一、redis的订阅与发布
什么是 发布和订阅
Redis 发布订阅 (pub/sub) 是一种消息通信模式:发送者 (pub) 发送消息,订阅者 (sub) 接收消息。
Redis 客户端可以订阅任意数量的频道。
客户端订阅频道发布的消息

频道发布消息 订阅者就可以收到消息
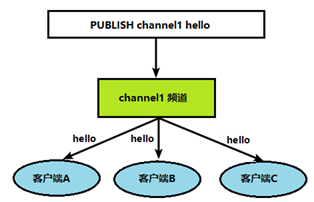
发布代码订阅的实现
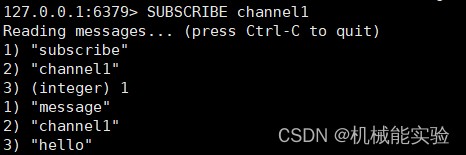
1、打开一个客户端订阅 channel1
SUBSCRIBE channel1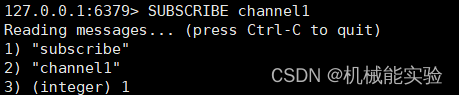
2、打开另一个客户端,给 channel1发布信息 hello
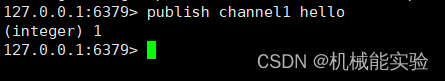
返回的 1 是订阅者数量,发送消息后第一个客户端出现感叹号
3、打开第一个客户端,可以看到发送的信息
二、Redis 事务
1.事务简介:
可以一次执行多个命令,本质是一组命令的集合。一个事务中的 所有命令都会序列化,按顺序地串行化执行而不会被其它命令插入,不许加塞。单独的隔离的操作。
MULTI、EXEC、DISCARD、WATCH。这四个指令构成了 redis 事务处理的基础。
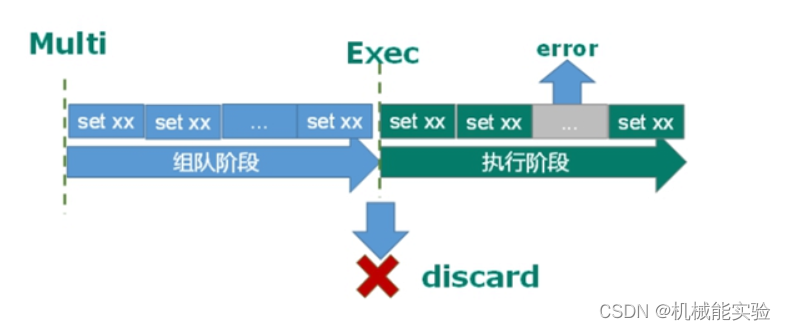
1.MULTI 用来组装一个事务;将命令存放到一个队列里面
2.EXEC 用来执行一个事务;//commit
3.DISCARD 用来取消一个事务;//rollback
4.WATCH 用来监视一些 key,一旦这些 key 在事务执行之前被改变,则取消事务的执行。
redis> MULTI //标记事务开始
OK
redis> INCR user_id //多条命令按顺序入队
QUEUED queued
redis> INCR user_id
QUEUED
redis> INCR user_id
QUEUED
redis> PING
QUEUED
redis> EXEC //执行
1) (integer) 1
2) (integer) 2
3) (integer) 3
4) PONG有关事务,经常会遇到的是两类错误:
1.调用 EXEC 之前的错误
“调用 EXEC 之前的错误”,有可能是由于语法有误导致的,也可能时由于内存不足导致的。只要出现某个命令无法成功写入缓冲队列的情况,redis 都会进行记录,在客户端调用 EXEC 时,redis 会拒绝执行这一事务
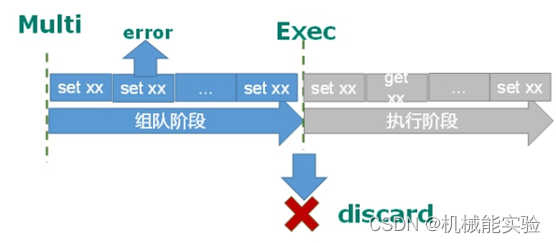
127.0.0.1:6379> multi
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> haha //一个错误的指令
(error) ERR unknown command 'haha'
127.0.0.1:6379> ping
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379> exec
//redis 拒绝了事务的执行,原因是“之前出现了错误”
(error) EXECABORT Transaction discarded because of previous errors.2、调用 EXEC 之后的错误
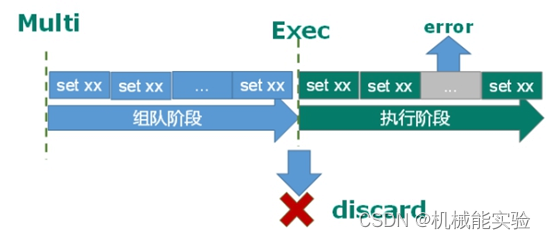
而对于“调用 EXEC 之后的错误”,redis 则采取了完全不同的策略,即 redis 不会理睬这些错误,而是继续向下执行事务中的其他命令。这是因为,对于应用层面的错误,并不是 redis 自身需要考虑和处理的问题,所以一个事务中如果某一条命令执行失败,并不会影响接下来的其他命令的执行例子:。
127.0.0.1:6379> multi
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> set age 23
QUEUED
//age 不是集合,所以如下是一条明显错误的指令
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd age 15
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379> set age 29
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379> exec //执行事务时,redis 不会理睬第 2 条指令执行错误
1) OK
2) (error) WRONGTYPE Operation against a key holding the wrong kind of value
3) OK
127.0.0.1:6379> get age
"29" //可以看出第 3 条指令被成功执行了2.redis事务冲突
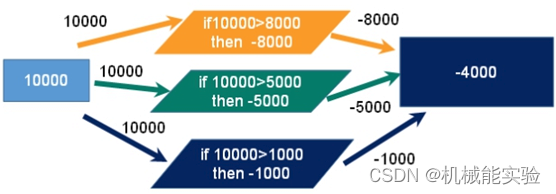
双十一去购物的时候使用同一张银行卡去付款10000
一个请求想给金额减8000
一个请求想给金额减5000
一个请求想给金额减1000
解决方案
悲观锁
select * from biao where 1=1 for update;
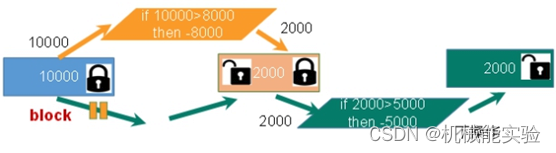
悲观锁(Pessimistic Lock), 顾名思义,就是很悲观,
每次去拿数据的时候都认为别人会修改,所以每次在拿数据的时候都会上锁,
这样别人想拿这个数据就会block直到它拿到锁。
传统的关系型数据库里边就用到了很多这种锁机制,
比如行锁,表锁等,读锁,写锁等,都是在做操作之前先上锁。
12306抢票
乐观锁
version 1
查余额 10000 version:1
10000>8000 -8000 update uuuu set moner-=8000 where version=1 1.1
10000 -5000 UPDATE uuuuu SET MONTY-=5000 WHERE VERSION=1
2000 2000>1000 UPDATE uuuu SET MONTY-=1000 WHERE VERSION=1.1 1.2
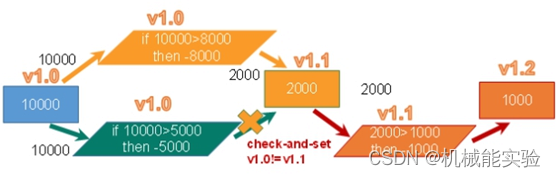
乐观锁(Optimistic Lock), 顾名思义,就是很乐观,
每次去拿数据的时候都认为别人不会修改,所以不会上锁,
但是在更新的时候会判断一下在此期间别人有没有去更新这个数据,
可以使用版本号等机制。乐观锁适用于多读的应用类型,
这样可以提高吞吐量。Redis就是利用这种check-and-set机制实现事务的。
3.WATCH
“WATCH”可以帮我们实现类似于“乐观锁”的效果,即 CAS(check and set)。
WATCH 本身的作用是“监视 key 是否被改动过”,而且支持同时监视多个 key,只要还没真正触发事务,WATCH 都会尽职尽责的监视,一旦发现某个 key 被修改了,在执行 EXEC 时就会返回 nil,表示事务无法触发。
127.0.0.1:6379> set age 23
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> watch age //开始监视 age
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> set age 24 //在 EXEC 之前,age 的值被修改了
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> multi
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> set age 25
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379> get age
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379> exec //触发 EXEC
(nil) //事务无法被执行事务回滚:
192.168.109.34:6379> multi
OK
192.168.109.34:6379> set testsy testq
QUEUED
192.168.109.34:6379> set testsy2 test2
QUEUED
192.168.109.34:6379> discard
OK三、Redis的使用
java 操作 redis 创建的是 maven
1、创建 java 项目
2、添加 redis 的依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
<version>3.2.0</version>
</dependency>3、相关的 api
key 的 api
@Test
public void testRedis() {
//设置连接的服务器 端口号默认是6379
// 服务器的默认值是localhost
Jedis jedis=new Jedis("8.140.27.154");
// redis的服务器的密码
jedis.auth("lh"); //设置密码
// 设置选中的数据库的下标
jedis.select(15);
// 设置键值对
jedis.set("k1", "v1");
jedis.set("k2", "v2");
jedis.set("k3", "v3");
//获取所有的key值
Set<String> keys = jedis.keys("*");
System.out.println(keys.size());
for (String key : keys) {
System.out.println(key);
}
// 判断key是否存在
System.out.println(jedis.exists("k1"));
//获取key的过期时间
System.out.println(jedis.ttl("k1"));
// 获取key对应的值
System.out.println(jedis.get("k1"));
}
}string -api
// 批量设置
jedis.mset("str1","v1","str2","v2","str3","v3");
//批量获取key
System.out.println(jedis.mget("str1","str2","str3"));hash-api
//设置 一个key叫做hash1 对应的field是username,value是lisi
jedis.hset("hash1","userName","lisi");
//获取key为hash1的对应的fileld为username的值
System.out.println(jedis.hget("hash1","userName"));
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<String,String>();
map.put("telphone","13838389438");
map.put("address","郑州");
map.put("email","abc@163.com");
//批量设置
jedis.hmset("hash2",map);
//批量获取
List<String> result = jedis.hmget("hash2", "telphone","email");
for (String element : result) {
System.out.println(element);
}set-api
jedis.sadd("orders", "order01");
jedis.sadd("orders", "order02");
jedis.sadd("orders", "order03");
jedis.sadd("orders", "order04");
Set<String> smembers = jedis.smembers("orders");
for (String order : smembers) {
System.out.println(order);
}
//删除集合中的元素
jedis.srem("orders", "order02");zset-api
jedis.zadd("zset01", 100d, "z3");
jedis.zadd("zset01", 90d, "l4");
jedis.zadd("zset01", 80d, "w5");
jedis.zadd("zset01", 70d, "z6");
Set<String> zrange = jedis.zrange("zset01", 0, -1);
for (String e : zrange) {
System.out.println(e);
}list-api
//添加
jedis.lpush("mylist","test1","test2","test3");
//获取list里面的值
List<String> mylist = jedis.lrange("mylist", 0, -1);
for (String s : mylist) {
System.out.println(s);
}redis整合springboot
1、创建springboot项目
2、加入 redis 的依赖
<!-- 添加第一个 添加 starter 组件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.commons</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-pool2</artifactId>
<version>2.6.0</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clients</groupId>
<artifactId>jedis</artifactId>
</dependency>3、编写配置文件
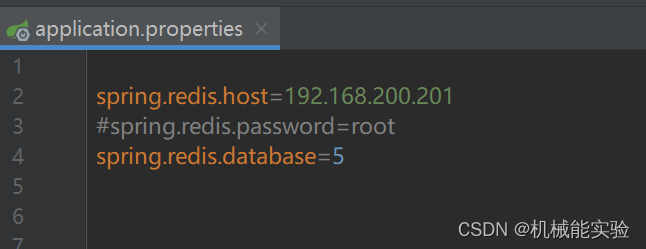
(application.properties)注入到spring容器中
要注意自己 redis.conf 里边的 端口号 和 密码 是否设置
如果配置和 redis.conf 里的不一样则会出现报错

4、设置 redis 信息
一般放在 controller 层 新建包 config 新建类 Redisconfig
Bean (key 序列化)
/**
* RedisTemplate
* @param factory
* @return
*/
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate<String, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
// 指定要序列化的域,field,get和set,以及修饰符范围,ANY是都有包括private和public
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
// 指定序列化输入的类型,类必须是非final修饰的,final修饰的类,比如String,Integer等会跑出异常
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
//key序列化方式
template.setKeySerializer(redisSerializer);
//value序列化
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
//value hashmap序列化
template.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return template;
}5、操作redis 编写代码
在测试类中编写操作 String 类型
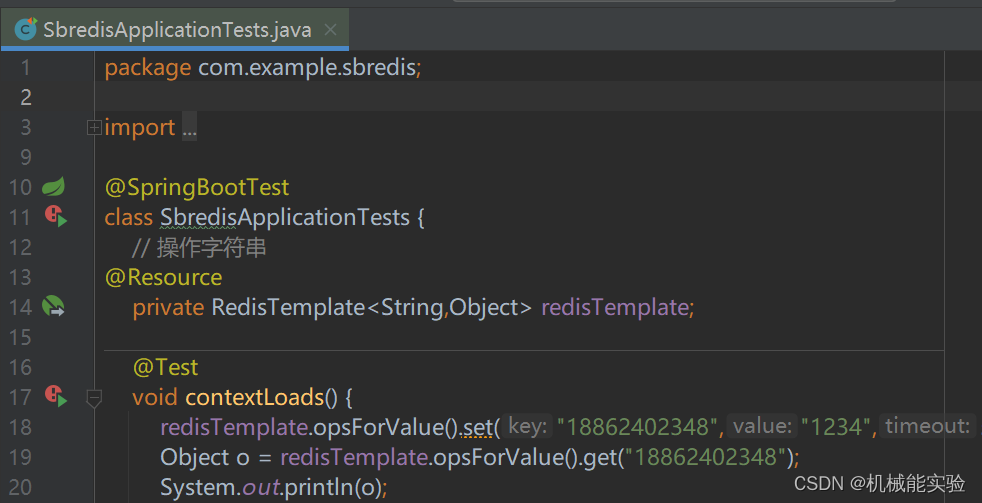
package com.example.sbredis;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@SpringBootTest
class SbredisApplicationTests {
// 操作字符串
@Resource
private RedisTemplate<String,Object> redisTemplate;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
// 过期时间 5 分钟
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("18862402348","1234",5, TimeUnit.MINUTES);
Object o = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("18862402348");
System.out.println(o);
}
}
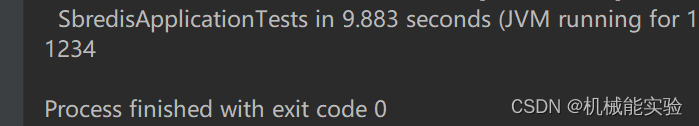
结果
spring-data-redis针对jedis提供了如下功能:
1. 连接池自动管理,提供了一个高度封装的“RedisTemplate”类
2. RedisTemplate 对五种数据结构分别定义了操作
操作字符串
redisTemplate.opsForValue();
操作hash
redisTemplate.opsForHash();
操作list
redisTemplate.opsForList();
操作set
redisTemplate.opsForSet();
操作有序set
redisTemplate.opsForZSet();
String类型常用方法
判断是否有key所对应的值,有则返回true,没有则返回false
redisTemplate.hasKey(key)
有则取出key值所对应的值
redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key)
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("key","val")
删除单个key值
redisTemplate.delete(key)
批量删除key
redisTemplate.delete(keys) //其中keys:Collection<K> keys
void set(K key, V value);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("num","123");
redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("num") 输出结果为123
void set(K key, V value, long timeout, TimeUnit unit);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("num","123",10, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("num")设置的是10秒失效,十秒之内查询有结果,十秒之后返回为null
TimeUnit.DAYS //天
TimeUnit.HOURS //小时
TimeUnit.MINUTES //分钟
TimeUnit.SECONDS //秒
TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS //毫秒
void set(K key, V value, long offset);
覆写(overwrite)给定 key 所储存的字符串值,从偏移量 offset 开始
template.opsForValue().set("key","hello world");
template.opsForValue().set("key","redis", 6);
System.out.println("***************"+template.opsForValue().get("key"));
结果:***************hello redis
V get(Object key);
template.opsForValue().set("key","hello world");
System.out.println("***************"+template.opsForValue().get("key"));
结果:***************hello world
getAndSet V getAndSet(K key, V value);
设置键的字符串值并返回其旧值
template.opsForValue().set("getSetTest","test");
System.out.println(template.opsForValue().getAndSet("getSetTest","test2"));
结果:test
append Integer append(K key, String value);
如果key已经存在并且是一个字符串,则该命令将该值追加到字符串的末尾。如果键不存在,则它被创建并设置为空字符串,因此APPEND在这种特殊情况下将类似于SET。
template.opsForValue().append("test","Hello");
System.out.println(template.opsForValue().get("test"));
template.opsForValue().append("test","world");
System.out.println(template.opsForValue().get("test"));
Hello
Helloworld
size Long size(K key);
返回key所对应的value值得长度
template.opsForValue().set("key","hello world");
System.out.println("***************"+template.opsForValue().size("key"));
***************11List类型
通过索引获取列表中的元素
redisTemplate.opsForList().index(key, index)
获取列表指定范围内的元素(start开始位置, 0是开始位置,end 结束位置, -1返回所有)
redisTemplate.opsForList().range(key, start, end)
存储在list的头部,即添加一个就把它放在最前面的索引处
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(key, value)
把多个值存入List中(value可以是多个值,也可以是一个Collection value)
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPushAll(key, value)
List存在的时候再加入
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPushIfPresent(key, value)
如果pivot处值存在则在pivot前面添加
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush(key, pivot, value)
按照先进先出的顺序来添加(value可以是多个值,或者是Collection var2)
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush(key, value)
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPushAll(key, value)
在pivot元素的右边添加值
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush(key, pivot, value)
设置指定索引处元素的值
redisTemplate.opsForList().set(key, index, value)
移除并获取列表中第一个元素(如果列表没有元素会阻塞列表直到等待超时或发现可弹出元素为止)
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPop(key)
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPop(key, timeout, unit)
移除并获取列表最后一个元素
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPop(key)
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPop(key, timeout, unit)
从一个队列的右边弹出一个元素并将这个元素放入另一个指定队列的最左边
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPopAndLeftPush(sourceKey, destinationKey)
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPopAndLeftPush(sourceKey, destinationKey, timeout, unit)
删除集合中值等于value的元素(index=0, 删除所有值等于value的元素; index>0, 从头部开始删除第一个值等于value的元素; index<0, 从尾部开始删除第一个值等于value的元素)
redisTemplate.opsForList().remove(key, index, value)
将List列表进行剪裁
redisTemplate.opsForList().trim(key, start, end)
获取当前key的List列表长度
redisTemplate.opsForList().size(key)Set类型
添加元素
redisTemplate.opsForSet().add(key, values)
移除元素(单个值、多个值)
redisTemplate.opsForSet().remove(key, values)
删除并且返回一个随机的元素
redisTemplate.opsForSet().pop(key)
获取集合的大小
redisTemplate.opsForSet().size(key)
判断集合是否包含value
redisTemplate.opsForSet().isMember(key, value)
获取两个集合的交集(key对应的无序集合与otherKey对应的无序集合求交集)
redisTemplate.opsForSet().intersect(key, otherKey)
获取多个集合的交集(Collection var2)
redisTemplate.opsForSet().intersect(key, otherKeys)
key集合与otherKey集合的交集存储到destKey集合中(其中otherKey可以为单个值或者集合)
redisTemplate.opsForSet().intersectAndStore(key, otherKey, destKey)
key集合与多个集合的交集存储到destKey无序集合中
redisTemplate.opsForSet().intersectAndStore(key, otherKeys, destKey)
获取两个或者多个集合的并集(otherKeys可以为单个值或者是集合)
redisTemplate.opsForSet().union(key, otherKeys)
key集合与otherKey集合的并集存储到destKey中(otherKeys可以为单个值或者是集合)
redisTemplate.opsForSet().unionAndStore(key, otherKey, destKey)
获取两个或者多个集合的差集(otherKeys可以为单个值或者是集合)
redisTemplate.opsForSet().difference(key, otherKeys)
差集存储到destKey中(otherKeys可以为单个值或者集合)
redisTemplate.opsForSet().differenceAndStore(key, otherKey, destKey)
随机获取集合中的一个元素
redisTemplate.opsForSet().randomMember(key)
获取集合中的所有元素
redisTemplate.opsForSet().members(key)
随机获取集合中count个元素
redisTemplate.opsForSet().randomMembers(key, count)
获取多个key无序集合中的元素(去重),count表示个数
redisTemplate.opsForSet().distinctRandomMembers(key, count)
遍历set类似于Interator(ScanOptions.NONE为显示所有的)
redisTemplate.opsForSet().scan(key, options)Hash类型
Long delete(H key, Object... hashKeys);
删除给定的哈希hashKeys
System.out.println(template.opsForHash().delete("redisHash","name"));
System.out.println(template.opsForHash().entries("redisHash"));
1
{class=6, age=28.1}
Boolean hasKey(H key, Object hashKey);
确定哈希hashKey是否存在
System.out.println(template.opsForHash().hasKey("redisHash","666"));
System.out.println(template.opsForHash().hasKey("redisHash","777"));
true
false
HV get(H key, Object hashKey);
从键中的哈希获取给定hashKey的值
System.out.println(template.opsForHash().get("redisHash","age"));
26
Set<HK> keys(H key);
获取key所对应的散列表的key
System.out.println(template.opsForHash().keys("redisHash"));
//redisHash所对应的散列表为{class=1, name=666, age=27}
[name, class, age]
Long size(H key);
获取key所对应的散列表的大小个数
System.out.println(template.opsForHash().size("redisHash"));
//redisHash所对应的散列表为{class=1, name=666, age=27}
3
void putAll(H key, Map<? extends HK, ? extends HV> m);
使用m中提供的多个散列字段设置到key对应的散列表中
Map<String,Object> testMap = new HashMap();
testMap.put("name","666");
testMap.put("age",27);
testMap.put("class","1");
template.opsForHash().putAll("redisHash1",testMap);
System.out.println(template.opsForHash().entries("redisHash1"));
{class=1, name=jack, age=27}
void put(H key, HK hashKey, HV value);
设置散列hashKey的值
template.opsForHash().put("redisHash","name","666");
template.opsForHash().put("redisHash","age",26);
template.opsForHash().put("redisHash","class","6");
System.out.println(template.opsForHash().entries("redisHash"));
{age=26, class=6, name=666}
List<HV> values(H key);
获取整个哈希存储的值根据密钥
System.out.println(template.opsForHash().values("redisHash"));
[tom, 26, 6]
Map<HK, HV> entries(H key);
获取整个哈希存储根据密钥
System.out.println(template.opsForHash().entries("redisHash"));
{age=26, class=6, name=tom}
Cursor<Map.Entry<HK, HV>> scan(H key, ScanOptions options);
使用Cursor在key的hash中迭代,相当于迭代器。
Cursor<Map.Entry<Object, Object>> curosr = template.opsForHash().scan("redisHash",
ScanOptions.ScanOptions.NONE);
while(curosr.hasNext()){
Map.Entry<Object, Object> entry = curosr.next();
System.out.println(entry.getKey()+":"+entry.getValue());
}
age:27
class:6
name:666| 命令 | 操作 | 返回值 |
| hash.delete(H key, Object... hashKeys) | 删除,可以传入多个map的key【hdel】 | Long |
| hash.hasKey(key, hashKey) | 查看hash中的某个hashKey是否存在【hexists】 | Boolean |
| hash.get(key, hashKey) | 获取值【hget】 | Object(HV 泛型约束对象) |
| hash.multiGet(H key, Collection<HK> hashKeys) | 批量获取集合中的key对应的值【hmget】 | List<HV> |
| hash.increment(H key, HK hashKey, long delta) | 对值进行+(delta值)操作【】 | Long |
| hash.increment(H key, HK hashKey, double delta) | ~ | double |
| hash.keys(key) | 返回map内hashKey的集合【hkeys】 | Set<HK> |
| hash.lengthOfValue(H key, HK hashKey) | 返回查询键关联的值的长度,为null则返回0【hstrlen】 | Long |
| hash.size(H key) | 获取hashKey的个数【hlen】 | Long |
| hash.putAll(H key, Map<? extends HK, ? extends HV> m) | 相当于map的putAll【hmset】 | void |
| hash.put(H key, HK hashKey, HV value) | 设置值,添加hashKey-value,hashKay相当于map的key 【hset】 | void |
| hash.putIfAbsent(H key, HK hashKey, HV value) | 仅当hashKey不存在时设置值 | Boolean |
| hash.values(key) | 返回value的集合【hvals】 | List<HV> |
| hase.entries(H key) | 获取map【hgetall】 | Map<HK, HV> |
| hash.scan(H key, ScanOptions options) | 基于游标的迭代查询【hscan】 | Cursor<Map.Entry<HK, HV>>(返回的Cursor要手动关闭,见下面示例2) |
| hash.getOperations() | 返回RedisOperation,它就是redis操作的接口 | RedisOperations<H, ?> |
ZSet类型
Boolean add(K key, V value, double score);
新增一个有序集合,存在的话为false,不存在的话为true
System.out.println(template.opsForZSet().add("zset1","zset-1",1.0));
true
Long add(K key, Set<TypedTuple<V>> tuples);
新增一个有序集合
ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object> objectTypedTuple1 = new DefaultTypedTuple<>("zset-5",9.6);
ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object> objectTypedTuple2 = new DefaultTypedTuple<>("zset-6",9.9);
Set<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object>> tuples = new HashSet<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object>>();
tuples.add(objectTypedTuple1);
tuples.add(objectTypedTuple2);
System.out.println(template.opsForZSet().add("zset1",tuples));
System.out.println(template.opsForZSet().range("zset1",0,-1));
[zset-1, zset-2, zset-3, zset-4, zset-5, zset-6]
Long remove(K key, Object... values);
从有序集合中移除一个或者多个元素
System.out.println(template.opsForZSet().range("zset1",0,-1));
System.out.println(template.opsForZSet().remove("zset1","zset-6"));
System.out.println(template.opsForZSet().range("zset1",0,-1));
[zset-1, zset-2, zset-3, zset-4, zset-5, zset-6]
1
[zset-1, zset-2, zset-3, zset-4, zset-5]
Long rank(K key, Object o);
返回有序集中指定成员的排名,其中有序集成员按分数值递增(从小到大)顺序排列
System.out.println(template.opsForZSet().range("zset1",0,-1));
System.out.println(template.opsForZSet().rank("zset1","zset-2"));
[zset-2, zset-1, zset-3, zset-4, zset-5]
0 //表明排名第一
Set<V> range(K key, long start, long end);
通过索引区间返回有序集合成指定区间内的成员,其中有序集成员按分数值递增(从小到大)顺序排列
System.out.println(template.opsForZSet().range("zset1",0,-1));
[zset-2, zset-1, zset-3, zset-4, zset-5]
Long count(K key, double min, double max);
通过分数返回有序集合指定区间内的成员个数
System.out.println(template.opsForZSet().rangeByScore("zset1",0,5));
System.out.println(template.opsForZSet().count("zset1",0,5));
[zset-2, zset-1, zset-3]
3
Long size(K key);
获取有序集合的成员数,内部调用的就是zCard方法
System.out.println(template.opsForZSet().size("zset1"));
6
Double score(K key, Object o);
获取指定成员的score值
System.out.println(template.opsForZSet().score("zset1","zset-1"));
2.2
Long removeRange(K key, long start, long end);
移除指定索引位置的成员,其中有序集成员按分数值递增(从小到大)顺序排列
System.out.println(template.opsForZSet().range("zset2",0,-1));
System.out.println(template.opsForZSet().removeRange("zset2",1,2));
System.out.println(template.opsForZSet().range("zset2",0,-1));
[zset-1, zset-2, zset-3, zset-4]
2
[zset-1, zset-4]
Cursor<TypedTuple<V>> scan(K key, ScanOptions options);
遍历zset
Cursor<ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object>> cursor = template.opsForZSet().scan("zzset1", ScanOptions.NONE);
while (cursor.hasNext()){
ZSetOperations.TypedTuple<Object> item = cursor.next();
System.out.println(item.getValue() + ":" + item.getScore());
}
zset-1:1.0
zset-2:2.0
zset-3:3.0
zset-4:6.0四、集成 Spring Cache (spring缓存注解)
1、一定要加 jar 包 和 整合 springboot 文件一样的 jar 包
<!-- 添加 starter 组件-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>2、编写配置文件
一定要注意 端口号 和 密码 和 redis.conf 里边配置的 一样
没有密码 就不写密码

3、引入第三方缓存 添加配置信息 添加缓存 Bean
添加在 config 包 的 Redisconfig 类
/**
* 缓存处理
* @param factory
* @return
*/
@Bean
public CacheManager cacheManager(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisSerializer<String> redisSerializer = new StringRedisSerializer();
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
//解决查询缓存转换异常的问题
ObjectMapper om = new ObjectMapper();
om.setVisibility(PropertyAccessor.ALL, JsonAutoDetect.Visibility.ANY);
om.enableDefaultTyping(ObjectMapper.DefaultTyping.NON_FINAL);
jackson2JsonRedisSerializer.setObjectMapper(om);
// 配置序列化(解决乱码的问题),过期时间600秒
RedisCacheConfiguration config = RedisCacheConfiguration.defaultCacheConfig()
.entryTtl(Duration.ofSeconds(600))
.serializeKeysWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(redisSerializer))
.serializeValuesWith(RedisSerializationContext.SerializationPair.fromSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer))
.disableCachingNullValues();
RedisCacheManager cacheManager = RedisCacheManager.builder(factory)
.cacheDefaults(config)
.build();
return cacheManager;
}4、添加数据库表 Dept 体验Redis使用缓存
1. mybatis 自动生成代码模板 数据库表 的 model 、 xml 等文件
添加依赖 pom文件
<!-- mp-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>3.5.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 自动生成-->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.baomidou</groupId>
<artifactId>mybatis-plus-generator</artifactId>
<version>3.5.3</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 模板-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.velocity</groupId>
<artifactId>velocity-engine-core</artifactId>
<version>2.3</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.freemarker</groupId>
<artifactId>freemarker</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>8.0.23</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>2、将自动生成的脚本代码放入 测试类 test文件夹下
新建 Mytest 类

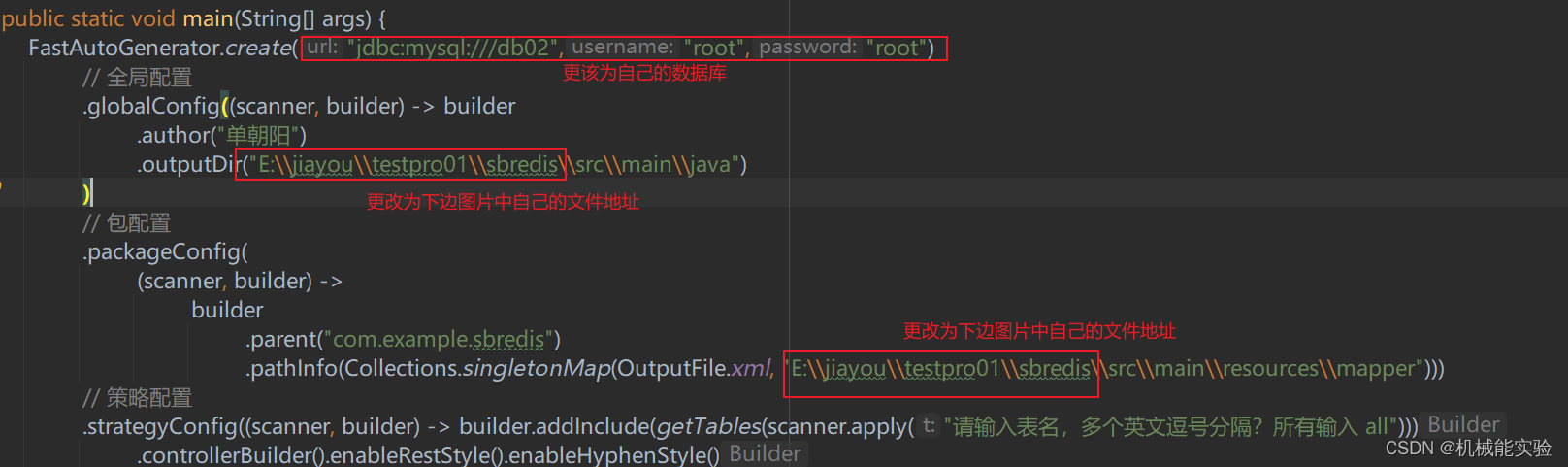
更改代码中的配置信息(更改地址以及数据库)
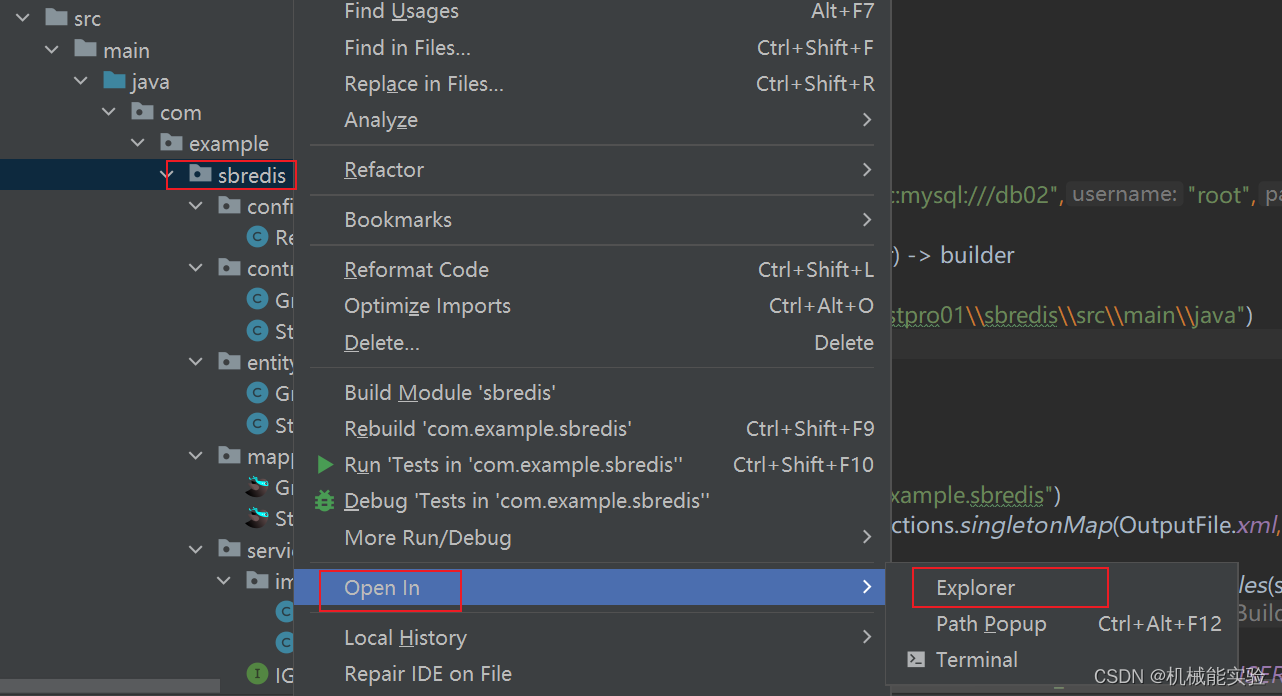
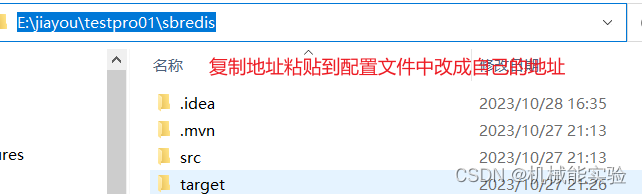
3、配置数据库信息,放在 application.properties中
记得更改自己的用户名 数据库 密码 以及 连接地址 ( 有的加cj 有的不加 )
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
spring.datasource.url=jdbc:mysql:///db02?serverTimezone=UTC&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf-8&useSSL=false
spring.datasource.username=root
spring.datasource.password=root
# ?? ?? ?? json ?????
spring.jackson.date-format=yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
spring.jackson.time-zone=GMT+8
spring.jackson.serialization.write-date-keys-as-timestamps=false
#logging.level.com.baomidou.ant.test.dao=debug
#mybatis-plus
# r_name rName setRName
mybatis-plus.configuration.map-underscore-to-camel-case=true
mybatis-plus.configuration.log-impl=org.apache.ibatis.logging.stdout.StdOutImpl
#mybatis-plus.configuration.log-impl=
mybatis-plus.mapper-locations=classpath:/mapper/*.xml
# ???? ?????0 ??? 1
mybatis-plus.global-config.db-config.logic-not-delete-value=0
mybatis-plus.global-config.db-config.logic-delete-value=14、运行Mytest 自动生成代码
5、对部门 Dept 进行查询 查询所有的部门信息
然后启动 service 层的 application 类
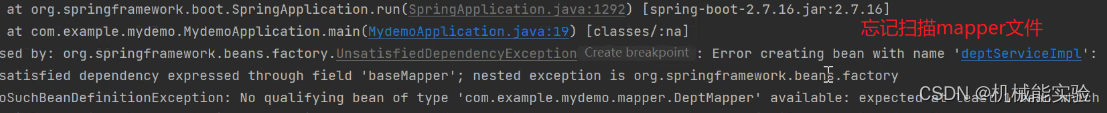
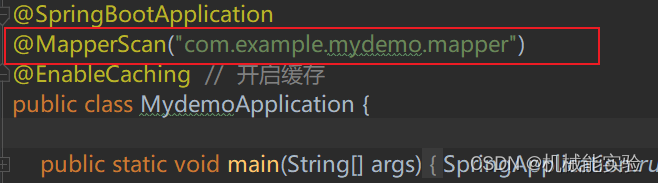
在 service 层的 application 类添加@MapperScan("com.example.mydemo.mapper")
或者在 dao 层添加mapper注解
使用 postman进行接口测试 查看数据
集成 Spring Cache (spring缓存注解) 开启缓存
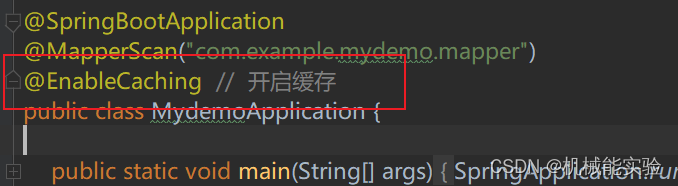
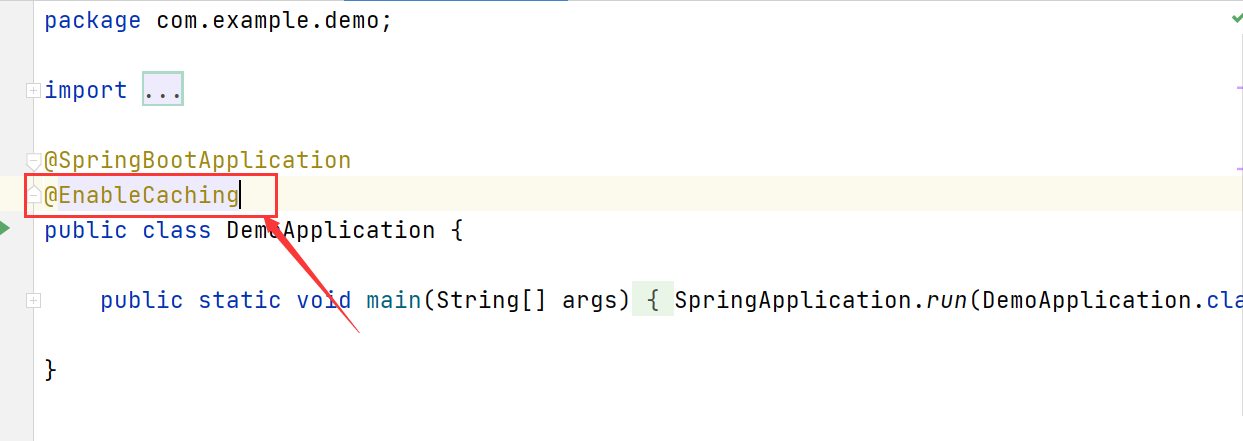
// @EnableCaching // 开启缓存
5、spring缓存注解
从3.1开始,Spring引入了对Cache的支持。其使用方法和原理都类似于Spring对事务管理的支持。Spring Cache是作用在方法上的,其核心思想是这样的:当我们在调用一个缓存方法时会把该方法参数和返回结果作为一个键值对存放在缓存中,等到下次利用同样的参数来调用该方法时将不再执行该方法,而是直接从缓存中获取结果进行返回。所以在使用Spring Cache的时候我们要保证我们缓存的方法对于相同的方法参数要有相同的返回结果。
使用Spring Cache需要我们做两方面的事:
1. 声明某些方法使用缓存
2. 配置Spring对Cache的支持
和Spring对事务管理的支持一样,Spring对Cache的支持也有基于注解和基于XML配置两种方式。下面我们先来看看基于注解的方式。(基于配置的自己私下去了解即可)
@Cacheable 一般写在 service 层 放在查询上边 (例子如下)
必须添加 value 不添加则不生效
6、启动 application
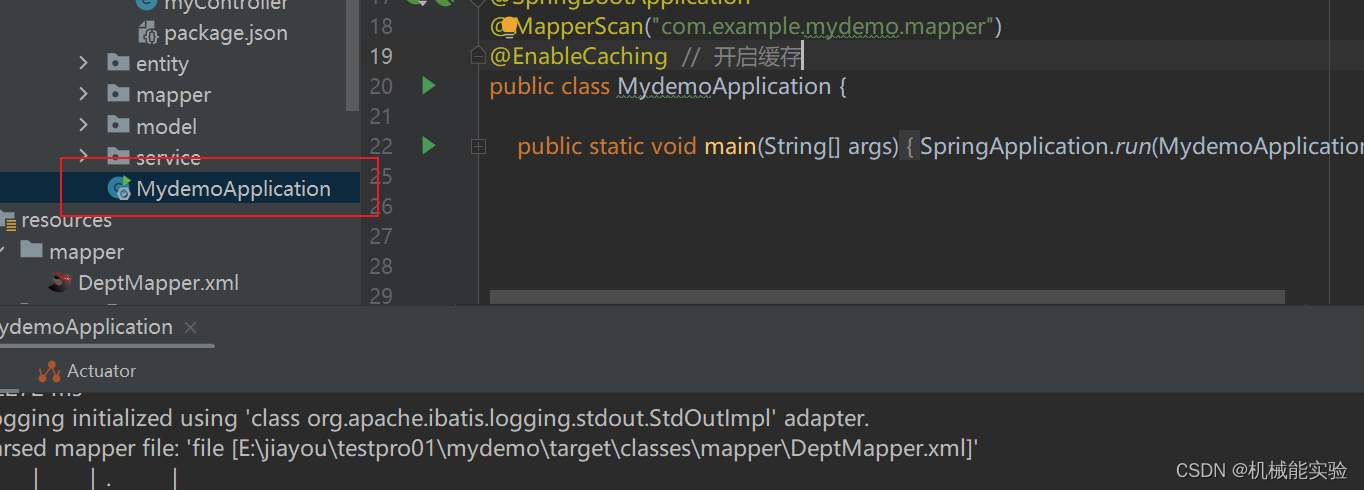
7、使用postman进行查询
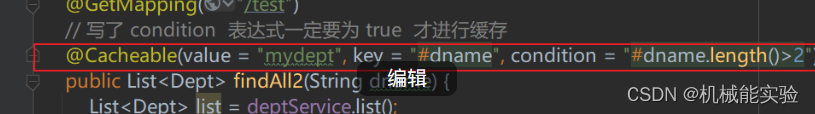
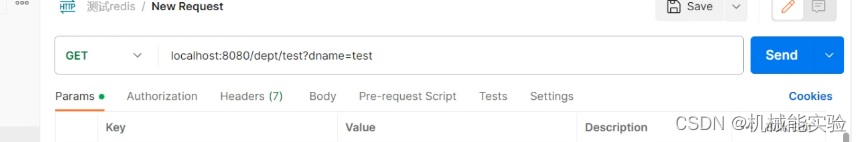
dnam的长度大于2才缓存到redis 因为 要满足 condition 的条件
8、在客户端查看是否存放在redis里边
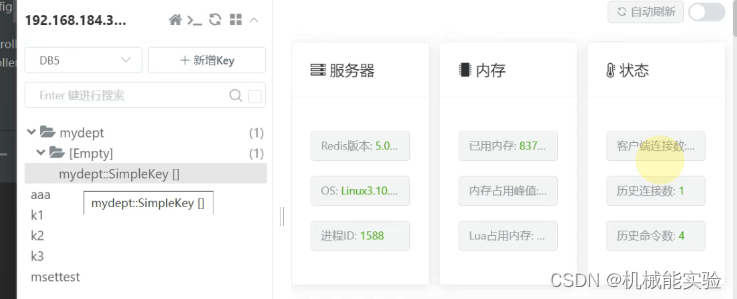
五、代码
查询数据的一般放在 service 层 impl
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/dept")
public class DeptController {
@Resource
private IDeptService deptService;
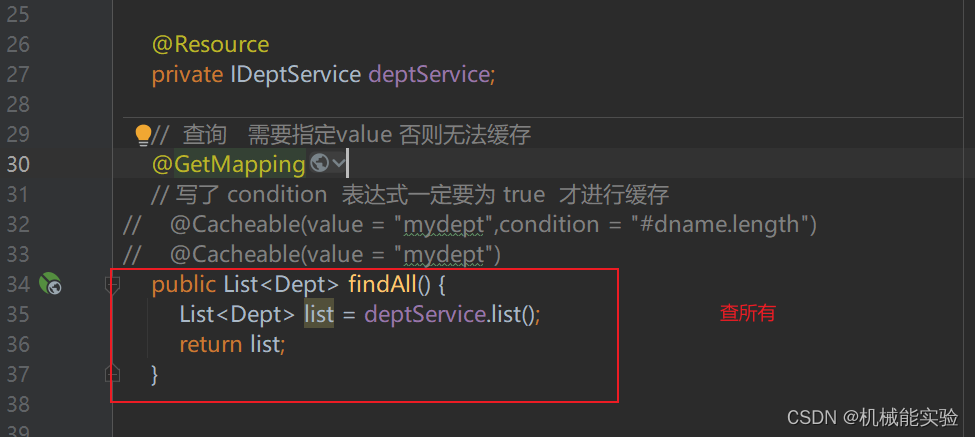
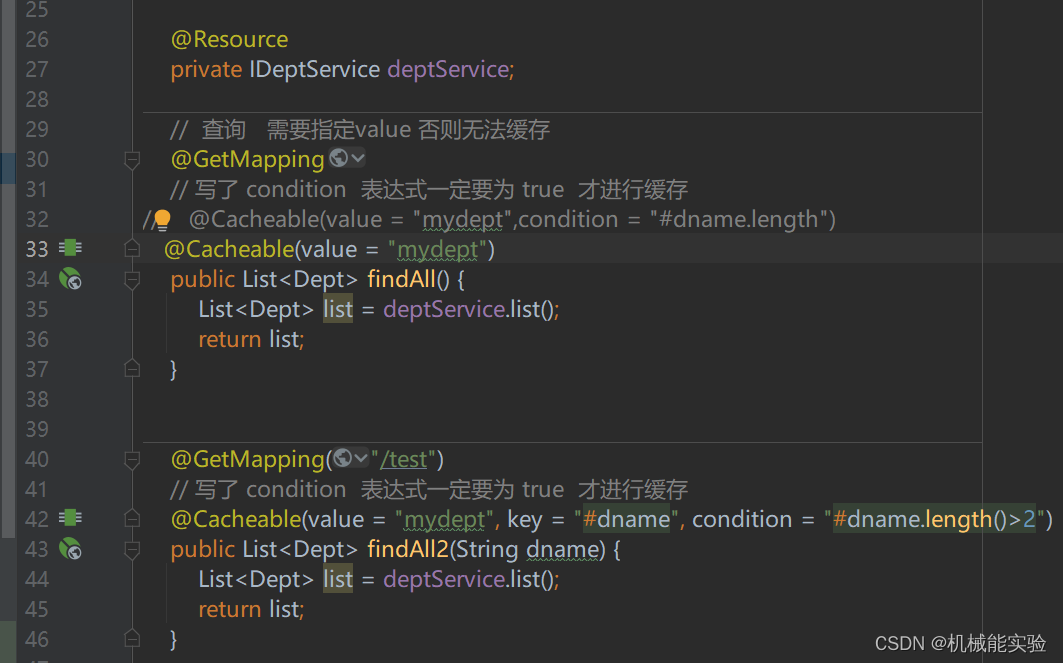
// 查询 需要指定value 否则无法缓存
@GetMapping
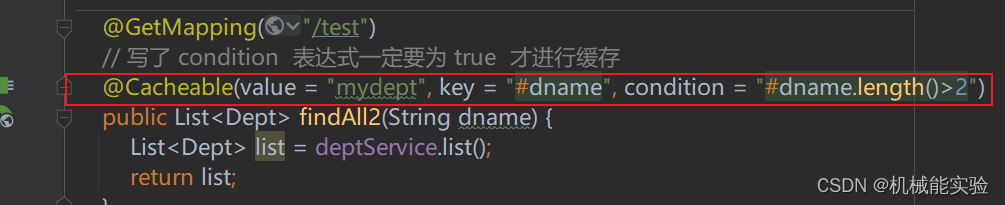
// 写了 condition 表达式一定要为 true 才进行缓存
// @Cacheable(value = "mydept",condition = "#dname.length")
@Cacheable(value = "mydept")
public List<Dept> findAll() {
List<Dept> list = deptService.list();
return list;
}
@GetMapping("/test")
// 写了 condition 表达式一定要为 true 才进行缓存
@Cacheable(value = "mydept", key = "#dname", condition = "#dname.length()>2")
public List<Dept> findAll2(String dname) {
List<Dept> list = deptService.list();
return list;
}
// 修改
@PutMapping
@CachePut(value = "mydept", key = "#dept.deptno")
public String updateDept(Dept dept) {
boolean b = deptService.updateById(dept);
System.out.println(b);
return b + "";
}
// 删除
@DeleteMapping
@CacheEvict(value = "mydept", key = "#deptno", allEntries = true)
public String deleteDept(Integer deptno) {
boolean b = deptService.removeById(deptno); // 从数据中溢出
// 数据中没有 id = 50 的信息
// redis 里边缓存的数据也应该删除
// 客户端查询 id=50 的数据 redis 也应该清除缓存中的元素
// allEntries = true 清除所有数据
System.out.println(b);
return b + "";
}
// 添加 使用 post 请求
@PostMapping
@CachePut(value = "mydept", key = "#dept.dname")
public String addDept(Dept dept) {
boolean b = deptService.save(dept);
System.out.println(b);
return b + "";
}六、基于注解的支持 @Cacheable 、@CachePut @CacheEvict
@Cacheable
@Cacheable可以标记在一个方法上,也可以标记在一个类上。当标记在一个方法上时表示该方法是支持缓存的,当标记在一个类上时则表示该类所有的方法都是支持缓存的。对于一个支持缓存的方法,Spring会在其被调用后将其返回值缓存起来,以保证下次利用同样的参数来执行该方法时可以直接从缓存中获取结果,而不需要再次执行该方法。
@Cacheable 的作用 主要针对方法配置,能够根据方法的请求参数对其结果进行缓存
@Cacheable可以指定三个属性,value、key和condition。
| 参数 | 解释 | example |
| value | 缓存的名称,在 spring 配置文件中定义,必须指定至少一个 | 例如: @Cacheable(value=”mycache”) @Cacheable(value={”cache1”,”cache2”} |
| key | 缓存的 key,可以为空,如果指定要按照 SpEL 表达式编写,如果不指定,则缺省按照方法的所有参数进行组合 | @Cacheable(value=”testcache”,key=”#userName”) |
| condition | 缓存的条件,可以为空,使用 SpEL 编写,返回 true 或者 false,只有为 true 才进行缓存 | @Cacheable(value=”testcache”,condition=”#userName.length()>2”) |
value属性指定Cache名称
value其表示当前方法的返回值是会被缓存在哪个Cache上的,对应Cache的名称。其可以是一个Cache也可以是多个Cache,当需要指定多个Cache时其是一个数组。
@Cacheable("cache1")//Cache是发生在cache1上的
public User find(Integer id) {
returnnull;
}
@Cacheable({"cache1", "cache2"})//Cache是发生在cache1和cache2上的
public User find(Integer id) {
returnnull;
}
使用key属性自定义key
key属性是用来指定Spring缓存方法的返回结果时对应的key的。该属性支持SpringEL表达式。当我们没有指定该属性时,Spring将使用默认策略生成key。我们这里先来看看自定义策略
自定义策略是指我们可以通过Spring的EL表达式来指定我们的key。这里的EL表达式可以使用方法参数及它们对应的属性。使用方法参数时我们可以直接使用“#参数名”或者“#p参数index”。下面是几个使用参数作为key的示例。
@Cacheable(value="users", key="#id")
public User find(Integer id) {
return null;
}
@Cacheable(value="users", key="#p0")
public User find(Integer id) {
returnnull;
}
@Cacheable(value="users", key="#user.id")
public User find(User user) {
returnnull;
}
@Cacheable(value="users", key="#p0.id")
public User find(User user) {
returnnull;
}除了上述使用方法参数作为key之外,Spring还为我们提供了一个root对象可以用来生成key。通过该root对象我们可以获取到以下信息。
| 属性名称 | 描述 | 示例 |
| methodName | 当前方法名 | #root.methodName |
| method | 当前方法 | #root.method.name |
| target | 当前被调用的对象 | #root.target |
| targetClass | 当前被调用的对象的class | #root.targetClass |
| args | 当前方法参数组成的数组 | #root.args[0] |
| caches | 当前被调用的方法使用的Cache | #root.caches[0].name |
当我们要使用root对象的属性作为key时我们也可以将“#root”省略,因为Spring默认使用的就是root对象的属性。如:
@Cacheable(value={"users", "xxx"}, key="caches[1].name")
public User find(User user) {
returnnull;
}condition属性指定发生的条件
有的时候我们可能并不希望缓存一个方法所有的返回结果。通过condition属性可以实现这一功能。condition属性默认为空,表示将缓存所有的调用情形。其值是通过SpringEL表达式来指定的,当为true时表示进行缓存处理;当为false时表示不进行缓存处理,即每次调用该方法时该方法都会执行一次。如下示例表示只有当user的id为偶数时才会进行缓存。
@Cacheable(value={"users"}, key="#user.id", condition="#user.id%2==0")
public User find(User user) {
System.out.println("find user by user " + user);
return user;
}@CachePut
在支持Spring Cache的环境下,对于使用@Cacheable标注的方法,Spring在每次执行前都会检查Cache中是否存在相同key的缓存元素,如果存在就不再执行该方法,而是直接从缓存中获取结果进行返回,否则才会执行并将返回结果存入指定的缓存中。@CachePut也可以声明一个方法支持缓存功能。与@Cacheable不同的是使用@CachePut标注的方法在执行前不会去检查缓存中是否存在之前执行过的结果,而是每次都会执行该方法,并将执行结果以键值对的形式存入指定的缓存中。
一般使用在保存,更新方法中。
@CachePut也可以标注在类上和方法上。使用@CachePut时我们可以指定的属性跟 @Cacheable是一样的。
@Cacheable(cacheNames = "user", key = "#id")//每次都会执行方法,并将结果存入指定的缓存中
public User find(Integer id) {
return null;
}@CacheEvict
@CacheEvict是用来标注在需要清除缓存元素的方法或类上的。当标记在一个类上时表示其中所有的方法的执行都会触发缓存的清除操作。@CacheEvict可以指定的属性有value、key、condition、allEntries和beforeInvocation。其中value、key和condition的语义与@Cacheable对应的属性类似。即value表示清除操作是发生在哪些Cache上的(对应Cache的名称);key表示需要清除的是哪个key,如未指定则会使用默认策略生成的key;condition表示清除操作发生的条件。下面我们来介绍一下新出现的两个属性allEntries和beforeInvocation。
1、 allEntries属性
allEntries是boolean类型,表示是否需要清除缓存中的所有元素。默认为false,表示不需要。当指定了allEntries为true时,Spring Cache将忽略指定的key。有的时候我们需要Cache一下清除所有的元素,这比一个一个清除元素更有效率。
@CacheEvict(value="users",key = "#id", allEntries=true)
public void delete(Integer id) {
System.out.println("delete user by id: " + id);
}2、 beforeInvocation属性
清除操作默认是在对应方法成功执行之后触发的,即方法如果因为抛出异常而未能成功返回时也不会触发清除操作。使用beforeInvocation可以改变触发清除操作的时间,当我们指定该属性值为true时,Spring会在调用该方法之前清除缓存中的指定元素。
@CacheEvict(value="users",key = "#id", beforeInvocation=true)
public void delete(Integer id) {
System.out.println("delete user by id: " + id);
}七、springboot基于注解的redis缓存
1.开启注解缓存
2.修改service
package com.example.demo.dept.service.impl;
import com.example.demo.dept.entity.Dept;
import com.example.demo.dept.dao.DeptMapper;
import com.example.demo.dept.service.IDeptService;
import com.baomidou.mybatisplus.extension.service.impl.ServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CacheEvict;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.CachePut;
import org.springframework.cache.annotation.Cacheable;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ListOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import java.util.List;
/**
* <p>
* 服务实现类
* </p>
*
* @author yuyongli
* @since 2021-03-04
*/
@Service
public class DeptServiceImpl extends ServiceImpl<DeptMapper, Dept> implements IDeptService {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Override
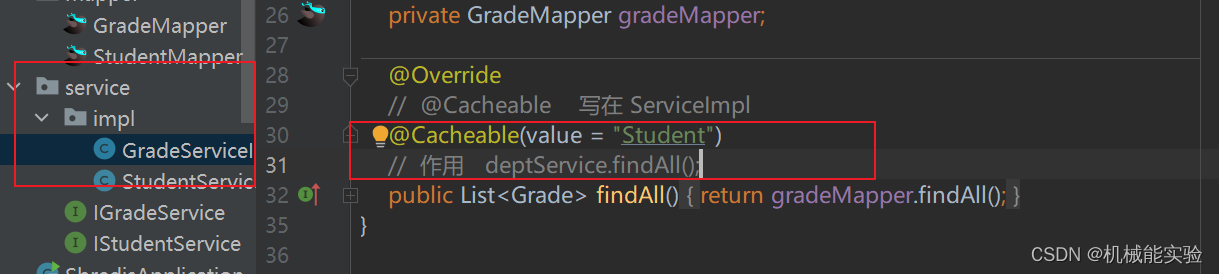
//@Cacheable(value = "depts",key = "#root.methodName")
@CachePut(value = "depts",key = "#root.targetClass")
public List<Dept> queryAll() {
List<Dept> users = this.list();
//将数据存到redis里面
return users;
//return
}
@Override
@CachePut(value = "dept",key = "#dept.deptno")
public boolean addDept(Dept dept) {
boolean save = this.save(dept);
return save;
}
@Override
@CacheEvict(value = "depts",key="#root.targetClass")
public boolean deleteDept(int deptno) {
boolean b = this.removeById(deptno);
return b;
}
}3.测试
package com.example.demo;
import com.example.demo.dept.entity.Dept;
import com.example.demo.dept.service.IDeptService;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Value;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisClusterConfiguration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisNode;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.jedis.JedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ClusterOperations;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.ValueOperations;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import redis.clients.jedis.HostAndPort;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisCluster;
import redis.clients.jedis.JedisPoolConfig;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Set;
@SpringBootTest
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
class DemoApplicationTests {
@Value("${spring.redis.cluster.nodes}")
private String clusterNodes;
@Autowired
private IDeptService deptService;
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String,String> redisTemplate;
@Test
public void testredis(){
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("myKey","myValue");
System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("myKey"));
//list类型
redisTemplate.opsForList().leftPush("testlist","yuyongli","yuyongli");
//取值
List<String> testlist = redisTemplate.opsForList().range("testlist", 0, -1);
System.out.println(testlist);
//set类型
redisTemplate.opsForSet().add("setkey","yuyongli","30","30");
Set<String> members = redisTemplate.opsForSet().members("setkey");
System.out.println(members);
}
@Test
public void testjiqun(){
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("test","yyl");
String test = redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("test");
System.out.println(test);
}
@Test
public void testQueryDept(){
List<Dept> depts = deptService.queryAll();
System.out.println(depts);
}
/**
* 测试添加
*/
@Test
public void addDept(){
Dept dept=new Dept();
dept.setDname("于永利测试1");
dept.setLoc("郑州");
deptService.addDept(dept);
}
@Test
public void delDept(){
deptService.deleteDept(12);
}
}






















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










