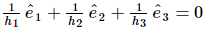
再看下源码:
//main.cpp
#include <igl/avg_edge_length.h>
#include <igl/barycenter.h>
#include <igl/grad.h>
#include <igl/jet.h>
#include <igl/readDMAT.h>
#include <igl/readOFF.h>
#include <igl/viewer/Viewer.h>
#include <iostream>
#include "tutorial_shared_path.h"
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
using namespace Eigen;
using namespace std;
MatrixXd V;
MatrixXi F;
// Load a mesh in OFF format
igl::readOFF(TUTORIAL_SHARED_PATH "/cheburashka.off", V, F);
// Read scalar function values from a file, U: #V by 1
VectorXd U;
igl::readDMAT(TUTORIAL_SHARED_PATH "/cheburashka-scalar.dmat",U);
// Compute gradient operator: #F*3 by #V
SparseMatrix<double> G;
igl::grad(V,F,G);
// V : 6669 by 3 6669个点
// F : 13334 by 3 13334个面
// G : 40002 by 6669 每3行代表一个面(x,y,z), 每一列代表第j个点在第i个三角形内的梯度方向,注意x,y,z不是连在一起的, 行的排列为:x (#F行),y (#F行), z(#F行)
// Compute gradient of U
MatrixXd GU = Map<const MatrixXd>((G*U).eval().data(),F.rows(),3);
// U : 6669 * 1 U代表标量在点处的值
// GU 13334 by 3 会将所有点对第i个三角形的梯度叠加起来,这样每一行就对应于一个三角形的梯度了
// Compute gradient magnitude
const VectorXd GU_mag = GU.rowwise().norm();
igl::viewer::Viewer viewer;
viewer.data.set_mesh(V, F);
// Compute pseudocolor for original function
MatrixXd C;
igl::jet(U,true,C);
// // Or for gradient magnitude
//igl::jet(GU_mag,true,C);
viewer.data.set_colors(C);
// Average edge length divided by average gradient (for scaling)
const double max_size = igl::avg_edge_length(V,F) / GU_mag.mean();
// Draw a black segment in direction of gradient at face barycenters
MatrixXd BC;
igl::barycenter(V,F,BC);
// 然后算每个三角形的质心
const RowVector3d black(0,0,0);
viewer.data.add_edges(BC,BC+max_size*GU, black);
// 在每个三角形的质心处画出梯度的方向
// Hide wireframe
viewer.core.show_lines = false;
viewer.launch();
}
//grad.cpp
// This file is part of libigl, a simple c++ geometry processing library.
//
// Copyright (C) 2013 Alec Jacobson <alecjacobson@gmail.com>
//
// This Source Code Form is subject to the terms of the Mozilla Public License
// v. 2.0. If a copy of the MPL was not distributed with this file, You can
// obtain one at http://mozilla.org/MPL/2.0/.
#include "grad.h"
#include <Eigen/Geometry>
#include <vector>
template <typename DerivedV, typename DerivedF>
IGL_INLINE void igl::grad(const Eigen::PlainObjectBase<DerivedV>&V,
const Eigen::PlainObjectBase<DerivedF>&F,
Eigen::SparseMatrix<typename DerivedV::Scalar> &G)
{
Eigen::Matrix<typename DerivedV::Scalar,Eigen::Dynamic,3>
eperp21(F.rows(),3), eperp13(F.rows(),3);
for (int i=0;i<F.rows();++i)
{
// renaming indices of vertices of triangles for convenience
int i1 = F(i,0);
int i2 = F(i,1);
int i3 = F(i,2);
// #F x 3 matrices of triangle edge vectors, named after opposite vertices
Eigen::Matrix<typename DerivedV::Scalar, 1, 3> v32 = V.row(i3) - V.row(i2);
Eigen::Matrix<typename DerivedV::Scalar, 1, 3> v13 = V.row(i1) - V.row(i3);
Eigen::Matrix<typename DerivedV::Scalar, 1, 3> v21 = V.row(i2) - V.row(i1);
// area of parallelogram is twice area of triangle
// area of parallelogram is || v1 x v2 ||
Eigen::Matrix<typename DerivedV::Scalar, 1, 3> n = v32.cross(v13);
// This does correct l2 norm of rows, so that it contains #F list of twice
// triangle areas
double dblA = std::sqrt(n.dot(n));
// now normalize normals to get unit normals
Eigen::Matrix<typename DerivedV::Scalar, 1, 3> u = n / dblA;
// rotate each vector 90 degrees around normal
double norm21 = std::sqrt(v21.dot(v21));
double norm13 = std::sqrt(v13.dot(v13));
eperp21.row(i) = u.cross(v21);
eperp21.row(i) = eperp21.row(i) / std::sqrt(eperp21.row(i).dot(eperp21.row(i)));//确定方向
eperp21.row(i) *= norm21 / dblA;//确定长度
eperp13.row(i) = u.cross(v13);
eperp13.row(i) = eperp13.row(i) / std::sqrt(eperp13.row(i).dot(eperp13.row(i)));
eperp13.row(i) *= norm13 / dblA;
//只需要算两个方向,另一个方向可以通过取负获得
//这里是第0个点,通过 -(1的梯度+2的梯度)获得
}
std::vector<int> rs;
rs.reserve(F.rows()*4*3);
std::vector<int> cs;
cs.reserve(F.rows()*4*3);
std::vector<double> vs;
vs.reserve(F.rows()*4*3);
// row indices
for(int r=0;r<3;r++)//处理x,y,z分量
{
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)//每行有四个元素, 复制四次行索引
{
for(int i=r*F.rows();i<(r+1)*F.rows();i++) rs.push_back(i);
//处理每个三角形
}
}
//这里的索引有点复杂,我们简化成只有一个三角形好了,那么行索引变为
// 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 2 2 2 2
// column indices
for(int r=0;r<3;r++)
{
for(int i=0;i<F.rows();i++) cs.push_back(F(i,1));
for(int i=0;i<F.rows();i++) cs.push_back(F(i,0));
for(int i=0;i<F.rows();i++) cs.push_back(F(i,2));
for(int i=0;i<F.rows();i++) cs.push_back(F(i,0));
}
//列索引变成
// 1 0 2 0 1 0 2 0 1 0 2 0
// values
for(int i=0;i<F.rows();i++) vs.push_back(eperp13(i,0));
for(int i=0;i<F.rows();i++) vs.push_back(-eperp13(i,0));
for(int i=0;i<F.rows();i++) vs.push_back(eperp21(i,0));
for(int i=0;i<F.rows();i++) vs.push_back(-eperp21(i,0));
for(int i=0;i<F.rows();i++) vs.push_back(eperp13(i,1));
for(int i=0;i<F.rows();i++) vs.push_back(-eperp13(i,1));
for(int i=0;i<F.rows();i++) vs.push_back(eperp21(i,1));
for(int i=0;i<F.rows();i++) vs.push_back(-eperp21(i,1));
for(int i=0;i<F.rows();i++) vs.push_back(eperp13(i,2));
for(int i=0;i<F.rows();i++) vs.push_back(-eperp13(i,2));
for(int i=0;i<F.rows();i++) vs.push_back(eperp21(i,2));
for(int i=0;i<F.rows();i++) vs.push_back(-eperp21(i,2));
// 可以发现值的前4个是x值,中间4个是y值,后面4个是z值,那么我们只需要看前面4个即可
// 0 1 eperp13(i,0)
// 0 0 -eperp13(i,0)
// 0 2 eperp21(i,0)
// 0 0 -eperp21(i,0)
// 在图片就相当于在第2个点的hat function 的梯度设置为 (1/h2)e2
// 在第3个点的hat function 的梯度设置为 (1/h3)e3
// 在第1个点的hat function 的梯度设置为 -(1/h2)e2-(1/h3)e3 = (1/h1)e1
// 证明请见:http://blog.csdn.net/seamanj/article/details/52075447
//为了清晰的说明 这里加上2个三角形的情况
//行索引为 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 2 3 2 3 2 3 2 3 4 5 4 5 4 5 4 5
//列索引为 1 4 0 3 2 5 0 3 1 4 0 3 2 5 0 3 1 4 0 3 2 5 0 3
//可以看到前面8个是x部分, 然后是y, z
//然后看前面8个元素 前行索引相同的分别拿出来为
// 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1
// 1 0 2 0 4 3 5 3
前面部分是第一个三角形的索引, 后面是另一个三角形的索引
// create sparse gradient operator matrix
G.resize(3*F.rows(),V.rows());
std::vector<Eigen::Triplet<typename DerivedV::Scalar> > triplets;
for (int i=0;i<(int)vs.size();++i)
{
triplets.push_back(Eigen::Triplet<typename DerivedV::Scalar>(rs[i],cs[i],vs[i]));
}
G.setFromTriplets(triplets.begin(), triplets.end());
}
#ifdef IGL_STATIC_LIBRARY
// Explicit template specialization
// template void igl::grad<double, int>(Eigen::Matrix<double, -1, -1, 0, -1,-1> const&, Eigen::Matrix<int, -1, -1, 0, -1, -1> const&,Eigen::SparseMatrix<double, 0, int>&);
template void igl::grad<Eigen::Matrix<double, -1, 3, 0, -1, 3>, Eigen::Matrix<int, -1, 3, 0, -1, 3> >(Eigen::PlainObjectBase<Eigen::Matrix<double, -1, 3, 0, -1, 3> > const&, Eigen::PlainObjectBase<Eigen::Matrix<int, -1, 3, 0, -1, 3> > const&, Eigen::SparseMatrix<Eigen::Matrix<double, -1, 3, 0, -1, 3>::Scalar, 0, int>&);
//template void igl::grad<Eigen::Matrix<double, -1, 3, 0, -1, 3>, Eigen::Matrix<int, -1, 3, 0, -1, 3> >(Eigen::PlainObjectBase<Eigen::Matrix<double, -1, 3, 0, -1, 3> > const&, Eigen::PlainObjectBase<Eigen::Matrix<int, -1, 3, 0, -1, 3> > const&, Eigen::SparseMatrix<Eigen::Matrix<double, -1, 3, 0, -1, 3>::Scalar, 0, int>&);
template void igl::grad<Eigen::Matrix<double, -1, -1, 0, -1, -1>, Eigen::Matrix<int, -1, -1, 0, -1, -1> >(Eigen::PlainObjectBase<Eigen::Matrix<double, -1, -1, 0, -1, -1> > const&, Eigen::PlainObjectBase<Eigen::Matrix<int, -1, -1, 0, -1, -1> > const&, Eigen::SparseMatrix<Eigen::Matrix<double, -1, -1, 0, -1, -1>::Scalar, 0, int>&);
#endif
it's similar for 'grad_tet' function.



























 4561
4561

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








