参考 求任意多边形内部水平方向似最大矩形算法实现_nullpo_的博客
原文是用 grooovy代码写的,不太好懂,这里把主要逻辑改成python版,测了下效果还行。
代码如下: )
import math
import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
from collections import deque
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from numba import jit
class Rectangle:
"""
矩形范围(包围盒).
"""
def __init__(self, minLon, maxLon, minLat, maxLat):
self.minLon = minLon
self.maxLon = maxLon
self.minLat = minLat
self.maxLat = maxLat
def myceil(d, scale):
"""
scale 表示精度如0.1, 0.01等
"""
n = int(1 / scale)
return math.ceil(d * n) / n
def myfloor(d, scale):
n = int(1 / scale)
return math.floor(d * n) / n
def min_enclosing_rectangle(pt_list):
"""
获取多边形区域的最小外接矩形.
"""
rec = Rectangle(
minLon=float('inf'), maxLon=float('-inf'),
minLat=float('inf'), maxLat=float('-inf')
)
pts = np.array(pt_list)
rec.minLon = np.min(pts[:, 0])
rec.maxLon = np.max(pts[:, 0])
rec.minLat = np.min(pts[:, 1])
rec.maxLat = np.max(pts[:, 1])
return rec
def compute_regional_slices(rec, scale):
"""
根据矩形和切分尺度获取切分矩阵的点阵.
为了减少计算量,这里输出的并不是真的矩形,由于是等距连续切分,直接输出切分的数据点即可,以左上角数据点作为标的.
"""
# 1.根据切分尺度标准化矩形
minLon = myfloor(rec.minLon, scale)
maxLon = myceil(rec.maxLon, scale)
minLat = myfloor(rec.minLat, scale)
maxLat = myceil(rec.maxLat, scale)
ndigit = int(math.log10(int(1 / scale))) + 1
# 2.切分(出于人类习惯,暂定从上往下按行切分,即按纬度从大到小,经度从小到大)
matrix = []
for posLat in np.arange(maxLat, minLat, -scale):
row = []
for posLon in np.arange(minLon, maxLon+scale, scale):
row.append([round(posLon, ndigit), round(posLat, ndigit)])
matrix.append(row)
return matrix
@jit(nopython=True)
def PNPoly(vertices, testp):
"""
返回一个点是否在一个多边形区域内(开区间) PNPoly算法
@param vertices: 多边形的顶点
@param testp: 测试点[x, y]
"""
n = len(vertices)
j = n - 1
res = False
for i in range(n):
if (vertices[i][1] > testp[1]) != (vertices[j][1] > testp[1]) and \
testp[0] < (vertices[j][0] - vertices[i][0]) * (testp[1] - vertices[i][1]) / (
vertices[j][1] - vertices[i][1]) + vertices[i][0]:
res = not res
j = i
return res
def isPolygonContainsPoint(pt_list, p):
"""
返回一个点是否在一个多边形区域内(开区间).
"""
nCross = 0
for i in range(len(pt_list)):
p1 = pt_list[i]
p2 = pt_list[(i + 1) % len(pt_list)]
if p1[1] == p2[1]:
continue
if p[1] < min(p1[1], p2[1]) or p[1] >= max(p1[1], p2[1]):
continue
x = p1[0] + (p2[0] - p1[0]) * (p[1] - p1[1]) / (p2[1] - p1[1])
if x > p[0]:
nCross += 1
return nCross % 2 == 1
def compute_mark_matrix(polygon, regionalSlices):
"""
根据切分矩形和多边形计算出标记矩阵.
"""
m = len(regionalSlices)
n = len(regionalSlices[0])
rectangleMarks = [[1] * (n - 1) for _ in range(m - 1)]
def inRange(num, min, max):
return num >= min and num <= max
for posM in range(m):
print(f'mark {posM}')
for posN in range(n):
p = regionalSlices[posM][posN]
if not PNPoly(polygon, p):
if inRange(posM - 1, 0, m - 2) and inRange(posN - 1, 0, n - 2):
rectangleMarks[posM - 1][posN - 1] = 0
if inRange(posM - 1, 0, m - 2) and inRange(posN, 0, n - 2):
rectangleMarks[posM - 1][posN] = 0
if inRange(posM, 0, m - 2) and inRange(posN - 1, 0, n - 2):
rectangleMarks[posM][posN - 1] = 0
if inRange(posM, 0, m - 2) and inRange(posN, 0, n - 2):
rectangleMarks[posM][posN] = 0
return rectangleMarks
def maximal_rectangle(matrix):
"""
根据标记矩阵求最大矩形,返回【最小行标 最大行标 最小列标 最大列标 最大面积】
"""
m = len(matrix)
n = len(matrix[0])
left = [[0] * n for _ in range(m)]
for i in range(m):
for j in range(n):
if matrix[i][j] == 1:
left[i][j] = (left[i][j-1] if j else 0) + 1
min_c, max_c, min_r, max_r, ret = -1, -1, -1, -1, 0
# 对于每一列,使用基于柱状图的方法
for j in range(n):
up = [0] * m
down = [0] * m
que = deque()
for i in range(m):
while len(que) > 0 and left[que[-1]][j] >= left[i][j]:
que.pop()
up[i] = que[-1] if que else -1
que.append(i)
que.clear()
for i in range(m-1, -1, -1):
while que and left[que[-1]][j] >= left[i][j]:
que.pop()
down[i] = que[-1] if que else m
que.append(i)
for i in range(m):
height = down[i] - up[i] - 1
area = height * left[i][j]
if area > ret:
ret = area
min_c = up[i] + 1
max_c = down[i] - 1
min_r = j - left[i][j] + 1
max_r = j
return min_c, max_c, min_r, max_r, ret
def largest_internal_rectangle(polygon):
"""
求一个多边形区域的水平方向最大内接矩形,由于是经纬度数据,精确到小数点后两位,误差(只小不大)约一公里.
"""
scale = 0.01
# 1.区域切块,不是真的切成矩形,而是切分成数据点
min_enclosing_rect = min_enclosing_rectangle(polygon)
# 2.标记矩阵,这里将点阵经纬度转换为矩形标记矩阵,每个矩形以左上角作为标的,
# 比如矩形marks[0][0]的左上角坐标为regionalSlices[0][0],右下角坐标为regionalSlices[1][1]
regional_slices = compute_regional_slices(min_enclosing_rect, scale)
marks = compute_mark_matrix(polygon, regional_slices)
# 3.计算最大内接矩阵,返回矩形
min_c, max_c, min_r, max_r, area = maximal_rectangle(marks)
minLon = regional_slices[0][min_r][0]
maxLon = regional_slices[0][max_r+1][0]
minLat = regional_slices[max_c+1][0][1]
maxLat = regional_slices[min_c][0][1]
return Rectangle(minLon, maxLon, minLat, maxLat)
def largest_internal_rectangle_recursion(polygon, minArea=64):
scale = 0.01
rect_list = []
# 1.区域切块,不是真的切成矩形,而是切分成数据点
min_enclosing_rect = min_enclosing_rectangle(polygon)
# 2.标记矩阵
regional_slices = compute_regional_slices(min_enclosing_rect, scale)
marks = compute_mark_matrix(polygon, regional_slices)
# 3. 把最大矩形的mark置零,剩余部分重新计算出最大矩形,直到面积小于minArea
while True:
min_c, max_c, min_r, max_r, area = maximal_rectangle(marks)
if area < minArea:
break
minLon = regional_slices[0][min_r][0]
maxLon = regional_slices[0][max_r+1][0]
minLat = regional_slices[max_c+1][0][1]
maxLat = regional_slices[min_c][0][1]
rect = Rectangle(minLon, maxLon, minLat, maxLat)
for i in range(min_c, max_c+1):
for j in range(min_r, max_r+1):
marks[i][j] = 0
rect_list.append(rect)
return rect_list
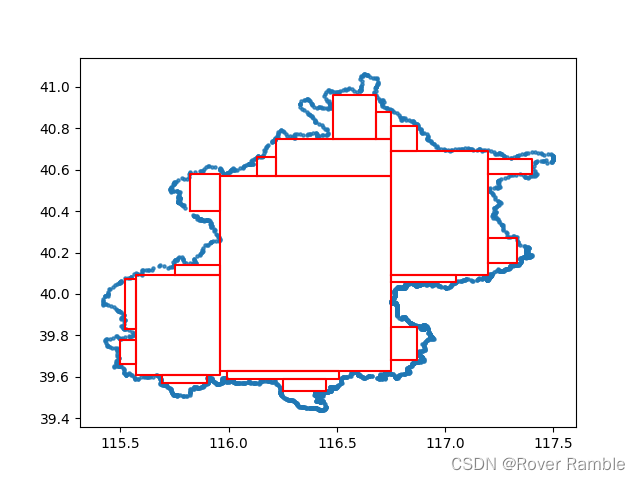
def plot_rect(df, rect_list):
# plot edge
plt.scatter(df['lng'], df['lat'], s=5, alpha=0.8)
for rect in rect_list:
points = np.array([[rect.minLon, rect.minLat], [rect.minLon, rect.maxLat],
[rect.maxLon, rect.maxLat], [rect.maxLon,rect.minLat],
[rect.minLon, rect.minLat]
])
plt.plot(*zip(*points), color='r')
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
df = pd.read_csv('D:/data/edge_points.csv')
point_list = df[['lng', 'lat']].values
ret_rect = largest_internal_rectangle_recursion(point_list, 64)
print('rect size {}'.format(len(ret_rect)))
plot_rect(df, ret_rect)
























 2043
2043

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








