目录
题外话
顺序表和链表优缺点以及特点
特点:顺序表,逻辑地址=物理地址。可以任意访问,访问时间复杂度O(1).。实现分配空 间,当空间不足时,要动态扩容。顺序表在销毁时可以直接free,但链表要一 个个删 除。
链表:不连续的空间靠指针指向下一个地址。不用实现分配空间。
优缺点:
顺序表:适和访问,不适合插入删除,时间负责度为O(N)。链表适和插入删除操 作。
一.栈的特点
(1)先进后出
(2)栈不能任意打印,栈只能访问栈顶
(3)栈只能尾插头删
二. 栈的操作
2.1初始化
void STInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = -1;
pst->capacity = 0;
}2.2 栈的销毁
2.3 栈的插入
注意:🤖
如果你初始化为0,那么就是先插入在++;
如果你初始化为-1,那就是先++,在插入。
}
//插入
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == pst->capacity-1)
{
int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->top++;
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
}
2.3 输出top

注意:
由于栈的特性,只能先进先出,尾插头删,不能任意输出,所以我们只能输出头。
void STTop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top >= -1);
return pst->a[pst->top];
}2.4 栈的删除
//删除
void STPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top>=-1);
pst->top--;

2.5 输出栈
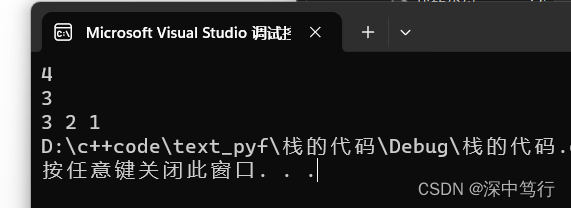
while (STEmpty(&st) != true) {
printf("%d ", STTop(&st));
STPop(&st);
} 
栈的完整代码
#pragma once
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct STack
{
STDataType* a; //数值的指针是下标
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
void STInit(ST* pst);
void STDestory(ST* pst);
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x);
void STPop(ST* pst);
bool STEmpty(ST* pst);
int STSize(ST* pst);
STDataType STTop(ST* pst);
#include"Stack.h"
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
void STInit(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = -1;
pst->capacity = 0;
}
void STDestory(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->top = -1;
pst->capacity = 0;
}
//插入
void STPush(ST* pst, STDataType x)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == pst->capacity-1)
{
int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
pst->top++;
pst->a[pst->top] = x;
}
//输出头结点
STDataType STTop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top >= -1);
return pst->a[pst->top];
}
//删除
void STPop(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
assert(pst->top>=-1);
pst->top--;
}
bool STEmpty(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->top == -1) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
int STSize(ST* pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->top;
}
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include"Stack.h"
void Test1() {
ST st;
STInit(&st);
STPush(&st, 1);
STPush(&st, 2);
STPush(&st, 3);
STPush(&st, 4);
printf("%d\n", STTop(&st));
STPop(&st);
printf("%d\n", STTop(&st));
while (STEmpty(&st) != true) {
printf("%d ", STTop(&st));
STPop(&st);
}
}
int main()
{
Test1();
return 0;
}






















 831
831











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








