树层去重树枝不去重,
//但是本题树层去重借用了集合,且本题要求取元素个数大于等于2的所有结点
public List<List<Integer>> findSubsequences(int[] nums) {
findSubsequences1(nums, 0);
return result;
}
public void findSubsequences1(int[] nums, int startIndex){
//需要最先收集元素个数大于等于2的结点的结果
if(path.size() > 1){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
}
//递归出口
if(startIndex >= nums.length){
return;
}
//因为nums元素个数最大为201个,且范围为-100~100,我们使用数组合桶法辅助树层去重
//防止下标越界习惯性多开一个空间
//为每一个树层都开一个used数组
int[] used = new int[201];
//递归回溯部分
for(int i = startIndex; i < nums.length; i++){
//非法条件:
//1、当前元素小于前一个元素
//2、树层去重,当前树层之前的集合中已经有当前元素时,需要砍掉这条分支
if(!path.isEmpty() && nums[i] < path.get(path.size() - 1) || used[nums[i] + 100] == 1){
continue;
}
used[nums[i] + 100] = 1;
path.add(nums[i]);
//递归部分,需要树枝防重,同一个元素只能取一次,同值的元素可以取多个
findSubsequences1(nums, i + 1);
//回溯部分
//因为每一个树层都开了used数组,用来记录该树层的元素以便树层去重
//所以这里的回溯串中无需复原used数组
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
}
}
46.全排列
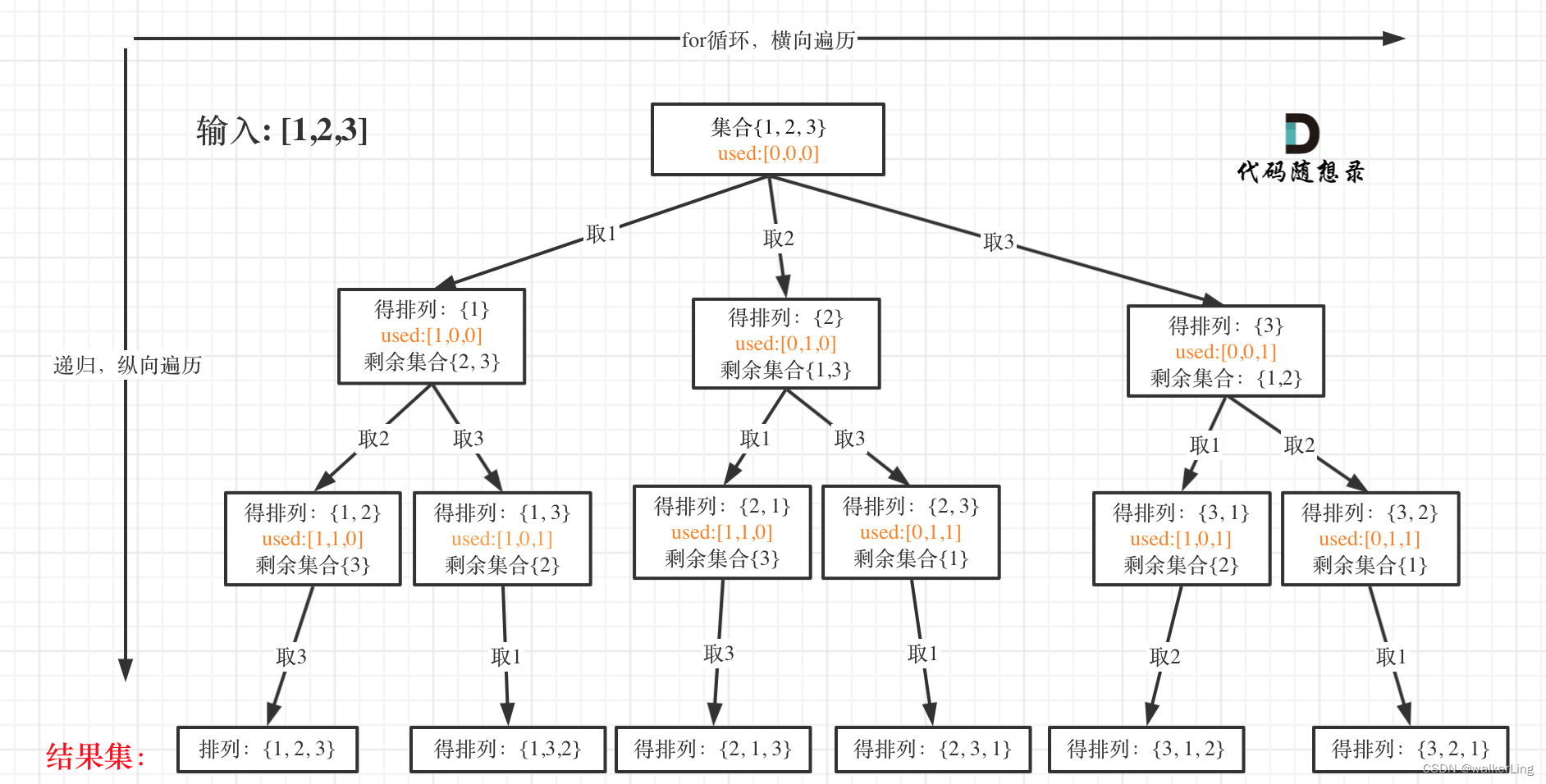
class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
//用来标记当前path中哪些元素已经用过
boolean[] used;
//排列问题与组合问题的区别在于:
//排列问题不再需要startIndex,而是每次都从0开始,
//通过used数组来跳过当前path中已经选择的元素,实现排列的选取
public List<List<Integer>> permute(int[] nums) {
if(nums.length == 0){
return result;
}
used = new boolean[nums.length];
//排列问题不需要传入startIndex
permute1(nums);
return result;
}
public void permute1(int[] nums){
//递归出口
if(path.size() == nums.length){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
//递归回溯部分
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
if(used[i] == true){
continue;
}
used[i] = true;
path.add(nums[i]);
//递归部分
permute1(nums);
//回溯部分
path.removeLast();
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
47.全排列 II

class Solution {
List<List<Integer>> result = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> path = new ArrayList<>();
boolean[] used;
//与全排列|的区别在于:
//本题中因为有重复的元素,所以需要同时进行树层去重
public List<List<Integer>> permuteUnique(int[] nums) {
//将used数组全部初始化为false
used = new boolean[nums.length];
Arrays.fill(used, false);
//因为树层去重,所以需要序列预排序
Arrays.sort(nums);
//传入used
permuteUnique1(nums);
return result;
}
public void permuteUnique1(int[] nums){
//递归出口
if(path.size() == nums.length){
result.add(new ArrayList<>(path));
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length; i++){
//树层去重
if(i > 0 && nums[i] == nums[i - 1] && !used[i - 1]){
continue;
}
if(used[i] == false){
used[i] = true;
path.add(nums[i]);
//递归
permuteUnique1(nums);
//回溯
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
}
 https://leetcode.cn/problems/non-decreasing-subsequences/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/non-decreasing-subsequences/description/ https://programmercarl.com/0491.%E9%80%92%E5%A2%9E%E5%AD%90%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97.html
https://programmercarl.com/0491.%E9%80%92%E5%A2%9E%E5%AD%90%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97.html https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1EG4y1h78v/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1EG4y1h78v/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062
 https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations/description/ https://programmercarl.com/0046.%E5%85%A8%E6%8E%92%E5%88%97.html
https://programmercarl.com/0046.%E5%85%A8%E6%8E%92%E5%88%97.html https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV19v4y1S79W/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV19v4y1S79W/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062
 https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations-ii/description/
https://leetcode.cn/problems/permutations-ii/description/ https://programmercarl.com/0047.%E5%85%A8%E6%8E%92%E5%88%97II.html
https://programmercarl.com/0047.%E5%85%A8%E6%8E%92%E5%88%97II.html https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1R84y1i7Tm/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1R84y1i7Tm/?vd_source=af4853e80f89e28094a5fe1e220d9062





















 1127
1127











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








