简介:本文从题目出发,带领大家快速入门,Java中的自带API,Queue的使用。
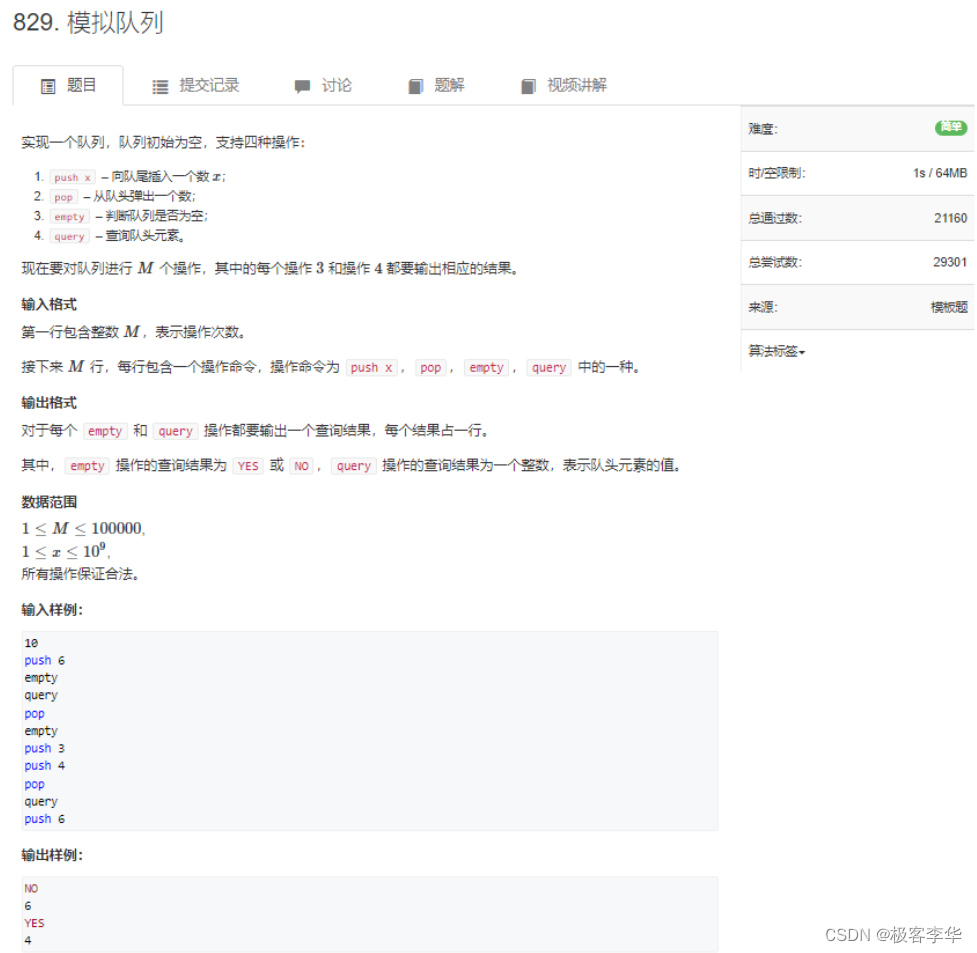
题解:
import java.util.*;
import java.io.*;
public class Main
{
static Queue<Integer> q = new LinkedList<Integer>(); // 如果要使用Queue的话 不能new Queue
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException
{
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader (new InputStreamReader(System.in));
int n = Integer.parseInt(reader.readLine());
while (n -- > 0)
{
String [] strs = reader.readLine().split(" ");
String str = strs[0];
if (str.equals("push")) q.add(Integer.parseInt(strs[1]));
else if (str.equals("pop")) q.poll();
else if (str.equals("empty")) System.out.println(q.isEmpty() ? "YES" : "NO");
else System.out.println(q.peek());
}
}
}
常用方法
boolean offer(E e) 在不违反容量限制的情况下 把指定元素入队 一般情况下 该方法和add方法差不多
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queue.add(1);
queue.add(1);
queue.add(1);
queue.add(1);
queue.add(1);
queue.offer(2);
System.out.println(queue);
/*[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2]*/
queue.add(1);
System.out.println(queue);
/*[1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 1]*/
}
E peek() 跟栈的那个一样 就是返回对首的元素 而且不删除这个元素 如果队列为空 返回null 和element() 作用相似
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queue.add(1);
queue.add(2);
queue.add(3);
System.out.println(queue.peek());
/*1*/
}
E poll() 删除并返回对首元素 如果队列为空 返回null
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queue.add(1);
queue.add(2);
queue.add(3);
System.out.println(queue.poll());
/*1*/
System.out.println(queue);
/*[2, 3]*/
}
遍历方式
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queue.add(1);
queue.add(2);
queue.add(3);
// 方法一
for (Integer i : queue)
{
System.out.print(i + " ");
}
/*1 2 3*/
System.out.println();
// 方法二
Iterator<Integer> it = queue.iterator();
while(it.hasNext())
{
System.out.print(it.next() + " ");
}
/*1 2 3*/
}
排序
public static void main(String[] args) {
Queue<Integer> queue = new LinkedList<Integer>();
queue.add(1);
queue.add(2);
queue.add(3);
// queue本身不支持排序 但是可以通过Queue 转 List 来进行自定义排序
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>(queue);
Collections.sort(list, new Comparator<Integer>() {
@Override
public int compare(Integer o1, Integer o2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
int num = 0;
if(o1 > o2) num = -1;
else num = 1;
return num;
}
});
System.out.println(list);
/*[3, 2, 1]*/
}























 483
483











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










