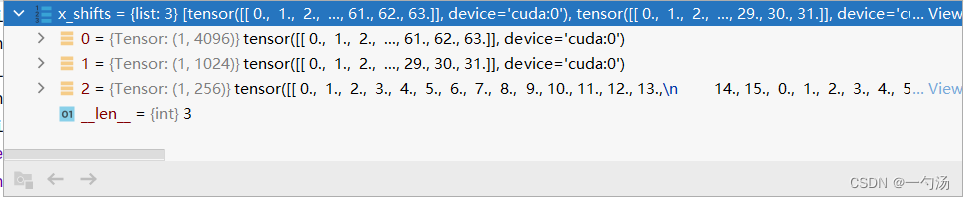
1.上一讲注意力机制后面便是loss部分,他输入的是图像、x_shifts是一张图片被分成了多少的网格数量、expanded_strides网格的长度、fc_output注意力机制后的特征、pred_idx预测
if self.training:
return self.get_losses(
imgs,
x_shifts,
y_shifts,
expanded_strides,
labels,
torch.cat(outputs, 1),
origin_preds,
dtype=xin[0].dtype,
refined_cls=fc_output,
idx=pred_idx,
pred_res=pred_result,
)
else:
class_conf, class_pred = torch.max(fc_output, -1, keepdim=False) #看哪个类别的概率最大
result, result_ori = postprocess(copy.deepcopy(pred_result), self.num_classes, fc_output,nms_thre=nms_thresh )
return result, result_ori # result2.这部分比较简单,获取每一帧图像的box、真实分类 [batch,120,class+xywh]、每张图片的预测框。
bbox_preds = outputs[:, :, :4] # [batch, n_anchors_all, 4]
obj_preds = outputs[:, :, 4].unsqueeze(-1) # [batch, n_anchors_all, 1]
cls_preds = outputs[:, :, 5:] # [batch, n_anchors_all, n_cls]
# calculate targets 判断标签的类别是否是5个
mixup = labels.shape[2] > 5
if mixup:
label_cut = labels[..., :5]
else:
label_cut = labels
nlabel = (label_cut.sum(dim=2) > 0).sum(dim=1) # number of objects 去除120中没有的标签 获取标签的真实个数
total_num_anchors = outputs.shape[1] # n_anchors_all
x_shifts = torch.cat(x_shifts, 1) # [1, n_anchors_all]
y_shifts = torch.cat(y_shifts, 1) # [1, n_anchors_all]
expanded_strides = torch.cat(expanded_strides, 1)
if self.use_l1: # 80轮之后的L1损失
origin_preds = torch.cat(origin_preds, 1)
cls_targets = []
reg_targets = []
l1_targets = []
obj_targets = []
fg_masks = []
ref_targets = []
num_fg = 0.0
num_gts = 0.0
ref_masks = []
for batch_idx in range(outputs.shape[0]): # batch的大小
num_gt = int(nlabel[batch_idx])
num_gts += num_gt
if num_gt == 0:
cls_target = outputs.new_zeros((0, self.num_classes))
reg_target = outputs.new_zeros((0, 4))
l1_target = outputs.new_zeros((0, 4))
obj_target = outputs.new_zeros((total_num_anchors, 1))
fg_mask = outputs.new_zeros(total_num_anchors).bool()
ref_target = outputs.new_zeros((idx[batch_idx].shape[0], self.num_classes + 1))
ref_target[:, -1] = 1
else:
gt_bboxes_per_image = labels[batch_idx, :num_gt, 1:5] # 每张图片的box
gt_classes = labels[batch_idx, :num_gt, 0] # 真实分类 [batch,120,class+xywh]
bboxes_preds_per_image = bbox_preds[batch_idx] # 每张图片的预测框3.这一步是获取每一帧图像上正样本的类别、mask掩码、iou、数量等。
输入是第几个batch、真实框的数量、所有框的数量(5379)、真实框、真实框的类别、每一帧图像的预测框(5376x4)、三个特征图与原图的缩放比、左上角的xy坐标、类别预测(8x5376x30)、框的预测(8x5376x4)、置信度预测(8x5376x1)、类别、图像。
try:
(
gt_matched_classes, # 正样本的类别
fg_mask, # 5376中正样本30 的mask掩码
pred_ious_this_matching, # 正样本与它对应真实框的iou
matched_gt_inds, # 正样本与真实框对应
num_fg_img, # 正样本的数量
) = self.get_assignments( # noqa
batch_idx,
num_gt,
total_num_anchors,
gt_bboxes_per_image,
gt_classes,
bboxes_preds_per_image,
expanded_strides,
x_shifts,
y_shifts,
cls_preds,
bbox_preds,
obj_preds,
labels,
imgs,
)
except RuntimeError:
logger.error(
"OOM RuntimeError is raised due to the huge memory cost during label assignment. \
CPU mode is applied in this batch. If you want to avoid this issue, \
try to reduce the batch size or image size."
)
torch.cuda.empty_cache()
(
gt_matched_classes,
fg_mask,
pred_ious_this_matching,
matched_gt_inds,
num_fg_img,
) = self.get_assignments( # noqa
batch_idx,
num_gt,
total_num_anchors,
gt_bboxes_per_image,
gt_classes,
bboxes_preds_per_image,
expanded_strides,
x_shifts,
y_shifts,
cls_preds,
bbox_preds,
obj_preds,
labels,
imgs,
"cpu",
)3.1这部分代码主要分成这几个模块:
1.将在预测框的中心点在真实框和自己设计的4.5x4.5大小框中的预测框选出来。
2.计算cost
def get_assignments(
self,
batch_idx,
num_gt,
total_num_anchors,
gt_bboxes_per_image,
gt_classes,
bboxes_preds_per_image,
expanded_strides,
x_shifts,
y_shifts,
cls_preds,
bbox_preds,
obj_preds,
labels,
imgs,
mode="gpu",
):
if mode == "cpu":
print("------------CPU Mode for This Batch-------------")
gt_bboxes_per_image = gt_bboxes_per_image.cpu().float()
bboxes_preds_per_image = bboxes_preds_per_image.cpu().float()
gt_classes = gt_classes.cpu().float()
expanded_strides = expanded_strides.cpu().float()
x_shifts = x_shifts.cpu()
y_shifts = y_shifts.cpu()
# 预测框的中心点既在真实框中也在4.5x4.5中的预测框
fg_mask, is_in_boxes_and_center = self.get_in_boxes_info(
gt_bboxes_per_image,
expanded_strides,
x_shifts,
y_shifts,
total_num_anchors,
num_gt,
)
# 根据是否在框中,删除不在框中的数据
bboxes_preds_per_image = bboxes_preds_per_image[fg_mask]
cls_preds_ = cls_preds[batch_idx][fg_mask]
obj_preds_ = obj_preds[batch_idx][fg_mask]
num_in_boxes_anchor = bboxes_preds_per_image.shape[0]
if mode == "cpu":
gt_bboxes_per_image = gt_bboxes_per_image.cpu()
bboxes_preds_per_image = bboxes_preds_per_image.cpu()
pair_wise_ious = bboxes_iou(gt_bboxes_per_image, bboxes_preds_per_image, False) # 计算真实框和预测框的iou
gt_cls_per_image = ( # 4x656x30 一张图片上有四个真实框 每个框的类别复制656 对应着656个预测框
F.one_hot(gt_classes.to(torch.int64), self.num_classes)
.float()
.unsqueeze(1)
.repeat(1, num_in_boxes_anchor, 1)
)
pair_wise_ious_loss = -torch.log(pair_wise_ious + 1e-8)
if mode == "cpu":
cls_preds_, obj_preds_ = cls_preds_.cpu(), obj_preds_.cpu()
with torch.cuda.amp.autocast(enabled=False):
cls_preds_ = ( # 置信度*类别
cls_preds_.float().unsqueeze(0).repeat(num_gt, 1, 1).sigmoid_() # 4x656x30 656x30 复制4份
* obj_preds_.unsqueeze(0).repeat(num_gt, 1, 1).sigmoid_() # 4x656x1
)
pair_wise_cls_loss = F.binary_cross_entropy( # 预测框的类别和真实框的类别做计算 得出他的类别
cls_preds_.sqrt_(), gt_cls_per_image, reduction="none"
).sum(-1)
del cls_preds_
cost = (
pair_wise_cls_loss #分类的一个损失
+ 3.0 * pair_wise_ious_loss #iou损失
+ 100000.0 * (~is_in_boxes_and_center) # 如果不在里面 给她一个很大的值,cos就不会选到他
)
(
num_fg,
gt_matched_classes,
pred_ious_this_matching,
matched_gt_inds,
) = self.dynamic_k_matching(cost, pair_wise_ious, gt_classes, num_gt, fg_mask)
del pair_wise_cls_loss, cost, pair_wise_ious, pair_wise_ious_loss
if mode == "cpu":
gt_matched_classes = gt_matched_classes.cuda()
fg_mask = fg_mask.cuda()
pred_ious_this_matching = pred_ious_this_matching.cuda()
matched_gt_inds = matched_gt_inds.cuda()
return (
gt_matched_classes,
fg_mask,
pred_ious_this_matching,
matched_gt_inds,
num_fg,
)3.1.1由于每一个格子有一个预测框,因此计算每一个格子的中心点,判断在真实框和自己设计的4.5x4.5大小的框中的中心点,去除不在这些框中的中心点。
def get_in_boxes_info(
self,
gt_bboxes_per_image,
expanded_strides,
x_shifts,
y_shifts,
total_num_anchors,
num_gt,
):
expanded_strides_per_image = expanded_strides[0]
x_shifts_per_image = x_shifts[0] * expanded_strides_per_image
y_shifts_per_image = y_shifts[0] * expanded_strides_per_image #左上角的坐标
x_centers_per_image = ( # 计算每一个格子的中心点的位置
(x_shifts_per_image + 0.5 * expanded_strides_per_image)
.unsqueeze(0)
.repeat(num_gt, 1)
) # [n_anchor] -> [n_gt, n_anchor]
y_centers_per_image = (
(y_shifts_per_image + 0.5 * expanded_strides_per_image) #每个格子的中心点
.unsqueeze(0)
.repeat(num_gt, 1)
)
#计算真实框的四边 l_x l_y r_x r_y
gt_bboxes_per_image_l = (
(gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 0] - 0.5 * gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 2]) #中心点和长宽
.unsqueeze(1)
.repeat(1, total_num_anchors)
)
gt_bboxes_per_image_r = (
(gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 0] + 0.5 * gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 2])
.unsqueeze(1)
.repeat(1, total_num_anchors)
)
gt_bboxes_per_image_t = (
(gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 1] - 0.5 * gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 3])
.unsqueeze(1)
.repeat(1, total_num_anchors)
)
gt_bboxes_per_image_b = (
(gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 1] + 0.5 * gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 3])
.unsqueeze(1)
.repeat(1, total_num_anchors)
)
# 判断5376个框那些中心点在真实框中
b_l = x_centers_per_image - gt_bboxes_per_image_l
b_r = gt_bboxes_per_image_r - x_centers_per_image
b_t = y_centers_per_image - gt_bboxes_per_image_t
b_b = gt_bboxes_per_image_b - y_centers_per_image
bbox_deltas = torch.stack([b_l, b_t, b_r, b_b], 2)
# 4x5376x4 四个真实框 5376个预测框 四个xy相减的值 -》4x5376 mask
is_in_boxes = bbox_deltas.min(dim=-1).values > 0.0
is_in_boxes_all = is_in_boxes.sum(dim=0) > 0 # 四个真实框都没有的预测框去除(这里真实框的数量为4,可能不同)
# in fixed center
#与上面一样
center_radius = 4.5 #生成一个4.5x4.5的格子
gt_bboxes_per_image_l = (gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 0]).unsqueeze(1).repeat(
1, total_num_anchors
) - center_radius * expanded_strides_per_image.unsqueeze(0)
gt_bboxes_per_image_r = (gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 0]).unsqueeze(1).repeat(
1, total_num_anchors
) + center_radius * expanded_strides_per_image.unsqueeze(0)
gt_bboxes_per_image_t = (gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 1]).unsqueeze(1).repeat(
1, total_num_anchors
) - center_radius * expanded_strides_per_image.unsqueeze(0)
gt_bboxes_per_image_b = (gt_bboxes_per_image[:, 1]).unsqueeze(1).repeat(
1, total_num_anchors
) + center_radius * expanded_strides_per_image.unsqueeze(0)
c_l = x_centers_per_image - gt_bboxes_per_image_l
c_r = gt_bboxes_per_image_r - x_centers_per_image
c_t = y_centers_per_image - gt_bboxes_per_image_t
c_b = gt_bboxes_per_image_b - y_centers_per_image
center_deltas = torch.stack([c_l, c_t, c_r, c_b], 2)
is_in_centers = center_deltas.min(dim=-1).values > 0.0
is_in_centers_all = is_in_centers.sum(dim=0) > 0
# in boxes and in centers
is_in_boxes_anchor = is_in_boxes_all | is_in_centers_all #两者并集 预测框或者在真实框或者在4.5x4.5中
is_in_boxes_and_center = (
is_in_boxes[:, is_in_boxes_anchor] & is_in_centers[:, is_in_boxes_anchor] #两者交集
)
return is_in_boxes_anchor, is_in_boxes_and_center




















 1547
1547











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








