前言
图的难度,并不在于算法难度,而在于图的表现形式多样,不同的题中的图表现形式不一样.
一个好的解决思路就是,用你喜欢的一种图结构,来实现所有的图算法,然后以后遇到不同的图表现形式,写一个接口函数,将这个表现形式转换为你熟悉的图结构,在用这个结构实现该算法
图的存储方式
图的存储方式一共有俩种,邻接表和邻接矩阵俩种形式,本文主要讲述邻接表方式,接下的算法也都由邻接表实现
package Graph;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
/*这个要补充一点说明,这个图结构是为了兼顾所有的图*/
public class GrapH {
/*注意:这里面实现的都是有向图*/
//key表示点的编号,Node表示实际结构
public HashMap<Integer,Node> nodes;//
//边集,装着所有的边
public HashSet<Edge> edges;
public GrapH(){
nodes=new HashMap<Integer, Node>();
edges=new HashSet<Edge>();
}
}
package Graph;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Node {
/*点集的结构有向图(无向图只是特殊的有向图而已)*/
public int value;//代表自己的这个点
public int in;//代表这个点有多少的入度
public int out;//代表这个点有多少的出度
public ArrayList<Node> nexts;//代表当前这个点直接到达的邻居(而且边要属于我)有哪些
public ArrayList<Edge> edges;//代表属于这个点的边有哪些
public Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
in=0;
out=0;
nexts = new ArrayList<>();
edges = new ArrayList<Edge>();
}
}
package Graph;
public class Edge {
public int weight;//代表这个边的权重
public Node from;//代表这个边来自那个点
public Node to ;//代表这个边去向哪里
public Edge(int weight, Node from, Node to) {
this.weight = weight;
this.from = from;
this.to = to;
}
}
深度优先遍历
思路:逮着一条路,使劲走,走不通或着走完了在返回
图的深度优先遍历
* 1利用栈实现,从给定节点开始把节点按照深度依次放入栈,然后弹出
* 2每弹出一个点,就把这个节点下一个没有进过栈的临接点放入栈中
* 3直到栈空
public static void DFS(Node node){
if (node == null)return;
Stack<Node> stack=new Stack<>();
HashSet<Node> set=new HashSet<>();
/*这个栈永远保持这个深度优先的路径*/
stack.add(node);
set.add(node);
System.out.println(node.value);
while (!stack.isEmpty()){
Node cur =stack.pop();
for (Node next : cur.nexts){
if (!set.contains(next)){
/*注意这里的细节,当邻居不在表set中,就要把原来的节点也要重新押入栈
* 在把邻居压入栈中,表中*/
stack.push(cur);
stack.push(next);
set.add(next);
System.out.println(next.value);
//输出语句同样可以换成别的数据操作语句
break;
//压入进去后,直接返回,继续查询
}
}
}
}
广度优先遍历
图的广度优先遍历:
1利用队列实现,从给定节点依次按照宽度进队列,然后弹出
2每弹出一个点,就把该节点所有没有进过队列的临接点,放入队列
3:重复上述过程
//图的广度优先遍历与二叉树的宽度优先遍历的不同点在于,图是可能有环的
public static void BFS(Node node){
if (node == null)return;
Queue<Node> queue= new LinkedList<>();
HashSet<Node> hashSet=new HashSet<>();
//set为队列服务,保证每一个点不重复进入,避免成环
queue.add(node);
hashSet.add(node);
while (!queue.isEmpty()){
Node cur = queue.poll();
System.out.println(cur.value);
//这个输出语句代表你要对这个数据进行的操作
for(Node next : cur.nexts){
/*这个循环代表者,把这个节点的所有临接点都进去*/
if (!hashSet.contains(next)){
queue.add(next);
hashSet.add(next);
}
}
}
}
拓扑排序算法
拓扑排序指的就是,完成一向A,需提前找到A的依赖比如说B,也就是说假如A有3个依赖BCD
如果实现A 就得 先实现BCD
实现思想
先找一个入度为0的点,记录下来,然后消除这个点的所有影响, 在重复上述过程
public static List<Node> sortedTopolgy(GrapH graph){
//key 某一个node
//value 剩余的依赖
HashMap<Node,Integer> inMap=new HashMap<Node, Integer>();
/*入度为0的进队列*/
Queue<Node> zeroInQueue =new LinkedList<Node>();
for (Node node : graph.nodes.values()){
/*将每个点都作为单独的一个集合,进入map,*/
inMap.put(node, node.in);
if (node.in == 0){
zeroInQueue.add(node);
}
}
List<Node> result=new LinkedList<>();
//结果集
while (!zeroInQueue.isEmpty()){
Node cur=zeroInQueue.poll();
result.add(cur);
for (Node next : cur.nexts){
inMap.put(next,inMap.get(next)-1);
if (inMap.get(next) == 0){
zeroInQueue.add(next);
}
}
}
return result;
}
最小生成树
给你一个图,找出一条路径得到的权值最小,这个路径就叫做最小生成树
无向图-Prim
Prim的思想为:
1:从任意一个点开始,解锁这个点引出的所有边的点
2:在这些新引出的点中,找一个权值最小的点重复上述过程
注意和K 算法区别,Prim可能出现的情况是,图不连通,K算法可能出现的情况是,形成环了
public static Set<Edge> primMST(GrapH grapH){
//解锁的边放到小跟堆里面去
PriorityQueue<Edge> priorityQueue=new PriorityQueue<>(new Comparator<Edge>() {
@Override
public int compare(Edge o1,Edge o2) {
return o1.weight-o2.weight;
}
});
//考察过的点都放入set中
HashSet<Node> set=new HashSet<Node>();
Set<Edge> result = new HashSet<>();
for (Node node : grapH.nodes.values()){//防止图不是连通的情况(如果是连通的这个for就没必要写)
//node是开始点
if (!set.contains(node)){
set.add(node);
for (Edge edge : node.edges){
priorityQueue.add(edge);//由一个边解锁所有的边
}
while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()){
Edge edge =priorityQueue.poll();//弹出最小的边
Node toNode = edge.to;//可能是一个新的点
if (!set.contains(toNode)){//不含的话,就是新的点
set.add(toNode);
result.add(edge);
for (Edge nextEdge :toNode.edges){//将新的点的边都放到队列中
priorityQueue.add(nextEdge);
}
}
}
}
}
return result;
}
无向图-kruskal
k算法的思路是:每次都找最小的边,然后如果这个边不形成环路的话就连接起来,如果会就不加
public static Set<Edge> kruskalMST(GrapH grapH){
/*unionFind 代表实现的一种并查集*//*
UnionFind unionFind=new UnionFind();
unionFind.makeSets(grapH.nodes.values());//初始化
PriorityQueue<Edge> priorityQueue=new PriorityQueue<>();
//将每一条边权值入队
for (Edge edge : grapH.edges){
priorityQueue.add(edge);
}
Set<Edge> result=new HashSet<Edge>();
*//*形成一个结果集*//*
while (!priorityQueue.isEmpty()){
Edge edge=priorityQueue.poll();
if (!unionFind.isSameSet(edge.from,edge.to)){//如果并查集中不成环路就加入到结果集中
result.add(edge);
unionFind.union(edge.from,edge.to);//如果入队后,就将俩个点集合到一起.
}
}
return result;*/
return new HashSet<>();
}
有向图-Dijkstra
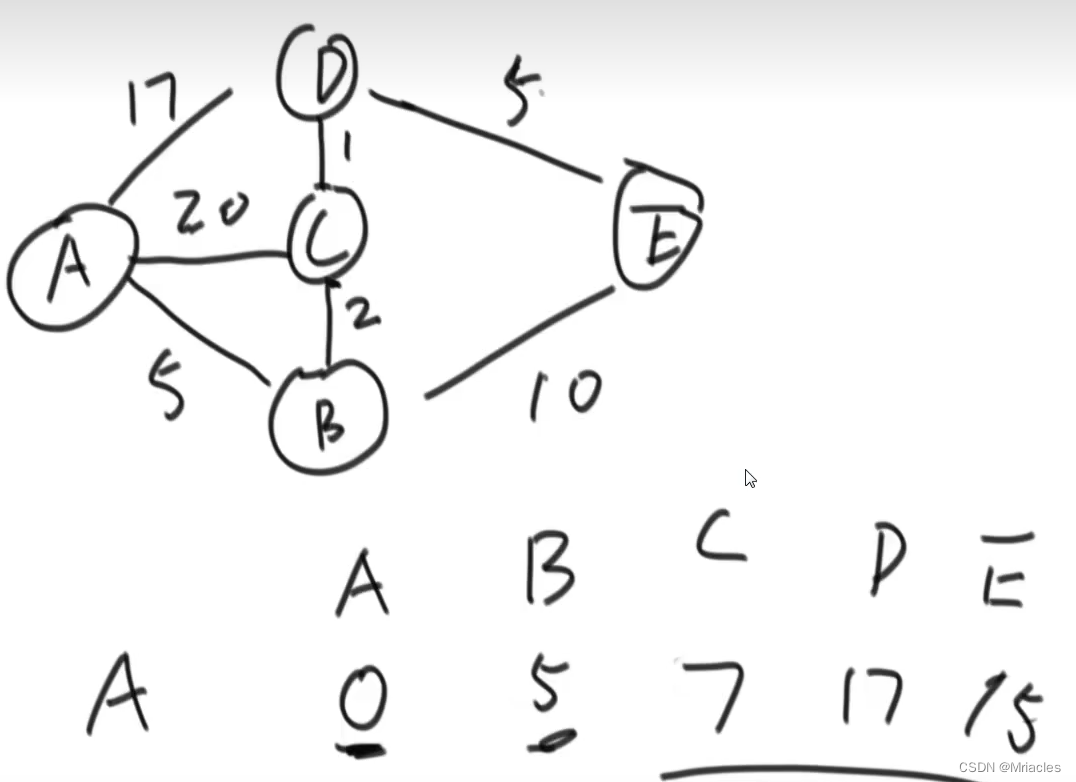
这个是有向图的最小生成树,思想还是很好理解的
Dijkstra要求这个图中没有权值为负数的边,和一定要给定一个出发点
从这个出发点,解锁到所有可达到点的距离(包括通过新的点来去别的点),不可达就设置为正无穷,同时将这个使用过的点锁死不让用了
然后遍历这些点,并更新最小距离,同时将新出现的点加入进去
重复上述过程
package Graph;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.Map;
public class Dijkstra {
/*用来记录理解,B站左成云老师的算法与数据结构
* 本类主要完成,迪杰特斯拉算法---用于有向图的最短路径算法
* 这个可以优化,比如使用堆,但是堆也得优化*/
public static HashMap<Node,Integer> dijkstral(Node head){
/*从head出发到所有点的最下举例
* key : 表示从head出发到达 key
* value : 从 head出发 到达 key的最小距离
* 如果在表中,没有T的记录,含义就是从head出发到T这个点的距离为正无穷*/
HashMap<Node,Integer> distanceMap=new HashMap<Node, Integer>();
distanceMap.put(head,0);
//已经求过距离的节点,存在selectedNodes中,以后再也不碰
HashSet<Node> selectNodes =new HashSet<Node>();
Node minNode = getMinDistanceAndUnselectdeNode(distanceMap,selectNodes);
//一开始会把头结点选出来
//getMinDistanceAndUnselectdeNode指从distanceMap找到一个最下的距离,但这个距离节点不能是选过的
while (minNode != null){
int distance = distanceMap.get(minNode);//拿到最小的点的距离
for (Edge edge: minNode.edges) {
Node toNode = edge.to ;
if (!distanceMap.containsKey(toNode)){
distanceMap.put(toNode,distance+edge.weight);//把这个点所有未存在的边(正无穷)存进去
}
distanceMap.put(edge.to,Math.min(distanceMap.get(toNode),distance+edge.weight));
//判断 之前的距离和现在的距离那个小入那个
}
selectNodes.add(minNode);//将这个点锁死不再用了
minNode =getMinDistanceAndUnselectdeNode(distanceMap,selectNodes);
}
return distanceMap;
}
public static Node getMinDistanceAndUnselectdeNode(
HashMap<Node,Integer> distanceMap,HashSet<Node> touchedNodes){
Node minNode=null;
int minDistance = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (Map.Entry<Node,Integer> entry:distanceMap.entrySet()){
Node node =entry.getKey();//遍历点
int distance =entry.getValue();//距离拿出来
if (!touchedNodes.contains(node) && distance < minDistance){
minNode =node;
minDistance=distance;
}
}
return minNode;
}
}
改进后的dijkstra算法
改进堆
public static class NodeHeap{
private Node[] nodes;
private HashMap<Node,Integer> heapIndexMap;
//heapIndexMap查node在堆上的那个位置
private HashMap<Node,Integer> distanceMap;
//distanceMap node到head的最短距离的值
private int size;//堆上有几个节点
public NodeHeap(int size){
nodes = new Node[size];
heapIndexMap = new HashMap<>();
distanceMap = new HashMap<>();
this.size =0;
}
public boolean isEmpty(){
return size == 0;
}
public void addOrUpadateOrIgnore(Node node,int distance){
if (inHeap(node)){
//如果heap 在堆上
distanceMap.put(node,Math.min(distanceMap.get(node),distance));
//把node 更新最小举例
insertHeapify(node,heapIndexMap.get(node));
//向上调整
}
if (!isEntered(node)){
//如果一个节点没进过堆
//创建节点,放入进去数组与哈希表中
nodes[size] = node;
heapIndexMap.put(node,size);
distanceMap.put(node,distance);
insertHeapify(node,size++);
//向上调整
}
}
public NodeRecord pop(){
NodeRecord nodeRecord = new NodeRecord(nodes[0],distanceMap.get(nodes[0]));
swap(0,size-1);//干掉堆顶
//调整哈希表
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[size-1],-1);
distanceMap.remove(nodes[size-1]);
//在堆上释放掉这个节点
nodes[size-1] = null;
//向下调整
heapify(0,--size);
return nodeRecord;
}
private void insertHeapify(Node node,int index){
while (distanceMap.get(nodes[index]) < distanceMap.get(nodes[(index-1)/2])){
swap(index,(index-1)/2);
index = (index-1)/2;
}
}
private void heapify(int index,int size){
int left = index*2 +1;
while (left < size){
//选择左右孩子的俩个其中的较小值
int smallest =left + 1 < size && distanceMap.get(nodes[left+1]) < distanceMap.get(nodes[left])
? left+1 : left;
smallest = distanceMap.get(nodes[smallest]) < distanceMap.get(index)?index:smallest;
if (smallest == index){
break;
}
swap(smallest,index);
index = smallest;
left = index *2 +1;
}
}
private boolean isEntered(Node node){
//指node 进没进来过这个堆中
return heapIndexMap.containsKey(node);
}
private boolean inHeap(Node node){
//标记这个节点进来过,但不在堆上所以标记为-1
return isEntered(node) && heapIndexMap.get(node) != -1;
}
private void swap(int index1 , int index2){
/*在这个堆上俩个节点要换位置,数组要换位置,哈希表也要改*/
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[index1],index2);
heapIndexMap.put(nodes[index2],index1);
Node tmp = nodes[index1];
nodes[index1] = nodes[index2];
nodes[index2] = tmp;
}
}
public static class NodeRecord{
public Node node;
public int distance;//到唯一出发点head的最短距离
public NodeRecord(Node node, int distance) {
this.node = node;
this.distance = distance;
}
}
public static HashMap<Node,Integer> dijkstra2(Node head,int size){
NodeHeap nodeHeap= new NodeHeap(size);
//堆得大小不要超过size
nodeHeap.addOrUpadateOrIgnore(head,0);
//到本身的距离 0
//如果有一个点的记录是第一次出现 add,如果值更小 update 如果不小,就Ignore
HashMap<Node,Integer> result=new HashMap<>();
while (!nodeHeap.isEmpty()){
NodeRecord record =nodeHeap.pop();
/*NodeRecord 代表弹出的最小值节点*/
Node cur = record.node;
int distance = record.distance;
for (Edge edge : cur.edges){
//遍历边集来更新(除之前用过节点的)距离,
nodeHeap.addOrUpadateOrIgnore(edge.to,edge.weight+distance);
}
result.put(cur,distance);
}
return result;
}






















 7925
7925











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








