1.两个进程间的通信
进程A代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//创建两个管道文件
if(mkfifo("./FIFO1",0775)==-1)
{
if(errno!=17)//排除文件已经存在的错误
{
perror("mkfifo");
return -1;
}
}
if(mkfifo("./FIFO2",0775)==-1)
{
if(errno!=17)
{
perror("mkfifo");
return -1;
}
}
//以写的方式打开管道1
int fp_w = open("./FIFO1",O_WRONLY);
//以读的方式打开管道2
int fp_r = open("./FIFO2",O_RDONLY);
printf("creat FIFO on success\n");
char buf[128] = "";
while(1)
{
//写
printf("我:");
fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);
buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '\0';//删除多余的换行
write(fp_w,buf,sizeof(buf));
if(strcmp(buf,"quit") == 0)
{
printf("你已退出聊天\n");
close(fp_w);
close(fp_r);
return -1;
}
//读
bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));//清空字符串防止上一次的结果干扰
if(read(fp_r,buf,sizeof(buf)) == -1)
{
perror("read");
return -1;
}
printf("B:");
printf("%s\n",buf);
if(strlen(buf) == 0)
{
printf("对方处于离线状态\n");
close(fp_w);
close(fp_r);
return -1;
}
if(strcmp(buf,"quit") == 0)
{
printf("对方已退出聊天\n");
close(fp_w);
close(fp_r);
return -1;
}
}
return 0;
}进程B代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//创建两个管道文件
if(mkfifo("./FIFO1",0775)==-1)
{
if(errno!=17)//排除文件已经存在的错误
{
perror("mkfifo");
return -1;
}
}
if(mkfifo("./FIFO2",0775)==-1)
{
if(errno!=17)
{
perror("mkfifo");
return -1;
}
}
//以读的方式打开管道1
int fp_r = open("./FIFO1",O_RDONLY);
//以写的方式打开管道2
int fp_w = open("./FIFO2",O_WRONLY);
printf("creat FIFO on success\n");
char buf[128] = "";
while(1)
{
//读
bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));//清空字符串防止上一次的结
if(read(fp_r,buf,sizeof(buf)) == -1)
{
perror("read");
return -1;
}
printf("A:");
printf("%s\n",buf);
if(strlen(buf) == 0)
{
printf("对方处于离线状态\n");
close(fp_w);
close(fp_r);
return -1;
}
if(strcmp(buf,"quit") == 0)
{
printf("对方已退出聊天\n");
close(fp_w);
close(fp_r);
return -1;
}
//写
printf("我:");
fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);
buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '\0';//删除多余的换行
write(fp_w,buf,sizeof(buf));
if(strcmp(buf,"quit") == 0)
{
printf("你已退出聊天\n");
close(fp_w);
close(fp_r);
return -1;
}
}
return 0;
}运行结果
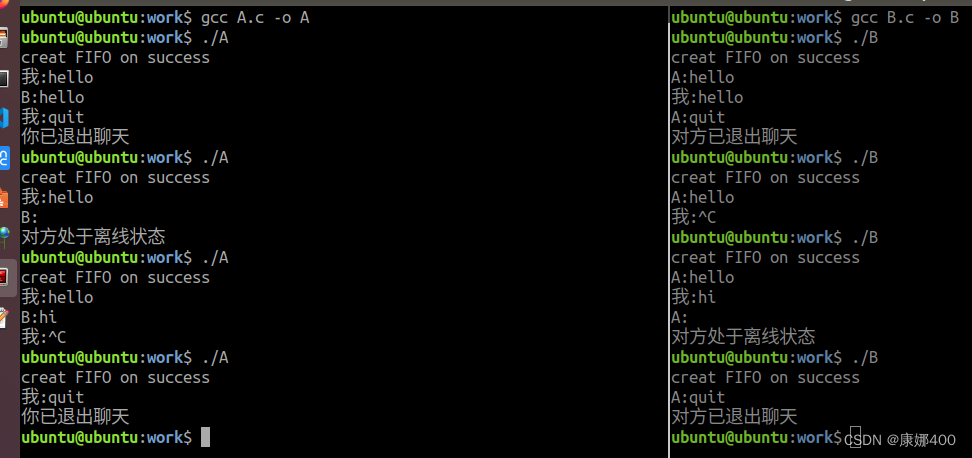
2.优化(实现随时都能发消息和接收)
进程A代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
//以写的方式打开管道1
void* f1_w(void* arg)
{
int fp_w = open("./FIFO1",O_WRONLY);
printf("\r连接成功 \n");
if(fp_w == -1)
{
perror("open");
return NULL;
}
char buf[128] = "";
while(1)
{
fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);
buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '\0';//去掉多余的回车
write(fp_w,buf,sizeof(buf));
if(strcmp(buf,"quit") == 0)//输入quit我们需要做的是结束两个子线程
{
close(fp_w);
pthread_cancel(*(pthread_t*)arg);//必须先结束另一个线程再结束自己
//也有一定概率没有关闭线程
pthread_exit(NULL);//顺序不能换
}
}
}//以读的方式打开管道2
void* f2_r(void* arg)
{
int fp_r = open("./FIFO2",O_RDONLY);
if(fp_r == -1)
{
perror("open");
return NULL;
}
char buf[128] = "";
while(1)
{
//读之前清空字符串防止上次读取信息的干扰
bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));
read(fp_r,buf,sizeof(buf));
printf("B:%s\n",buf);
if(strcmp(buf,"quit") == 0 || strlen(buf) == 0)
{
close(fp_r);
pthread_cancel(*(pthread_t*)arg);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
}
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
printf("连接中...");
fflush(stdout);
//创建管道文件
if(mkfifo("./FIFO1",0775)==-1)
{
if(errno!=17)//排除文件已经存在的错误码
{
perror("mkfifo");
return -1;
}
}
if(mkfifo("./FIFO2",0775)==-1)
{
if(errno!=17)
{
perror("mkfifo");
return -1;
}
}
//创建线程
pthread_t tid_w,tid_r;
if(pthread_create(&tid_w,NULL,f1_w,(void*)&tid_r)!=0)//把另一个线程的id传进去方便同时退出
{
fprintf(stderr,"creat pthread on error\n");
return -1;
}
if(pthread_create(&tid_r,NULL,f2_r,(void*)&tid_w)!=0)
{
fprintf(stderr,"creat pthread on error\n");
return -1;
}
//阻塞,等待子线程结束
pthread_join(tid_w,NULL);
pthread_join(tid_r,NULL);
return 0;
}进程B代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <unistd.h>
//以写的方式打开管道2
void* f1_w(void* arg)
{
int fp_w = open("./FIFO2",O_WRONLY);
printf("\r连接成功 \n");
if(fp_w == -1)
{
perror("open");
return NULL;
}
char buf[128] = "";
while(1)
{
fgets(buf,sizeof(buf),stdin);
buf[strlen(buf)-1] = '\0';//去掉多余的回车
write(fp_w,buf,sizeof(buf));
if(strcmp(buf,"quit") == 0)
{
close(fp_w);
pthread_cancel(*(pthread_t*)arg);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
}
}//以读的方式打开管道1
void* f2_r(void* arg)
{
int fp_r = open("./FIFO1",O_RDONLY);
if(fp_r == -1)
{
perror("open");
return NULL;
}
char buf[128] = "";
while(1)
{
//读之前清空字符串防止上次读取信息的干扰
bzero(buf,sizeof(buf));
read(fp_r,buf,sizeof(buf));
printf("A:%s\n",buf);
if(strcmp(buf,"quit") == 0 || strlen(buf) == 0)
{
close(fp_r);
pthread_cancel(*(pthread_t*)arg);
pthread_exit(NULL);
}
}
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
printf("连接中...");
fflush(stdout);
//创建管道文件
if(mkfifo("./FIFO1",0775)==-1)
{
if(errno!=17)//排除文件已经存在的错误码
{
perror("mkfifo");
return -1;
}
}
if(mkfifo("./FIFO2",0775)==-1)
{
if(errno!=17)
{
perror("mkfifo");
return -1;
}
}
//创建线程
pthread_t tid_w,tid_r;
if(pthread_create(&tid_w,NULL,f1_w,(void*)&tid_r)!=0)
{
fprintf(stderr,"creat pthread on error\n");
return -1;
}
if(pthread_create(&tid_r,NULL,f2_r,(void*)&tid_w)!=0)
{
fprintf(stderr,"creat pthread on error\n");
return -1;
}
//阻塞,等待子线程结束
pthread_join(tid_w,NULL);
pthread_join(tid_r,NULL);
return 0;
}运行结果
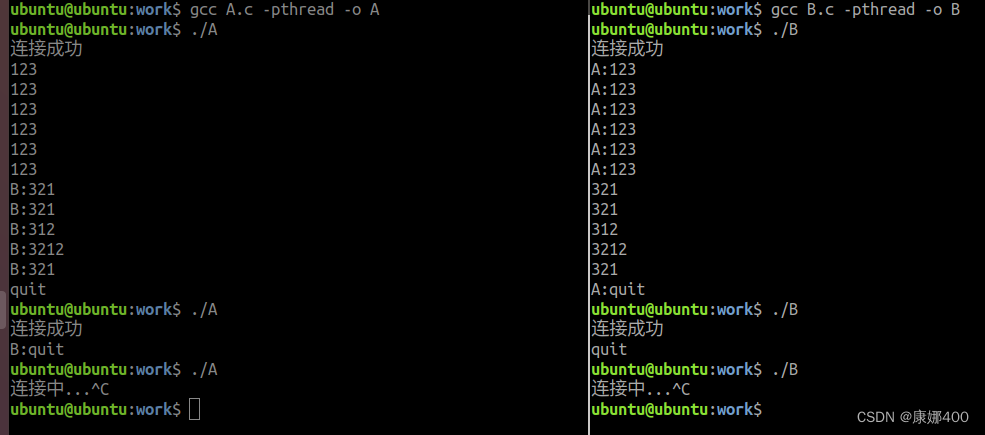






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








