Previously we have seen how to create a flexible disk storage using LVM. Here, we are going to see how to extend volume group, extend and reduce a logical volume. Here we can reduce or extend the partitions in Logical volume management (LVM) also called as flexible volume file-system.
Requirements
When do we need to reduce volume?
May be we need to create a separate partition for any other use or we need to expand the size of any low space partition, if so we can reduce the large size partition and we can expand the low space partition very easily by the following simple easy steps.
My Server Setup – Requirements
- Operating System – CentOS 6.5 with LVM Installation
- Server IP – 192.168.0.200
How to Extend Volume Group and Reduce Logical Volume
Logical Volume Extending
Currently, we have One PV, VG and 2 LV. Let’s list them one by one using following commands.
There are no free space available in Physical Volume and Volume group. So, now we can’t extend the lvm size, for extending we need to add one physical volume (PV), and then we have to extend the volume group by extending the vg. We will get enough space to extend the Logical volume size. So first we are going to add one physical volume.
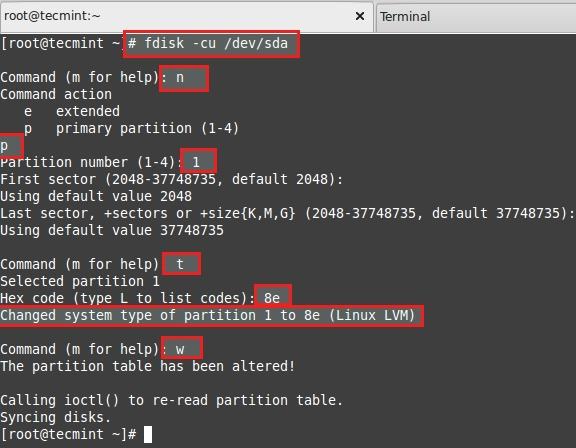
For adding a new PV we have to use fdisk to create the LVM partition.
- To Create new partition Press n.
- Choose primary partition use p.
- Choose which number of partition to be selected to create the primary partition.
- Press 1 if any other disk available.
- Change the type using t.
- Type 8e to change the partition type to Linux LVM.
- Use p to print the create partition ( here we have not used the option).
- Press w to write the changes.
Restart the system once completed.
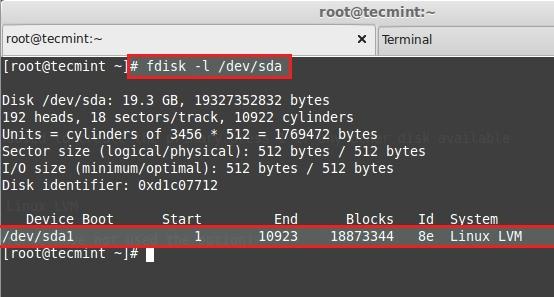
List and check the partition we have created using fdisk.
Next, create new PV (Physical Volume) using following command.
Verify the pv using below command.
Extending Volume Group
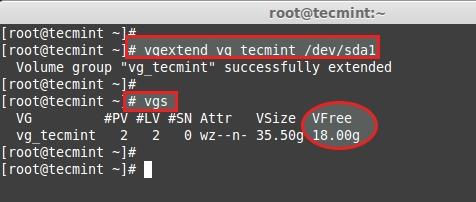
Add this pv to vg_tecmint vg to extend the size of a volume group to get more space for expanding lv.
Let us check the size of a Volume Group now using.
We can even see which PV are used to create particular Volume group using.
Here, we can see which Volume groups are under Which Physical Volumes. We have just added one pv and its totally free. Let us see the size of each logical volume we have currently before expanding it.
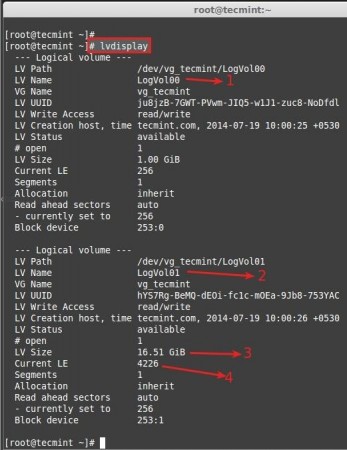
- LogVol00 defined for Swap.
- LogVol01 defined for /.
- Now we have 16.50 GB size for / (root).
- Currently there are 4226 Physical Extend (PE) available.
Now we are going to expand the / partition LogVol01. After expanding we can list out the size as above for confirmation. We can extend using GB or PE as I have explained it in LVM PART-I, here I’m using PE to extend.
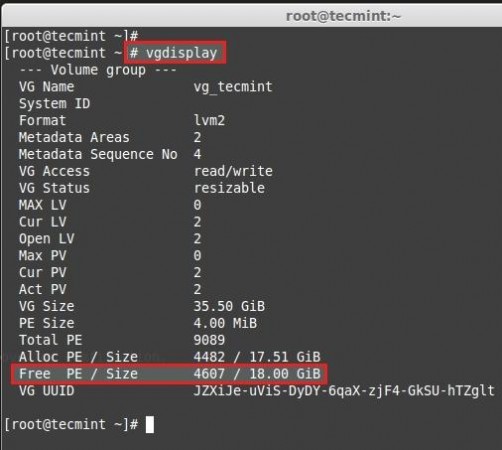
For getting the available Physical Extend size run.
There are 4607 free PE available = 18GB Free space available. So we can expand our logical volume up-to 18GBmore. Let us use the PE size to extend.
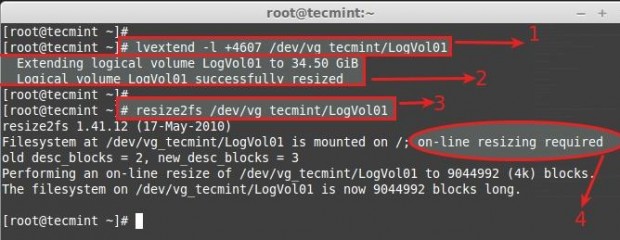
Use + to add the more space. After Extending, we need to re-size the file-system using.
- Command used to extend the logical volume using Physical extends.
- Here we can see it is extended to 34GB from 16.51GB.
- Re-size the file system, If the file-system is mounted and currently under use.
- For extending Logical volumes we don’t need to unmount the file-system.
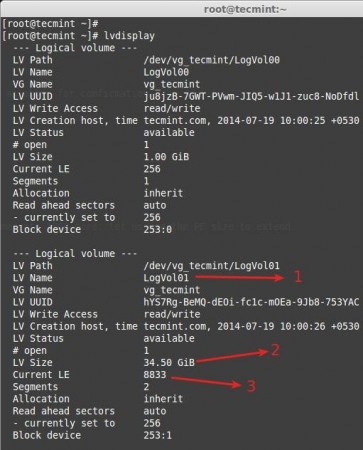
Now let’s see the size of re-sized logical volume using.
- LogVol01 defined for / extended volume.
- After extending there is 34.50GB from 16.50GB.
- Current extends, Before extending there was 4226, we have added 4607 extends to expand so totally there are 8833.
Now if we check the vg available Free PE it will be 0.
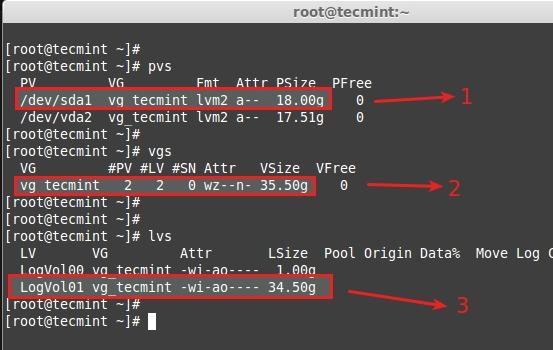
See the result of extending.
- New Physical Volume added.
- Volume group vg_tecmint extended from 17.51GB to 35.50GB.
- Logical volume LogVol01 extended from 16.51GB to 34.50GB.
Here we have completed the process of extending volume group and logical volumes. Let us move towards some interesting part in Logical volume management.
Reducing Logical Volume (LVM)
Here we are going to see how to reduce the Logical Volumes. Everyone say its critical and may end up with disaster while we reduce the lvm. Reducing lvm is really interesting than any other part in Logical volume management.
- Before starting, it is always good to backup the data, so that it will not be a headache if something goes wrong.
- To Reduce a logical volume there are 5 steps needed to be done very carefully.
- While extending a volume we can extend it while the volume under mount status (online), but for reduce we must need to unmount the file system before reducing.
Let’s wee what are the 5 steps below.
- unmount the file system for reducing.
- Check the file system after unmount.
- Reduce the file system.
- Reduce the Logical Volume size than Current size.
- Recheck the file system for error.
- Remount the file-system back to stage.
For demonstration, I have created separate volume group and logical volume. Here, I’m going to reduce the logical volume tecmint_reduce_test. Now its 18GB in size. We need to reduce it to 10GB without data-loss. That means we need to reduce 8GB out of 18GB. Already there is 4GB data in the volume.
While reducing size, we need to reduce only 8GB so it will roundup to 10GB after the reduce.
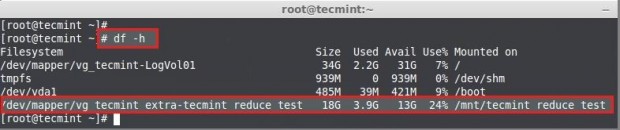
Here we can see the file-system information.
- The size of the Volume is 18GB.
- Already it used upto 3.9GB.
- Available Space is 13GB.
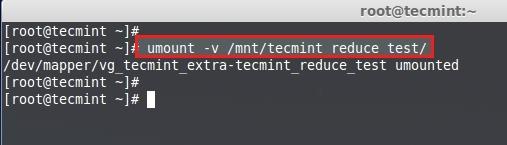
First unmount the mount point.
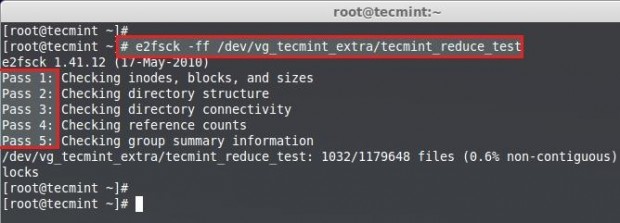
Then check for the file-system error using following command.
Note: Must pass in every 5 steps of file-system check if not there might be some issue with your file-system.
Next, reduce the file-system.
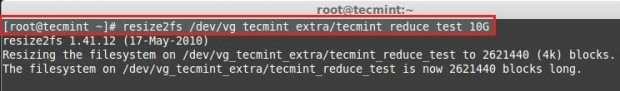
Reduce the Logical volume using GB size.
To Reduce Logical volume using PE Size we need to Know the size of default PE size and total PE size of a Volume Group to put a small calculation for accurate Reduce size.
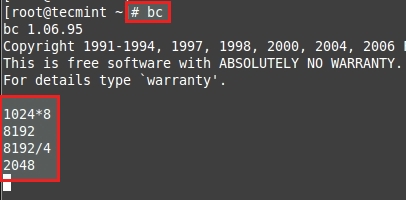
Here we need to do a little calculation to get the PE size of 10GB using bc command.
Press CRTL+D to exit from BC.
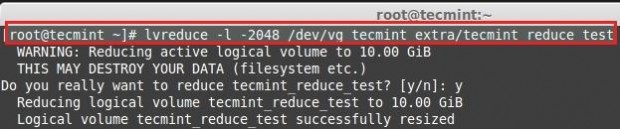
Reduce the size using PE.
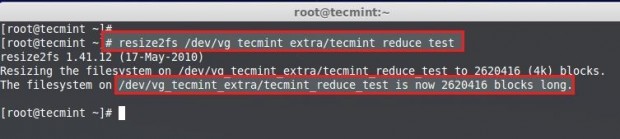
Re-size the file-system back, In this step if there is any error that means we have messed-up our file-system.
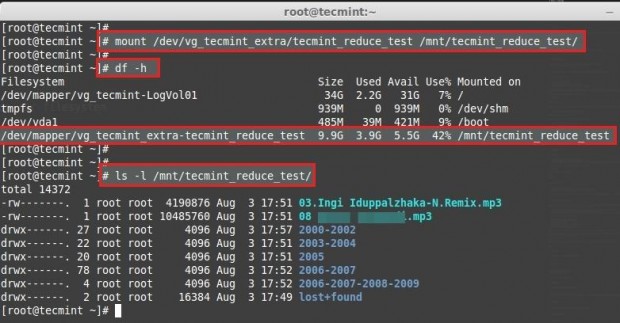
Mount the file-system back to same point.
Check the size of partition and files.
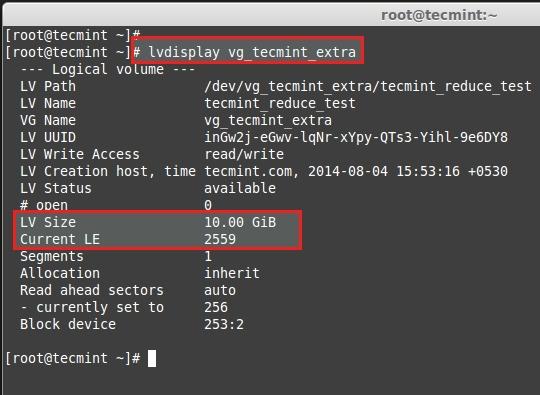
Here we can see the final result as the logical volume was reduced to 10GB size.
In this article, we have seen how to extend the volume group, logical volume and reduce the logical volume. In the next part (Part III), we will see how to take a Snapshot of logical volume and restore it to earlier stage.
Reference: http://www.tecmint.com/extend-and-reduce-lvms-in-linux/




























 7115
7115











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








