原文地址:http://blog.csdn.net/liu1028701143/article/details/7075272
一.选项卡:
TabHost组件,可以方便的放置多个标签页,每个标签页相当于获得了一个与外部容器相同大小的组件,通过这种方式就可以在一个容器里放置更多组件,;
TabHost仅仅是一个简单的容器,可以通过一下两种方法来创建选项卡,添加选项卡;
1. newTabSpec(String tag):创建
2. addTab(TabHost.TabSpectabSpec);添加选项卡;
使用TabHost的一般步骤为:
)1、在界面布局中定义TabHost组件,并为该组件定义该选项卡的内容,
)2、Activity应该继承TabActivity.
)3、调用TabActivity的getTabHost方法获取Tabhost对象。
)4、通过TabHost对象的方法来创建选项卡,添加选项卡;
下面通过一个实例来示范选项卡的用法;
程序布局文件:
- <?xml version="1.0"encoding="utf-8"?>
- <TabHost xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent"
- android:background="@drawable/gallery_selected_pressed">
- 第一个标签的内容
- <LinearLayout
- android:id="@+id/tab1"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:orientation="vertical">
- </LinearLayout>
- 第二个标签的内容
- <LinearLayout
- android:id="@+id/tab2"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:orientation="vertical">
- </LinearLayout>
- 第三个标签的内容
- <LinearLayout
- android:id="@+id/tab3"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:orientation="vertical">
- </LinearLayout>
- </TabHost>
通过上面的布局文件定义我们创建了三个组件,可以为TabHost添加三个标签页。
JAVA代码:
- public class UIWorkActivity extends TabActivity {
- TabHost tabhost = null;
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- tabhost = this.getTabHost();
- LayoutInflater in = LayoutInflater.from(this);
- in.inflate(R.layout.main, tabhost.getTabContentView(),true);
- tabhost.addTab(tabhost.newTabSpec("tab1").setIndicator("高兴",getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.emo_im_laughing))
- .setContent(R.id.tab1));
- tabhost.addTab(tabhost.newTabSpec("tab2").setIndicator("难
- //添加标签图片的方法
- 过",getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.emo_im_sad))
- .setContent(R.id.tab2));
- tabhost.addTab(tabhost.newTabSpec("tab3").setIndicator("兴奋",getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.emo_im_money_mouth))
- .setContent(R.id.tab3));
- }
运行效果演示:

二、进度条(ProgressBar):
进度条通常用于向用户显示某个耗时操作的完成的百分比,可以动态的显示进度,
1.通过style属性可以为progressBar指定风格,
| @android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Horizontal | 水平 |
| @android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Small | 小进度条 |
| @android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.inverse | 普通大小 |
| @android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Large | 大进度条 |
| @android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Large.inverse | 大进度条 |
| @android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Small.inverse | 小进度条 |
2.ProgressBar还支持以下的常用属性:
| Android:max | 进度条的最大值 |
| Android:progress | 进度条已完成的进度值 |
| Android:progressDrawable | 进度条轨道的绘制形式 |
| Android:indeterminate | 属性设为true:设置进度条不精确显示进度 |
| Android:indeterminateDrawable | 设置不显示进度的进度条的Drawable对象 |
| Android:indeterminateDuration | 设置不精确显示进度的持续时间 |
| XML属性值 | 说明 |
3.ProgressBar提供了一下方法设置进度的完成百分比;
1、setProgress(int) 设置完成进度的百分比;
2、incrementProgressBy(int):设置进度条的进度增加或减少,当参数为正数是进度增加,当为负值是进度减少;
下面用实例来说明一下ProgressBar的使用:
- public class proessDemoextends Activity {
- ProgressBar bar = null;
- int i = 0;
- int barmax = 0;
- Handler handler = new Handler();
- public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.progressbar);
- findViews();
- }
- private void findViews() {
- bar = (ProgressBar) this.findViewById(R.id.bar2);
- bar.setMax(1000);
- barmax = bar.getMax();
- new Thread(new Runnable() {
- public void run() {
- while (i < barmax) {
- i = dowork();
- handler.post(new Runnable() {
- public void run() {
- bar.setProgress(i);
- }
- });
- try {
- Thread.sleep(50);
- } catch (InterruptedException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- }
- }).start();
- }
- public int dowork() {
- return i += 1;
- }
Xml布局文件的配置:
- <?xml version="1.0"encoding="utf-8"?>
- <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="fill_parent"
- android:orientation="vertical" >
- <TextView
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="进度条演示" />
- <ProgressBar
- android:id="@+id/bar1"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:max="530"
- android:progress="100"
- />
- <ProgressBar
- android:id="@+id/bar2"
- style="@android:style/Widget.ProgressBar.Small"
- android:layout_marginTop="30dp"
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:max="530"
- android:progress="100"
- android:secondaryProgress="300"/>
- </LinearLayout>
运行效果演示:
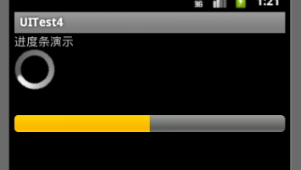
三、拖动条(SeekBar):
拖动条和进度条很相似,知识进度是通过颜色填充来显示进度完成的程度,而拖动条是则通过滑块的位置来识别标识,
下面来通过一个实例来说明拖动条的作用,
Xml:
- <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent"
- android:orientation="vertical" >
- <TextView
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:text="seekbar演示"
- />
- <SeekBar
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:max="1000"
- android:id="@+id/seekbar"
- />
- </LinearLayout>
Java文件:
- public class SeekbarDemo extends Activity implements OnSeekBarChangeListener {
- SeekBar seekbar = null;
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- this.setContentView(R.layout.seekbar);
- findViews();
- }
- private void findViews() {
- seekbar = (SeekBar) this.findViewById(R.id.seekbar);
- seekbar.setOnSeekBarChangeListener(this);
- }
- public void onProgressChanged(SeekBar seekBar, int progress,
- boolean fromUser) {
- }
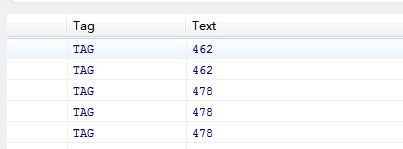
- public void onStartTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar) {
- Log.d("TAG", String.valueOf(seekbar.getProgress()));
- }
- public void onStopTrackingTouch(SeekBar seekBar) {
- Log.d("TAG", String.valueOf(seekbar.getProgress()));
- }
- }
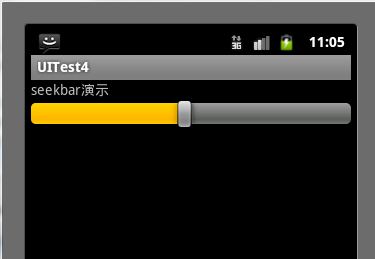
运行效果:
移动进度条
日志信息输出的变化:
四、图像视图:(ImageView)
ImageView是继承View的组件,主要功能是显示图片,并且任何的Drawable对象都可以使用ImageView来显示;
下面是ImageView支持的XML属性和相关方法,
| Xml属性 | 相关method | 说明 |
| android: adjustViewBounds | setAdjustViewBounds(boolean) | 设置是否需要调整自己边界 |
| android:maxHeight | SetMaxwidth(int) | 设置最大高度 |
| android:maxWidth | SetMaxHeight(int) | 设置最大宽度 |
| android:scaleType | SetScaleType(ImageViewScaleType) | 设置显示图片如何移动或缩放以适应ImageView的尺寸 |
| android:src | setImageResource(int) | 设置显示图片的ID |
实例演示:
XML文件,
- <ImageView
- android:layout_width="fill_parent"
- android:layout_height="300dp"
- android:src="@drawable/ic_launcher"
- android:background="#cccccc"
- android:scaleType="fitCenter"
- android:id="@+id/imageview1"
- />
- <ImageView
- android:layout_width="100dp"
- android:layout_height="100dp"
- android:background="#cccccc"
- android:scaleType="fitStart"
- android:id="@+id/imageview2"
- android:layout_marginTop="20dp"
- />
Java文件:
- public class ImageDemo extends Activity implements OnTouchListener {
- ImageView imageView1, imageView2;
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- this.setContentView(R.layout.image);
- findViews();
- }
- private void findViews() {
- imageView1 = (ImageView) this.findViewById(R.id.imageview1);
- imageView2 = (ImageView) this.findViewById(R.id.imageview2);
- imageView1.setOnTouchListener(this);
- }
- public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
- float scale = 412 / 320;
- int x = (int) (event.getX() * scale);
- int y = (int) (event.getY() * scale);
- int width = (int) (100 * scale);
- int height = (int) (100 * scale);
- BitmapDrawable bitmapDrawable = (BitmapDrawable) imageView1
- .getDrawable();
- imageView2.setImageBitmap(Bitmap.createBitmap(
- bitmapDrawable.getBitmap(), x, y, width, height));
- return false;
- }
- }
运行效果:
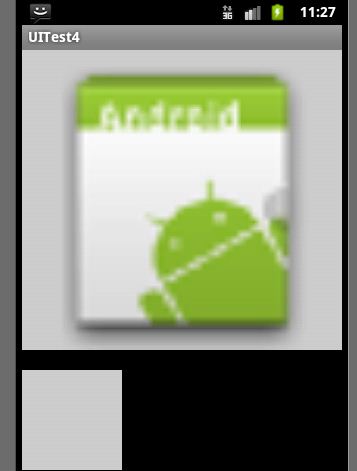
























 1211
1211

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








