引言
精通设计模式是从码农脱颖而出的条件之一。跟着《图解设计模式》这本书学习设计模式,从今天开始,一天总结一个设计模式。
迭代器模式(一个一个遍历)
用处
隐藏遍历集合的内部结构,遍历不同数据结构的集合。
角色
- Iterator
迭代器接口,其中定义了获取下一个迭代的集合元素的方法next,以及判断下个元素是否存在的方法hasNext - Aggregate
集合接口,定义了获取能遍历该结构的迭代器的方法 - ConcreteAggregate
集合接口的实现类,存放了不同的数据结构,重写了获取能遍历该结构的迭代器的方法 - ConcreteIterator
迭代器接口的实现类,聚合 (或组合,图中为聚合,下文例子中为组合) Aggregate接口,以保存其接口实现类,使得ConcreteIterator类能针对不同的Aggregate接口实现类,去重写hasNext,next方法。
类图
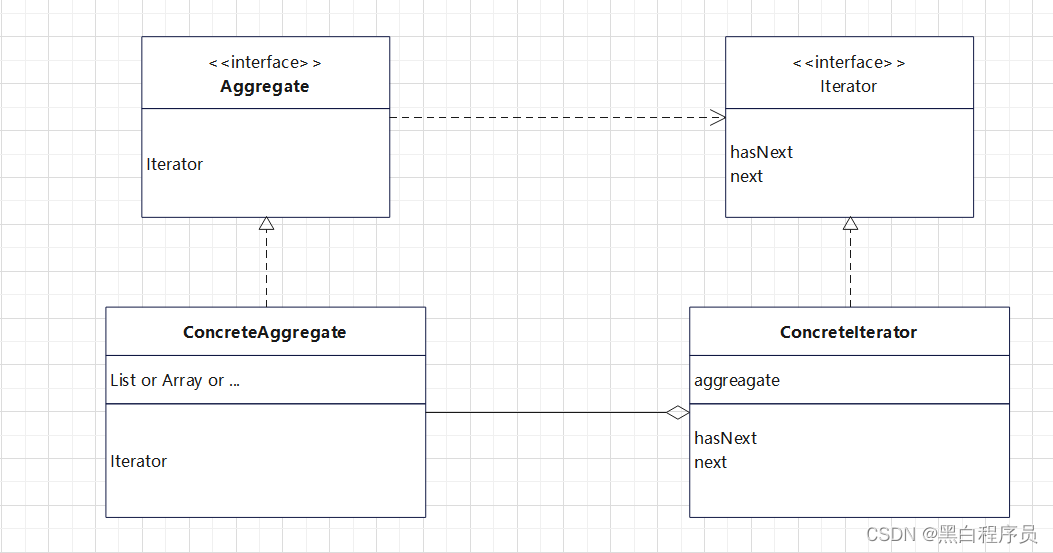
由这张图可以看出,这些角色之间的关系是
- ConcreteAggrate 实现了 Aggregate接口,通过其Iterator方法获取ConcreteIterator
- 构造出ConcreteIterator后,通过聚合ConcreteAggregate,使ConcreteIterator可以根据不同的ConcreteAggregate重写不同的迭代方法(hasNext,next)。
这样,客户端只需要创建对应ConcreteAggregate类,以及ConcreteIterator类,通过ConcreteAggregate实例 获取 ConcreteIterator实例,再调用ConcreteIterator实例的迭代方法(hasNext,next)即可完成对于不同数据结构的集合的遍历。
举例
语言描述起来很复杂,用代码解释起来很简单
public class ClientTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//添加三本书
Book book1 = new Book(1,"西游记");
Book book2 = new Book(2,"红楼梦");
Book book3 = new Book(3,"水浒传");
Book[] books = {book1,book2,book3};
//将三本书添加到书架
BookShelf bookShelf = new BookShelf(books);
//获取迭代器
Iterator iterator = bookShelf.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
Book book = (Book)iterator.next();
System.out.println(book.code+" "+book.name);
}
}
}
//Iterator角色
interface Iterator{
boolean hasNext();
Object next();
}
//ConcreteIterator角色
class BookShelfIterator implements Iterator{
BookShelf bookShelf;
int index = 0;
public BookShelfIterator(BookShelf bookShelf) {
this.bookShelf = bookShelf;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if(index < bookShelf.books.length){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
@Override
public Object next() {
Book book = bookShelf.books[index];
index ++;
return book;
}
}
//Aggregate角色
interface Aggregate {
//获取ConcreteIterator的方法
Iterator iterator();
}
//ConcreteAggregate角色
class BookShelf implements Aggregate{
Book[] books;
public BookShelf(Book[] books) {
this.books = books;
}
public Iterator iterator(){
return new BookShelfIterator(this);
}
}
class Book{
public int code ;
public String name;
public Book(int code, String name) {
this.code = code;
this.name = name;
}
}
运行结果

如果想要扩展遍历ArrayList结构,只需要新增两个类即可。
public class ClientTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//添加三本书
// Book book1 = new Book(1,"西游记");
// Book book2 = new Book(2,"红楼梦");
// Book book3 = new Book(3,"水浒传");
// Book[] books = {book1,book2,book3};
//
// //将三本书添加到书架
// BookShelf bookShelf = new BookShelf(books);
//
// //获取迭代器
// Iterator iterator = bookShelf.iterator();
Book book1 = new Book(1,"龙珠");
Book book2 = new Book(2,"海贼王");
Book book3 = new Book(3,"火影忍者");
List<Book> bookList = new ArrayList<>();
bookList.add(book1);
bookList.add(book2);
bookList.add(book3);
MangaShelf mangaShelf = new MangaShelf(bookList);
Iterator iterator = mangaShelf.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
Book book = (Book)iterator.next();
System.out.println(book.code+" "+book.name);
}
}
}
class MangaShelf implements Aggregate{
List<Book> books;
public MangaShelf(List<Book> books) {
this.books = books;
}
public Iterator iterator(){
return new MangaShelfIterator(this);
}
}
class MangaShelfIterator implements Iterator{
MangaShelf mangaShelf;
int index = 0;
public MangaShelfIterator(MangaShelf mangaShelf) {
this.mangaShelf = mangaShelf;
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
if(index < mangaShelf.books.size()){
return true;
}else{
return false;
}
}
@Override
public Object next() {
Book book = mangaShelf.books.get(index);
index ++;
return book;
}
}
总结
- 迭代器模式符合开闭原则(对修改关闭,对扩展开放,增加功能只需要增加类,不需要修改原有的代码)
- 符合了单一职责原则,将管理对象(Aggregate),和迭代对象(Iterator)的责任在不同的类中实现。
- 提供一个统一的方法遍历对象,客户不用再考虑数据的具体类型,使用一种方法就可以
遍历对象了。 - 在遍历相似对象,或遍历一组相同对象时,适合使用迭代器模式























 280
280











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










