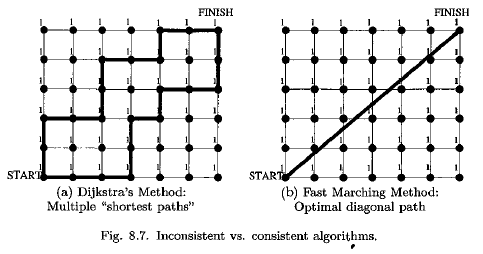
Fast Marching method 跟 dijkstra 方法类似,只不过dijkstra方法的路径只能沿网格,而Fast Marching method的方法可以沿斜线.
[Level Set Methods and Fast Marching Methods p94-95

]
这里
u
理解为到达点的时间,
然后就可以跟Boundary Value Formulation对应起来了.
[Level Set Methods and Fast Marching Methods p7

]
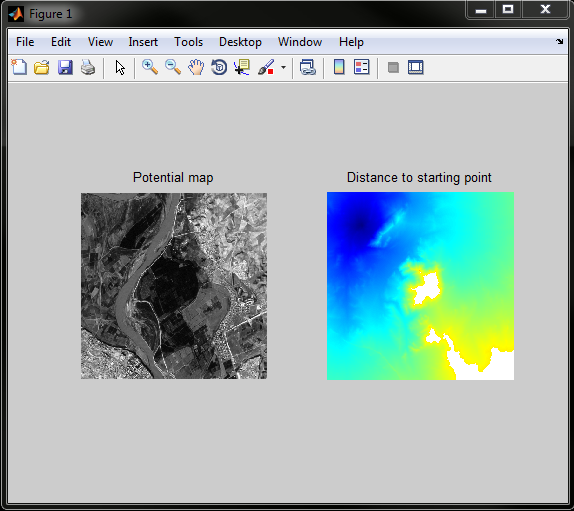
本例,首先加载一张灰度图片, 将里面像素的值W作为该点的流速F. 然后算到达该点的时间,也就是程序里面的距离D.
matlab部分源代码如下:
example1.m
n = 400;
[M,W] = load_potential_map('road2', n);
%start_point = [16;219];
%end_point = [394;192];
% You can use instead the function
[start_point,end_point] = pick_start_end_point(W);
clear options;
options.nb_iter_max = Inf;
options.end_points = end_point; % stop propagation when end point reached
[D,S] = perform_fast_marching(W, start_point, options);
% nicde color for display
A = convert_distance_color(D);
imageplot({W A}, {'Potential map' 'Distance to starting point'});
colormap gray(256);perform_front_propagation_2d_slow.m
function [D,S,father] = perform_front_propagation_2d_slow(W,start_points,end_points,nb_iter_max,H)
% [D,S] = perform_front_propagation_2d_slow(W,start_points,end_points,nb_iter_max,H);
%
% [The mex function is perform_front_propagation_2d]
%
% 'D' is a 2D array containing the value of the distance function to seed.
% 'S' is a 2D array containing the state of each point :
% -1 : dead, distance have been computed.
% 0 : open, distance is being computed but not set.
% 1 : far, distance not already computed.
% 'W' is the weight matrix (inverse of the speed).
% 'start_points' is a 2 x num_start_points matrix where k is the number of starting points.
% 'H' is an heuristic (distance that remains to goal). This is a 2D matrix.
%
% Copyright (c) 2004 Gabriel Peyr?
data.D = W.*0 + Inf; % action 先把所有点的距离标为Inf
start_ind = sub2ind(size(W), start_points(1,:), start_points(2,:));
data.D( start_ind ) = 0; %将起点的距离设置为0
data.O = start_points; % 将起点加入Open list
% S=1 : far, S=0 : open, S=-1 : close
data.S = ones(size(W));% 将所点的状态设为Far
data.S( start_ind ) = 0; % 将起点的状态设为open(trial)
data.W = W;
data.father = zeros( [size(W),2] );% father维度400*400*2,父节点有两个,因为走斜线
verbose = 1;
if nargin<3
end_points = [];
end
if nargin<4
nb_iter_max = round( 1.2*size(W,1)^2 );
end
if nargin<5
data.H = W.*0;
else
if isempty(H)
data.H = W.*0;
else
data.H = H;
end
end
if ~isempty(end_points)
end_ind = sub2ind(size(W), end_points(1,:), end_points(2,:));
else
end_ind = [];
end
str = 'Performing Fast Marching algorithm.';
if verbose
h = waitbar(0,str);
end
i = 0;
while i<nb_iter_max && ~isempty(data.O) && isempty( find( data.S(end_ind)==-1 ) )
i = i+1;
data = perform_fast_marching_step(data);
if verbose
waitbar(i/nb_iter_max, h, sprintf('Performing Fast Marching algorithm, iteration %d.', i) );
end
end
if verbose
close(h);
end
D = data.D;
S = data.S;
father = data.father;
function data1 = perform_fast_marching_step(data)%有多个起点也是一样的,只需将他们的距离都设为0即可
% perform_fast_marching_step - perform one step in the Fast Marching algorithm
%
% data1 = perform_fast_marching_step(data);
%
% Data is a structure that records the state before/after a step
% of the FM algorithm.
%
% Copyright (c) 2004 Gabriel Peyr?
% some constant
kClose = -1;
kOpen = 0;
kFar = 1;
D = data.D; % action, a 2D matrix
O = data.O; % open list
S = data.S; % state, either 'O' or 'C', a 2D matrix
H = data.H; % Heuristic
W = data.W; % weight matrix, a 2D array (speed function)
father = data.father;
[n,p] = size(D); % size of the grid, n,p都为400
% step size
h = 1/n;
if isempty(O)%看开集是否为空
data1 = data;
return;
end
ind_O = sub2ind(size(D), O(1,:), O(2,:));%获取开集里面的顶点的索引
[m,I] = min( D(ind_O)+H(ind_O) ); %m里面是最小值,I里面是该最小值在被检测矩阵里面的索引
I = I(1);%取第一个索引
% selected vertex
% 取开集中的第I个点的索引
i = O(1,I);
j = O(2,I);
O(:,I) = []; % pop from open ,将此点从开集中移除
S(i,j) = kClose; % now its close, 将此点加入闭集(known set)中
% its neighbor
% 准备遍历他的右,上,左,下的邻近点
nei = [1,0; 0,1; -1,0; 0,-1 ];
for k = 1:4
ii = i+nei(k,1);
jj = j+nei(k,2);
if ii>0 && jj>0 && ii<=n && jj<=p
f = [0 0]; % current father
%%% update the action using Upwind resolution
P = h/W(ii,jj);
% neighbors values
a1 = Inf;
if ii<n
a1 = D( ii+1,jj );
f(1) = sub2ind(size(W), ii+1,jj);
end
if ii>1 && D( ii-1,jj )<a1
a1 = D( ii-1,jj );
f(1) = sub2ind(size(W), ii-1,jj);
end
a2 = Inf;
if jj<n
a2 = D( ii,jj+1 );
f(2) = sub2ind(size(W), ii,jj+1);
end
if jj>1 && D( ii,jj-1 )<a2
a2 = D( ii,jj-1 );
f(2) = sub2ind(size(W), ii,jj-1);
end
if a1>a2 % swap to reorder
tmp = a1; a1 = a2; a2 = tmp;
f = f([2 1]);
end
% now the equation is (a-a1)^2+(a-a2)^2 = P^2, with a >= a2 >= a1.
% 书上95页公式为:(ux^2 + uy^2)^(1/2)=1/Fijk
% u理解为到达点的时间,Fijk理解为在点ijk处的流速
% 那么 ux = (a-a1)/(1/400), uy = (a-a2)/(1/400)
% 所以方程变为:((a-a1)^2/(1/400))^2+((a-a2)^2/(1/400))^2 = (1/Wij)^2
% 把1/400移到右边,则得P
if P^2 > (a2-a1)^2%delta 大于0
delta = 2*P^2-(a2-a1)^2;
A1 = (a1+a2+sqrt(delta))/2;
else%否则用dijkstra方法,沿着格子走,公式为:max|ux,uy|=1/Fijk
% (a-a1) / (1/400) = 1 / Wij
A1 = a1 + P;
f(2) = 0;%将第2个父节点设为0
end
switch S(ii,jj)
case kClose%闭集不用更新
% check if action has change. Should not appen for FM
if A1<D(ii,jj)
% warning('FastMarching:NonMonotone', 'The update is not monotone');
% pop from Close and add to Open
if 0 % don't reopen close points
O(:,end+1) = [ii;jj];
S(ii,jj) = kOpen;
D(ii,jj) = A1;
end
end
case kOpen%开集才更新
% check if action has change.
if A1<D(ii,jj)
D(ii,jj) = A1;
father(ii,jj,:) = f;
end
case kFar%远集不仅更新,而且加入开集
if D(ii,jj)~=Inf
warning('FastMarching:BadInit', 'Action must be initialized to Inf');
end
% add to open
O(:,end+1) = [ii;jj];
S(ii,jj) = kOpen;
% action must have change.
D(ii,jj) = A1;
father(ii,jj,:) = f;
otherwise
error('Unknown state');
end
end
end
data1.D = D;
data1.O = O;
data1.S = S;
data1.W = W;
data1.H = H;
data1.father = father;运行结果:
























 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








