摘要
本篇文档主要用来介绍英飞凌电源管理芯片TLF35584的使用,基于电动助力转向应用来介绍。包含一些安全机制的执行。
TLF35584介绍
TLF35584是英飞凌推出的针对车辆安全应用的电源管理芯片,符合ASIL
D安全等级要求,具有高效多电源输出通道,宽电压输入范围,根据不同的型号有3.3V和5.0V两种命名。可以为MCU提供600mA的电源,可以提供200mA的电源给通信,还可以提供精确的参考电压给ADC使用,具有SPI通信,可以监控和配置该芯片。我们以TLF35584QVVS2型号的使用来做介绍。TLF35584的封装类型以及电压分类如下表所示:
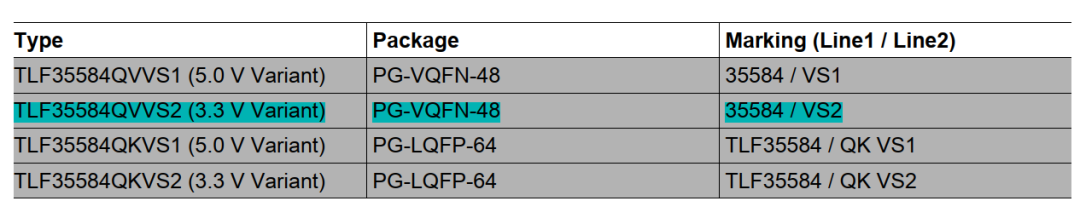
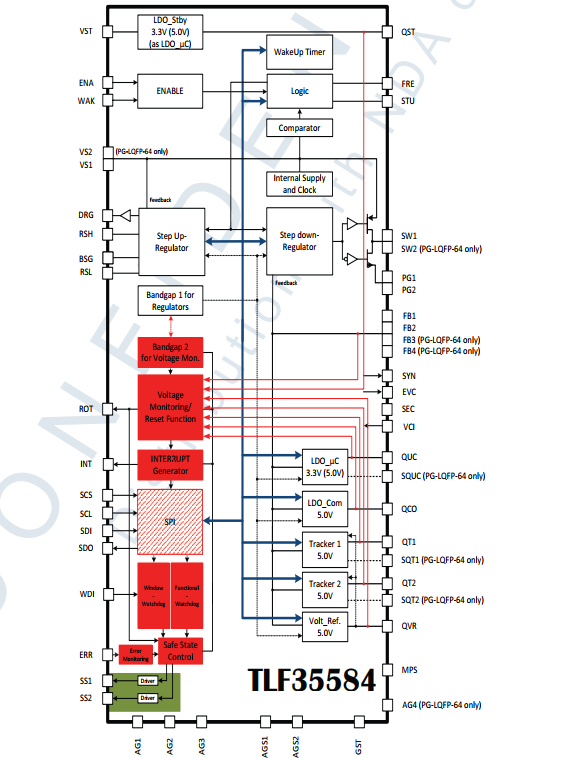
TLF35584系统框图
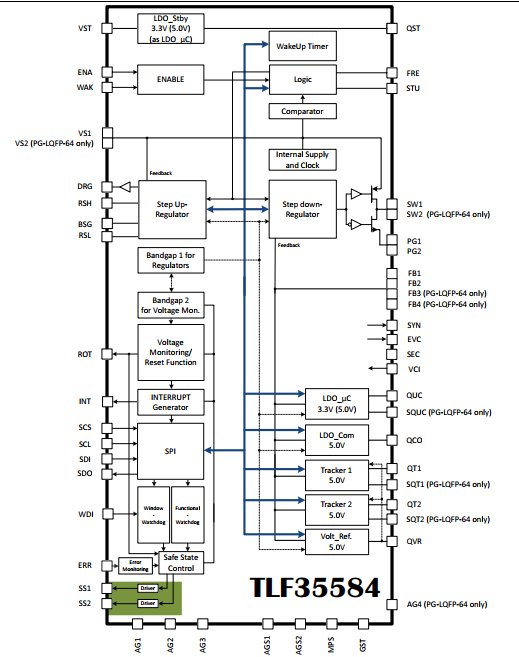
管脚介绍
| Pin | Symbol | Function |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | BSG | Boost driver ground: |
| Connect this pin to ground at the low side of an external current sense | ||
| resistor to | ||
| decouple the driver noise from the sensitive ground. If step up pre regulator | ||
| option | ||
| is not used, connect to ground. | ||
| 2 | VST | Supply voltage standby regulator, input: |
| Connect this input to supply (battery) voltage with reverse protection diode | ||
| and | ||
| capacitor between pin and ground. An EMC filter is recommended. | ||
| 3 | ENA | Enable Input: |
| A positive edge signal at this pin will wake the device. In case of not used | ||
| connect | ||
| to ground. | ||
| 4 | WAK | Wake/Inhibit Input: |
| A high level signal of defined length at this pin will wake the device. In | ||
| case of not | ||
| used, connect to ground | ||
| 5 | QST | Output standby LDO: |
| Connect a capacitor as close as possible to pin. | ||
| 6 | AG1 | Analogue ground, pin 1: |
| Connect this pin directly (low ohmic and low inductive) to ground. | ||
| 7 | AG2 | Analogue ground, pin 2: |
| Connect this pin directly (low ohmic and low inductive) to ground. | ||
| 8 | AGS1 | Analogue ground, safety, pin 1: |
| Connect this pin directly (low ohmic and low inductive) to ground. | ||
| In case a safety switch is used, connect directly to the source of the NMOS | ||
| used. | ||
| 9 | AGS2 | Analogue ground, safety, pin 2: |
| Connect this pin directly (low ohmic and low inductive) to ground. | ||
| In case a safety switch is used, connect directly to the source of the NMOS | ||
| used. | ||
| 10 | SS2 | Safe state signal 2: |
| Safe state output signal 2, sets the application into a safe state. Signal is | ||
| delayed against SS1, delay can be adjusted via SPI command. | ||
| 11 | SS1 | Safe state signal 1: |
| Safe state output signal 1, sets the application into a safe state. | ||
| 12 | SDI | Serial peripheral interface, signal data input: |
| SPI signalling port, connect to SPI port “data output” of micro processor to | ||
| receive commands during SPI communication. | ||
| 13 | SDO | Serial peripheral interface, signal data output: |
| SPI signalling port, connect to SPI port “data input” of micro processor to | ||
| send | ||
| status information during SPI communication. | ||
| 14 | SCL | Serial peripheral interface, signal clock: |
| SPI signalling port, connect to SPI port “clock” of micro processor to clock | ||
| the | ||
| device for SPI communication. | ||
| 15 | SCS | Serial peripheral interface, signal chip select: |
| SPI signalling port, connect to SPI port “chip select” of micro processor to | ||
| address | ||
| the device for SPI communication. | ||
| 16 | WDI | Watchdog input, trigger signal: |
| Input for trigger signal, connect the “trigger signal output” of the micro | ||
| processor to | ||
| this pin. In case of not used, leave open (internal pull-down). | ||
| 17 | ROT | Reset output: |
| Open drain structure with internal pull-up current source. A low signal at | ||
| this pin indicates a reset event. | ||
| 18 | INT | Interrupt signal: |
| Push-pull-stage. A low pulse at this pin indicates an interrupt, the micro | ||
| processor shall read out the SPI status registers. Connect to a non maskable | ||
| interrupt port (NMI) of the micro processor core supply voltage. | ||
| 19 | SYN | Synchronization output signal: |
| Connect this output to the optional external switch mode post regulator | ||
| synchronization input. The signal delivers the step down regulator switching | ||
| frequency either in phase or shifted by 180° (selectable via SPI command). The | ||
| switch mode post regulator shall synchronize to the rising edge. If not used, | ||
| leave open. | ||
| 20 | ERR | Error signal input: |
| Input for error signal from micro processor safety managing unit (SMU, | ||
| internal | ||
| failure detection of the micro processor). Connect the “error signal output” | ||
| of the | ||
| micro processor to this pin. | ||
| 21 | EVC | Enable external post regulator for core supply: |
| Connect this pin to the enable input of the external post regulator. If not | ||
| used, leave | ||
| open. | ||
| 22 | MPS | Microcontroller programming support pin: |
| Pull down this pin to ground for operation. Optionally, this pin can be used | ||
| for | ||
| microcontroller debugging and programming purposes. For details please refer | ||
| to | ||
| Chapter 11.7. | ||
| 23 | SEC | Configuration pin for external post regulator for core supply: |
| Connect this pin to ground if the option external post regulator is not used. | ||
| If the | ||
| option external post regulator is used, leave open. | ||
| 24 | FRE | Frequency adjustment pin: |
| Connect pin to ground for low frequency range or leave open for high frequency | ||
| range. | ||
| 25 | STU | Configuration pin for step up converter: |
| Connect this pin to ground if the option step up pre regulator is not used. If | ||
| the | ||
| option step up pre regulator is used, leave open. | ||
| 26 | VCI | Input for optional external post regulator output voltage (core |
| supply): | ||
| Connect an external resistor divider to adjust the over and under voltage | ||
| thresholds of reset output signal ROT. | ||
| If the option external post regulator is not used, leave open. | ||
| 27 | GST | Gate stress pin: |
| Not for customer use. Connect this pin directly (low ohmic and low inductive) | ||
| to | ||
| ground. | ||
| 28 | AG3 | Analogue ground, pin 3: |
| Connect this pin directly (low ohmic and low inductive) to ground. | ||
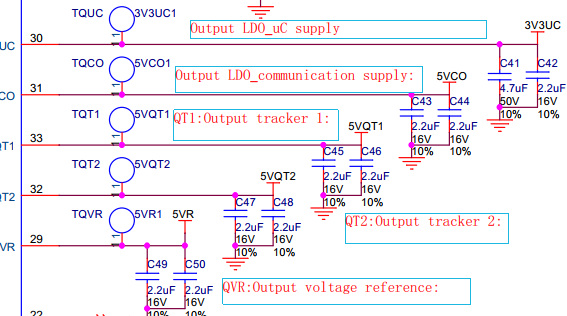
| 29 | QVR | Output voltage reference: |
| Connect a capacitor as close as possible to pin. | ||
| 30 | QUC | Output LDO_uC supply (micro processor supply): |
| Connect a capacitor as close as possible to pin. | ||
| 31 | QCO | Output LDO_communication supply: |
| Connect a capacitor as close as possible to pin. | ||
| 32 | QT2 | Output tracker 2: |
| Connect a capacitor as close as possible to pin. | ||
| 33 | QT1 | Output tracker 1: |
| Connect a capacitor as close as possible to pin. | ||
| 34 | N.C. | Internally not connected: |
| This pin is electrically not connected internally and can be kept | ||
| open/floating, | ||
| connected to GND or any other signal. Consider neighboring signals for | ||
| potential | ||
| failures. | ||
| 20 | ERR | Error signal input: |
| Input for error signal from micro processor safety managing unit (SMU, | ||
| internal | ||
| failure detection of the micro processor). Connect the “error signal output” | ||
| of the | ||
| micro processor to this pin. | ||
| 21 | EVC | Enable external post regulator for core supply: |
| Connect this pin to the enable input of the external post regulator. If not | ||
| used, leave | ||
| open. | ||
| 22 | MPS | Microcontroller programming support pin: |
| Pull down this pin to ground for operation. Optionally, this pin can be used | ||
| for | ||
| microcontroller debugging and programming purposes. For details please refer | ||
| to | ||
| Chapter 11.7. | ||
| 23 | SEC | Configuration pin for external post regulator for core supply: |
| Connect this pin to ground if the option external post regulator is not used. | ||
| If the | ||
| option external post regulator is used, leave open. | ||
| 24 | FRE | Frequency adjustment pin: |
| Connect pin to ground for low frequency range or leave open for high frequency | ||
| range. | ||
| 25 | STU | Configuration pin for step up converter: |
| Connect this pin to ground if the option step up pre regulator is not used. If | ||
| the | ||
| option step up pre regulator is used, leave open. | ||
| 26 | VCI | Input for optional external post regulator output voltage (core |
| supply): | ||
| Connect an external resistor divider to adjust the over and under voltage | ||
| thresholds of reset output signal ROT. | ||
| If the option external post regulator is not used, leave open. | ||
| 27 | GST | Gate stress pin: |
| Not for customer use. Connect this pin directly (low ohmic and low inductive) | ||
| to | ||
| ground. | ||
| 28 | AG3 | Analogue ground, pin 3: |
| Connect this pin directly (low ohmic and low inductive) to ground. | ||
| 29 | QVR | Output voltage reference: |
| Connect a capacitor as close as possible to pin. | ||
| 30 | QUC | Output LDO_uC supply (micro processor supply): |
| Connect a capacitor as close as possible to pin. | ||
| 31 | QCO | Output LDO_communication supply: |
| Connect a capacitor as close as possible to pin. | ||
| 32 | QT2 | Output tracker 2: |
| Connect a capacitor as close as possible to pin. | ||
| 33 | QT1 | Output tracker 1: |
| Connect a capacitor as close as possible to pin. | ||
| 34 | N.C. | Internally not connected: |
| This pin is electrically not connected internally and can be kept | ||
| open/floating, | ||
| connected to GND or any other signal. Consider neighboring signals for | ||
| potential | ||
| failures. | ||
| 46 | DRG | Driver output for external step up regulator power stage, connect to |
| gate: | ||
| Gate of low side switch of step up pre regulator: Connect to the gate of an | ||
| external | ||
| N-channel mosfet, line to be straight and as short as possible. If step up pre | ||
| regulator option is not used, leave open. | ||
| 47 | RSH | Sense resistor for external step up regulator power stage, high side: |
| Connect this pin to the high side of an external current sense resistor to | ||
| determine | ||
| the maximum current threshold through the external N-channel mosfet. If step | ||
| up | ||
| pre regulator option is not used, connect to ground. | ||
| 48 | RSL | Sense resistor for external step up regulator power stage, low side: |
| Connect this pin to the low side of an external current sense resistor to | ||
| determine | ||
| the maximum current threshold through the external N-channel mosfet. If step | ||
| up | ||
| pre regulator option is not used, connect to ground. | ||
| EP1 | Edge pin no 1: | |
| Keep area below this pin free of ground or other signals, do not solder this | ||
| pin to | ||
| ground or any other signal. This pin must be kept free of soldering. |
EP2| Edge pin no 2:
Keep area below this pin free of ground or other signals, do not solder this
pin to
ground or any other signal. This pin must be kept free of soldering.|
EP3| Edge pin no 3:
Keep area below this pin free of ground or other signals, do not solder this
pin to
ground or any other signal. This pin must be kept free of soldering.|
EP4| Edge pin no 4:
Keep area below this pin free of ground or other signals, do not solder this
pin to
ground or any other signal. This pin must be kept free of soldering.|
Coolin
g Tab| GND| Cooling Tab.
Connect externally to GND and heat sink area.
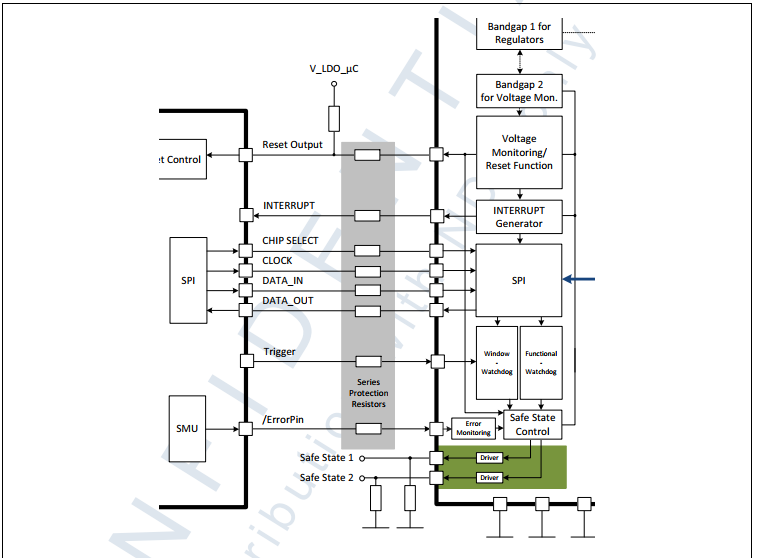
典型应用框图
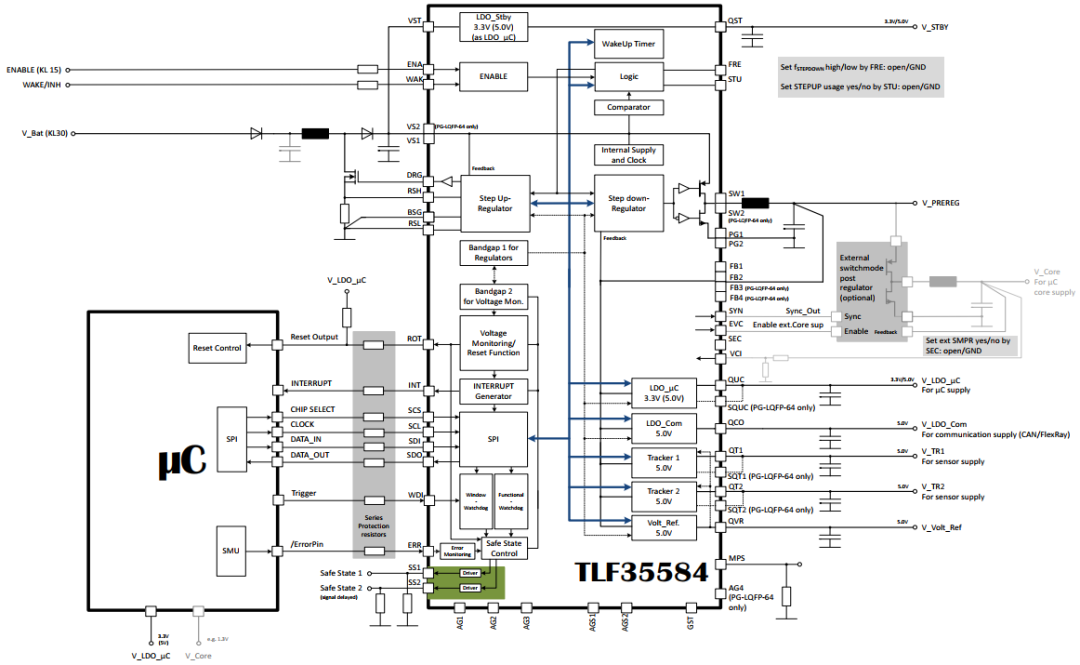
安全功能
TLF35584提供了很多安全功能来保证系统的安全
- 输出电源轨监控
1. Vprereg
2. VQUC
3. VQST
4. VQVR
5. VVCI
6. VQT1, VQT2
7. VQCO
- 提供MCU外部安全机制的时序时间监控服务
1. 监控MCU的SMU ERR输出功能
2. 监控MCU的看门狗输出服务
- 二次安全关断能力
TSR
TSR01 -在所有产生和监控的输出电压上检测和响应故障。违反将会导致系统级的单点失效
TSR02 -检测并响应MCU安全管理单元(SMU)的错误触发。违反会导致潜伏失效或者多点失效
TSR03 -检测并响应由MCU错误触发的定时监控服务,违反会导致潜伏失效或者多点失效
TSR04 -内部需要时激活二次关断信号,违反TSR04可能会导致潜伏失效
安全功能应用
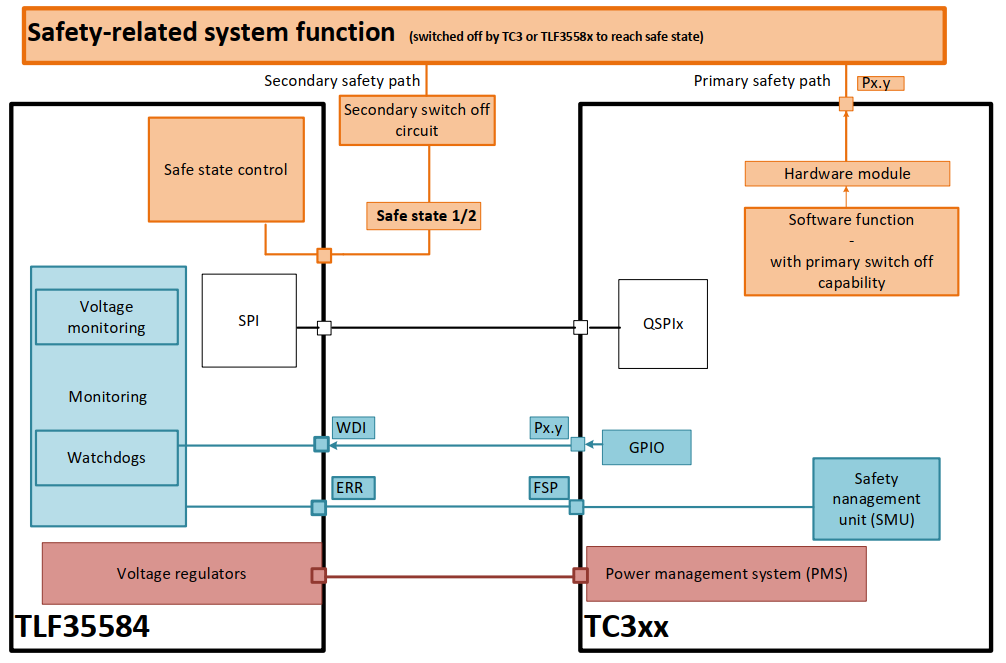
安全路径
安全路径是信号链和电路使能并维持系统的安全状态。对于一些TLF35584目标应用,达到了安全状态
通过禁用执行器、通信通道或整个系统。在这样的系统中,安全路径是安全停机路径。
首要安全路径
主要安全路径不是由PMIC管理的,而是由MCU单片机控制的。因此,主安全路径不依赖于PMIC的安全逻辑。通常,这类安全路径是通过安全MCU建立的。该单片机可以使应用程序始终处于安全状态,使用的条件在有效范围内,外部安全机制可用。
二次安全路径
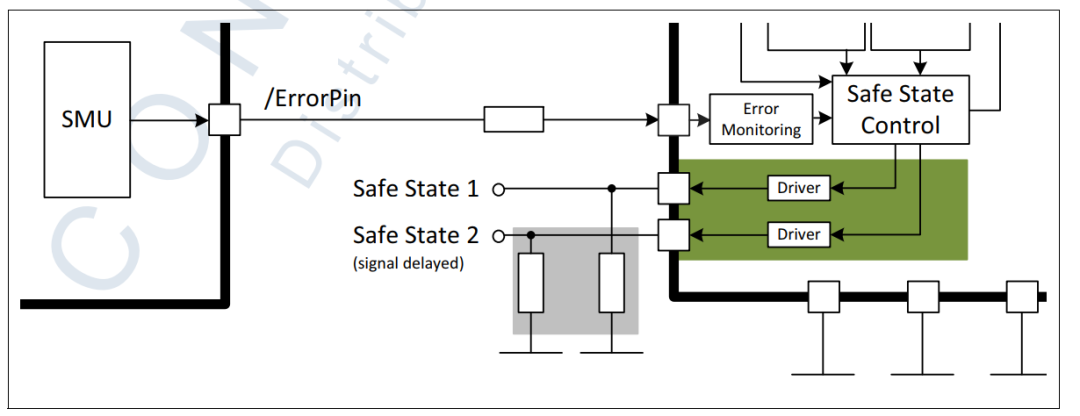
二次安全路径或者叫二次关断路径是通过PMIC的安全功能实现的。在PMIC的安全功能TSR需求中,系统的安全状态是通过PMIC的安全状态输出达到的,也就是说通过TLF35584的SS1和SS2输出连接到系统电路可以释放或者进入安全状态,这种机制可以在检测到关键失效时候进入安全状态已达到安全目标。
安全状态
系统的安全状态被认为是没有任何不合理的高水平风险的运行模式
Assumption: [SM_00_01]
只要TLF35584处于安全状态(通过激活二次安全关机路径,即SS1/SS2处于低电平表示),则子系统处于安全状态。
TLF35584包括许多安全设计功能和安全机制,以支持实现技术安全分析总结报告中定义的安全级别的安全要求.
安全特性
安全特性概览
安全特性如下图中标红色部分所示
输出电压监控
TLF35584为所有输出提供了独立的电源监控功能,每一路输出都包含独立的过压和欠压监控
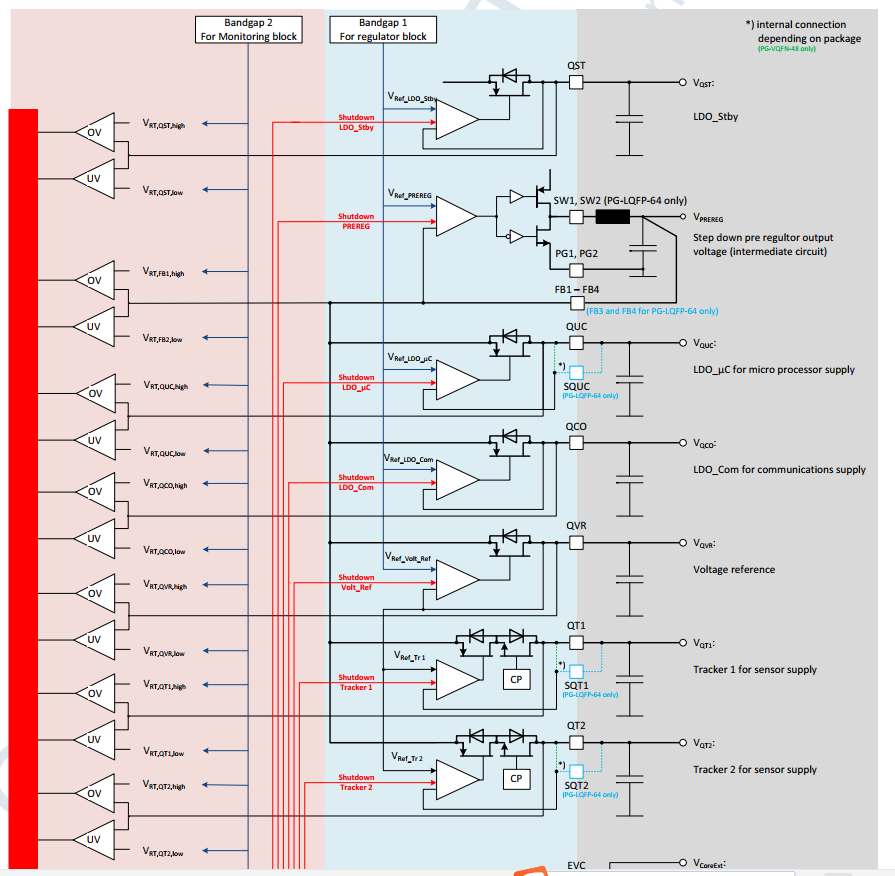
带隙基准和内部电压监控
所有的内部电压也会被监控,如果出现异常会进入POWNDOWN状态。TLF35584包含两路互相独立的带隙基准参考电压互相监控对方的操作。如果超过某一预设的门限值,TLF35584将会产生一个中断给到外部,MCU可以利用这个中断做一些响应。
热关断
TLF35584包含热监控以保护设备在高温条件下损坏,内部有多点的温度保护来防止器件损坏,如果检测到过温,会产生中断给到MCU,
MCU应当作出一些反映,如可以关断某路电源输出。
错误管脚监控
TLF35584提供一个可以通过ERR脚监控MCU的安全管理单元SMU,一个预定义的频率范围的翻转方波信号必须给到TLF35584的ERR脚,如果是超过频率范围的信号给到ERR脚会引起报故障,TLF35584将会进入INT状态。默认情况下ERR脚功能是使能的。
窗口看门狗
TLF35584包含一个窗口看门狗来监控MCU的运行,需要一定间隔内收到触发信号,可以通过WDI脚或者SPI,在一定的开窗时间内或者超时触发都会被认为是无效的看门狗触发,无效看门狗触发事件将会引起内部错误计数器加2,并且产生中断,有效的看门狗触发事件将会引起错误计数减1,如果错误计数器超过配置的门限值,TLF35584将会跳转到INT状态。默认条件下窗口看门狗是使能的,需要注意的是窗口看门狗和功能看门狗是相互独立的,可以同时使能使用。
功能看门狗
功能看门狗稍微复杂一些,也叫问答看门狗,通过多个SPI通信帧完成。TLF35584产生一个问题,同时心跳计数器开始从0向上计数,直到心跳周期结束,心跳周期可以通过SPI调整配置,4个字节的响应答案必须在心跳周期结束之前收到。最后一个收到的响应必须同步写入同步寄存器以复位心跳计数器。如果接收到正确的答案响应,认为是一次有效的看门狗触发事件,有效的看门狗触发事件会导致内部错误计数器减1,无效的看门狗触发事件将会导致内部错误计数器加2,并且产生中断。如果错误计数器超过预设的门限值,将会跳转到INT状态。默认情况下功能看门狗是禁止的,和窗口看门狗可以独立使用,互不干涉。
二次安全关断能力
TLF35584具有二次安全关断能力,在应用中安全状态输出引脚SS1和SS2的状态用来表明设备的安全状态。
软错误检测和修正
TLF35584通过一些寄存器提供了软错误的检测和修正安全机制,包括单个位错误的检测和修正,以及两个位错误的检测。两个位错误会引起中断。
安全机制软件需求
TLF35584在安全相关应用中用作微处理器电源。安全机制必须由相应的微处理器执行,以保证系统的正确运行。
SPI通信
来自微处理器的SPI通信用于配置TLF35584,服务看门狗和监控状态寄存器,由于SPI通信是用来传输安全相关信息的,因此需要采取措施保证其数据的完整性
奇偶校验
Assumption: [SM_SPI_01]
SPI通信中的奇偶校验位为每次通信进行检查。具有无效奇偶校验信息的数据必须被忽略。
奇偶校验位在SPI期间防止单比特故障和奇数比特错误的故障沟通。为了提供更全面的误差覆盖范围,可以考虑额外的措施。如果在读操作过程中奇偶校验信息不正确,微处理器必须忽略数据和重做读操作
如果写操作过程中的校验信息不正确,TLF35584将忽略该数据并产生中断。微处理器应该响应中断并检查中断源,即检查是否SPI.PARE位置位。如果写操作失败,微处理器应该重复这个操作。
配置
Assumption: [SM_SPI_02]
write-verify-
apply过程用于对安全相关配置的写访问。因此,数据应是在写入数据之后和应用于应用程序之前进行验证。预期配置的验证至少每次配置校验一次,并根据应用程序可以重新配置。
所有与安全相关的配置寄存器(称为“受保护的寄存器”)都由定义的LOCK/UNLOCK过程,允许在数据激活之前对其进行验证。
清除状态和中断寄存器
所有状态和中断标志在清除之前被正确读取。挂起的中断没有正确清除服务
中断信号
Assumption: [SM_INT_01]
根据具体的应用,在将中断信号用作安全功能的应用中,对每个中断信号的正确功能进行验证。
中断的处理,当产生中断,应遵循:
可以实施超时,其到期应视为测试失败。持续时间超时时间应根据所选择的中断源设置
读取中断状态寄存器并验证中断标志是否与生成的特定中断相匹配
中断响应
Assumption: [SM_INT_02]
微处理器检查每个中断事件的中断源,并根据应用程序做出反应要求。
Assumption: [SM_INT_03]
如果通过中断状态标志SYSSF.CFGE检测到一个配置错误,MCU应该对设备进行重新配置
复位输出使用
Assumption: [SM_ROT_01]
TLF35584的复位输出脚ROT连接到MCU的复位输入引脚,当有复位引脚输出,主要安全路径激活。
备用Stand-by LDO使用
Assumption: [SM_SBL_01]
在备用LDO用作微控制器的存储器电源供给时,需要每个周期确认验证下此LDO是否安全。
独立的二次安全关断路径
Assumption: [SM_SS_01]
必须确保主要安全关断路径和二次安全关断路径的独立性,不能存在任何的依赖关系。
一次关断路径或者脚主要关断路径由MCU控制。
Assumption: [SM_SS_02]
在将二次关断路径用作安全功能的应用中,根据不同的应用,要验证其正确的功能,每个周期至少需要一次安全功能验证。
窗口看门狗
Assumption: [SM_WWD_01]
在将窗口看门狗用作安全功能的应用程序中,根据应用至少在每个驾驶周期验证一次窗口看门狗的正确性
Assumption: [SM_WWD_02]
在将窗口看门狗用作安全功能的应用程序中,其正确的功能包括微处理器复位信号ROT和安全状态输出的激活在每个周期至少验证一次。
功能看门狗
Assumption: [SM_FWD_01]
在将功能看门狗用作安全功能的应用中,至少要验证其正确的功能,每个驾驶周期一次,取决于应用程序。
Assumption: [SM_FWD_02]
在功能看门狗作为安全功能发布的应用程序中,其正确的功能包括微处理器复位信号ROT和安全状态输出的激活在每次驾驶中至少验证一次,周期取决于应用程序。
ERR引脚监控
Assumption: [SM_ERR_01]
在将ERR引脚用作安全功能的应用程序中,每次至少验证一次其正确功能,驱动周期取决于应用。
Assumption: [SM_ERR_02]
在ERR引脚用作安全功能的应用中,其正确的功能包括微处理器复位信号ROT和安全状态输出的激活在每个驾驶周期至少验证一次。
请注意,测试程序的可用性取决于错误引脚监控的配置应用:立即行动与恢复延迟
监控组件
Assumption: [SM_MON_01]
在监控块用作安全功能的应用程序中,监视器的正确功能,每个使用的监视器每个驱动周期至少验证一次对中断信号的监控。
Assumption: [SM_MON_02]
在监控块用作安全功能的应用程序中,监视器的正确功能在对每个已使用的监视器至少进行一次验证,以激活安全状态输出周期取决于应用程序。
ABIST
ABIST的检测由MCU发起请求
详细执行规则可以参考SM手册要求,这里不在赘述。
监控功能恢复
如果对设备的监督功能的测试导致异常或失败,则相应的监督功能应被认为是非活性的,并应考虑相应的系统反应以确保安全操作。由于缺乏监督功能并不一定意味着违反了安全目标,微控制器可以控制场景,以增加系统的可用性。进一步讲系统集成者可以预见恢复机制,使监管恢复有效运作。,如可以重新配置有问题的配置,或者重启TLF35584.
硬件需求
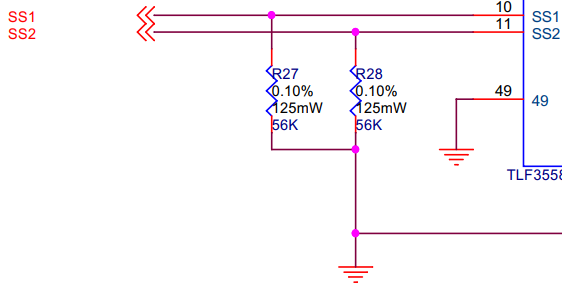
二次关断路径
Assumption: [SM_SS_03]
在应用中要确保SS1和SS2的高电平输出被认为是使二次安全关断路径无效,低电平或者高阻态被认为是激活安全关断路径的信号。
Assumption: [SM_SS_04]
SS1和SS2之间的延迟不能被视为安全特性
最大额定值
Assumption: [SM_ABS_01]
在任何操作下都不能违反数据手册中电气参数的最大额定值
电压电流
温度
外部器件的选择
反相保护
因为TLF35584本身不能够处理反相供电的情况,所以需要外部系统层的额外电路来处理电池电压的反接情况。
输入滤波
为了使TLF35584都在额定电气参数范围内操作,强烈建议添加输入滤波器,以限制电源线上的尖峰,相关的参数可以从TLF35584的EMC测试报告中获取。
过流限制
强烈建议在管脚添加限流电阻,防止引脚的电流超过手册的限制值。输入电压VST的限制主要靠前级降压器件来提供可靠输入。如我们的应用中的LM5085.
主要分为两类
一类是连接到电池电压等级的ENA和WAK脚必须小心处理过流和反相,至少大于10K的串联电阻
第二类是像SPI(SCS,SCL,SDI,SDO),INT,ROT,WDI,SYN,EVC 至少串联一个大于50欧姆的电阻,电阻布局的位置也需在系统级考虑。
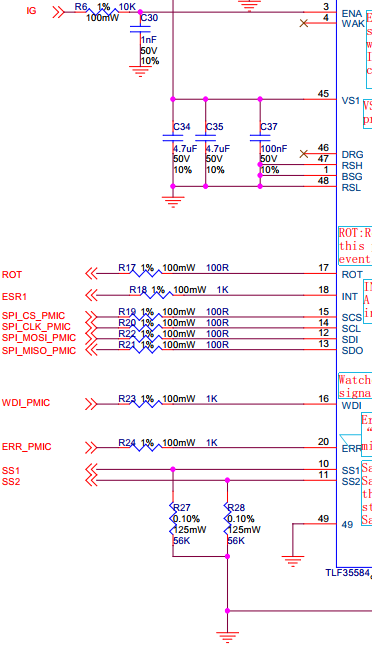
ERR脚保护
在MCU的SMU故障输出脚P33.8和TLF35584的ERR脚之间串联大于1K的电阻。
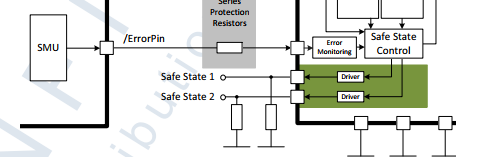

电压域的分离
强烈建议将ECU内的高、低压区分开,在不同组的信号之间的电路以减少短路的风险。这可以通过在PCB布线中使用足够的间隙来完成任何外部高压和内部低压信号之间。在这种情况下应给予特别考虑不同域的信号在引脚上连接。
外部被动元器件
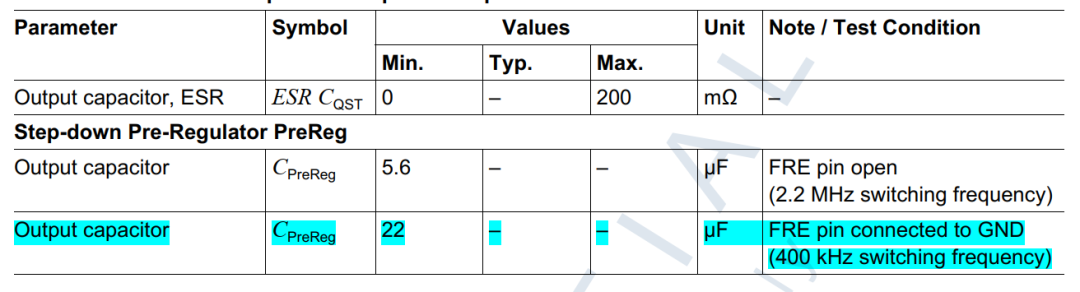
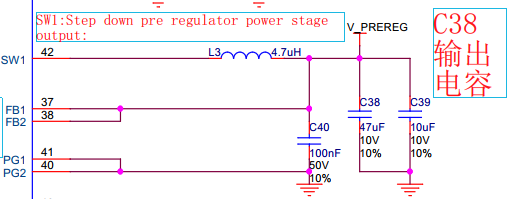
必须强制确保连接到TLF35584的外部器件在数据手册要求的范围内,如输出电感,电容等。外部器件组件的失效必须在系统层级覆盖,可以使用冗余外部器件,提高系统层级的可靠性。可以参考数据手册有关外部器件要求更详细的信息,这里只给出简单的要求
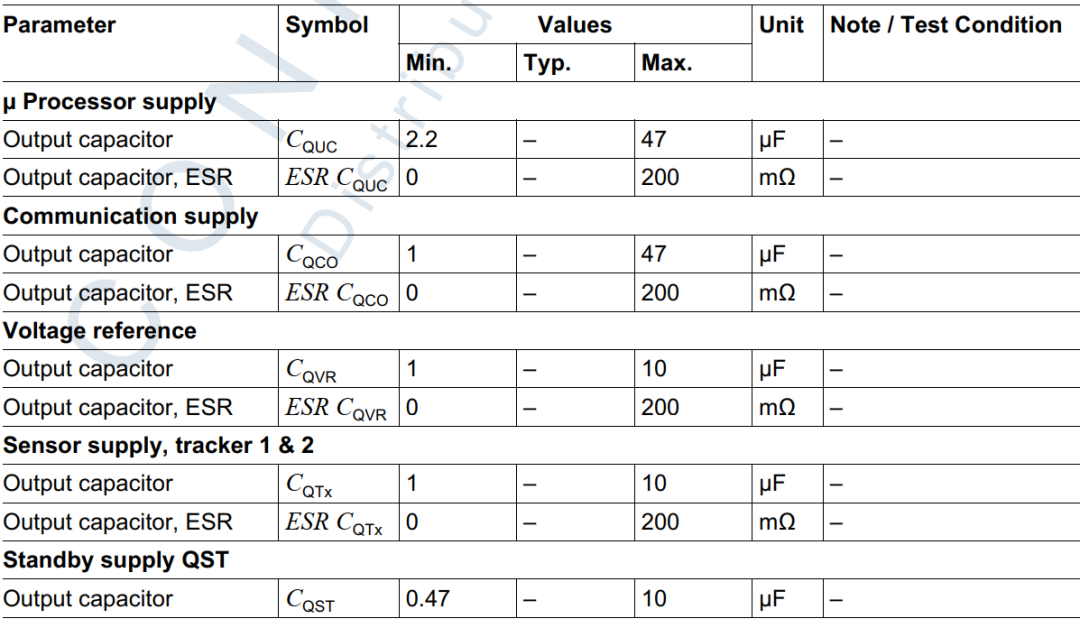
总结:
要根据自己的应用选择内外安全机制去执行,提高系统的安全。
网络安全工程师(白帽子)企业级学习路线
第一阶段:安全基础(入门)

第二阶段:Web渗透(初级网安工程师)

第三阶段:进阶部分(中级网络安全工程师)

如果你对网络安全入门感兴趣,那么你需要的话可以点击这里👉网络安全重磅福利:入门&进阶全套282G学习资源包免费分享!
学习资源分享






















 908
908

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








