引言
什么是UBIFS文件系统
UBIFS是UBI file system的简称,用于裸的flash设备,作为jffs2的后继文件系统之一。UBIFS通过UBI子系统处理与MTD设备之间动作。UBIFS文件系统更适合MLCNAND FLASH。需要注意的是UBIFS并不是为SSD,MMC,SD,Compact Flash等之类的基于flash的存储设备,其是针对于裸flash设备。
裸flash有以下特点:
l 其包含的块被称为可擦除块,而对于SSD这类的设备,并无可擦除块的概念,取而代之的是扇区的概念。
l 包括读、写、擦除可擦除块三种操作。
l 硬件并不管理坏的可擦除块,而SSD之类的设备则具有专门的控制器处理坏块。
l 可擦除块的读写寿命从几千到几十万之间不等。
图0.1中给出的设备是MMC、SD类型的,该设备具有flash转换层的硬件控制器,该硬件控制器的损耗平衡算法属于商业秘密,华为的dorado 系列高端存储器的文档对其损耗平衡(动态和静态)原理讲解的非常透彻,感兴趣的可以自己找找。对于UBIFS使用的场景,通常只有NANDFLASH那一个模块,其和控制器的接口通常是专门的NAND flash接口。由于这类设备的速率比较慢,所以通常用在相对而言比较低端的嵌入式设备,追求加载速度快一点嵌入式设备通常会选择使用emmc存储器,其文件系统通常会选择UFS。
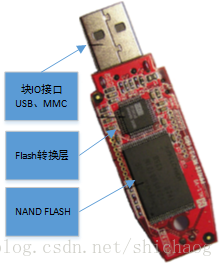
图0.1 具有flash转换层的设备
UBI/UBIFS 协议栈
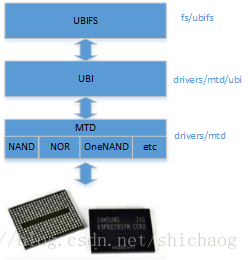
图0.2 UBIFS实现的协议栈
MTD(Memory Technology Devices)对闪存存储器提供了一个抽象,隐藏了特定flash的独特之处,提供统一的API存取各种类型的flash。
MTD在内核层的API是struct mtd_device而用户空间的API接口是/dev/mtd0,这些接口提供了设备信息,读写可擦除块,擦除一个可擦除块,标记一个可擦除块是坏块,检查可擦除块是否是坏块。MTD的API并不隐藏坏的可擦除块也不做任何损耗平衡。
UBI(Unsorted Block Images)的内核API是include/mtd/ubi-user.h,用户空间的则是/dev/ubi0,提供损耗平衡,隐藏坏块,允许运行时容量创建、删除和修改,有点类似LVM功能。UBI线性扩展,在初始化时会读取所有的可擦除块头,所以当flash容量越大,初始化所花费的时间越多,但是就可扩展性而言比JFFS2要好很多。
LEB(logic eraseblock),PEB(physical erase block);将LEB映射到PEB,任何一个LEB可能映射到任何一个PEB,可擦除块头存储的是映射信息以及擦除计数值。
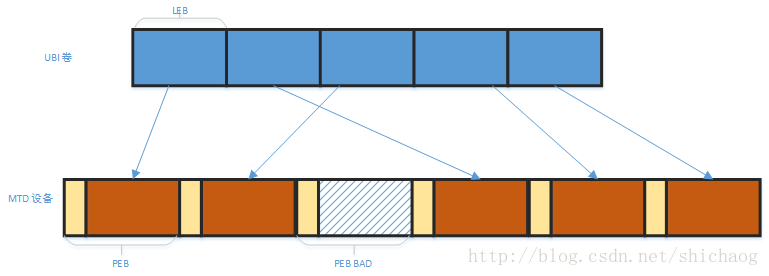
UBI坏的可擦除块处理:
l 为坏的可擦除块预留1%的PEB
l 如果一个PEB变成坏块,则相应的LEB会被映射到一个好的PEB中
l I/O错处处理对上层并未隐藏。
写错误处理
假设用户写数据到LEB0可擦除块,选择一个好的PEB可擦除块(这里假设选择PEB4)来恢复数据,恢复数据实际上就是将数据拷贝到PEB4,然后重新映射LEB0到PEB4,映射完毕后将新数据再次写入PEB4,这是恢复就完成了,将回到UBI层,后台会将PEB1标记为坏块。

图0.4 写错误处理示例
原子改变LEB
这对UBIFS非常重要,假设LEB0需要被原子改变,这一过程是这样的:
首先选择一个合适的PEB块,加入这里选择了PEB0,然后向这个块写入新数据,写入完成后需要将原始映射PEB4解映射同时将LEB0映射到PEB0,这是就完成了原子更新操作返回UBI层,但是PEB4的数据会被后台擦除。
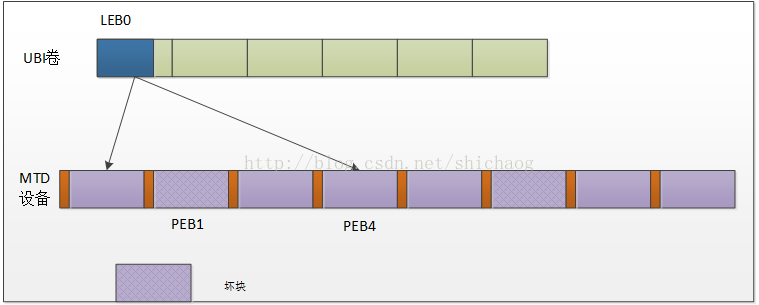
图0.5 原子改变LEB
对UBI底层的操作有了一些了解后,可以开始UBIFS的介绍了,首先UBIFS并不关系可擦除坏块了,这一信息依赖于UBI层,损耗平衡依赖于UBI层而不是UBIFS,LEB的更改是原子性的。
UBIFS文件索引
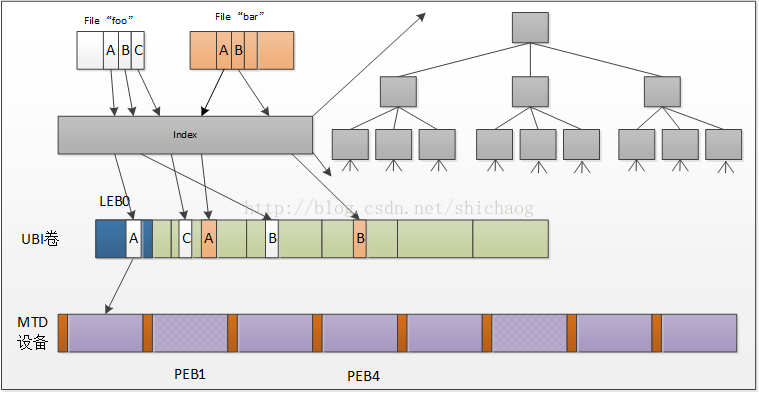
索引允许查找任何数据片段的物理地址。索引采用B+2的结构,图中右上半部分,只有叶子节点包含数据,数的扇出可配,缺省值是8。UBIFS的索引在flash上存储和维护。
图0.6 UBIFS索引
UBIFS日志
日志比较小,为节省功耗只扫描日志并不扫描flash所有数据,这一结果会让挂载很快完成。文件系统所有更改将被日志记录,索引信息只在内存修改,并不在flash上修改。
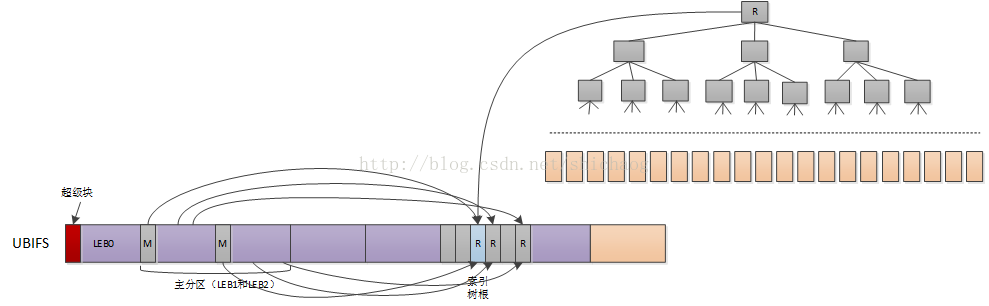
主节点存在于LEB1和LEB2,这两个块存储的是一样的,用于备份恢复之用,主节点指向根索引,主分区在挂载时可以很快被找到。
图0.7 索引和UBIFS的关系
超级块
超级块存储在LEB0位置处,对于UBIFS文件系统只读,但是可以被用户空间工具修改,存储如索引树扇出等一些配置信息,缺省使用zlib或者LZO进行压缩,在挂载该文件系统时,UBIFS的mount方法将被调用读取该超级块。
树节点缓存(TreeNode Cache)
为了加速文件的操作,每次更新flash上的索引树的速率较慢,所以在内存中建立树节点缓存以加快索引树查找。
垃圾回收
有一个空的LEB专门为垃圾回收保留。垃圾回收的一个例子如下:
首先选择一个脏LEB,比如LEB1被选中,然后将其有效数据拷贝的到LEB5,LEB1这时就可以被擦除了,然后再选择一个脏LEB区,如LEB6,同样将数据拷贝到LEB5,拷贝完成后LEB6上的原有数据可能被擦除掉,LEB1将未垃圾回收预留,LEB6这时处于可用状态。索引处理方法,只是将Tree Node Cache的索引节点标记为脏。这样垃圾回收完成。但是还进行一个确认操作,确认操作肯定是可以完成的,会为索引预留至少3倍的空闲空间。
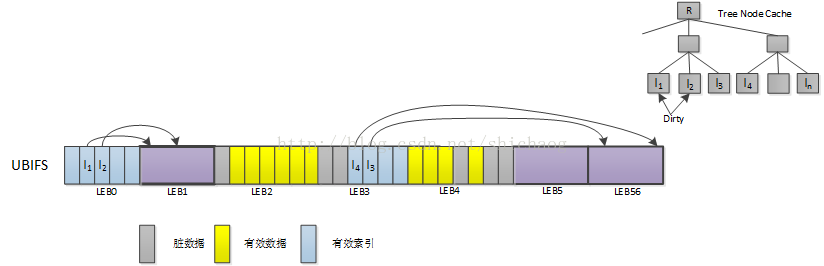
LPT(LEB Properites Tree)
是一个B+树,但是大小固定,比主索引树小很多,管理方法类似于主索引树。
UBIFS初始化
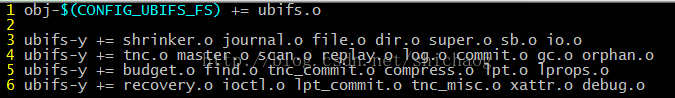
UBIFS的文件系统需要编译的文件如下fs/ubifs/Makefile ,最后会编译成ubifs.o这个文件,链接时会将该文件链接到镜像文件中去。
Shrinker是动态调整树大小的。Journal是UBIFS的日志功能实现的文件,file、dir、super、sb以及io是文件、目录、超级块以及io操作实现;
Tnc(tree nodecache)模块,commit是在垃圾回收确认会用到的操作。gc是垃圾回收实现源码。
为了知道该模块的注册过程,首先查找相关的init函数。
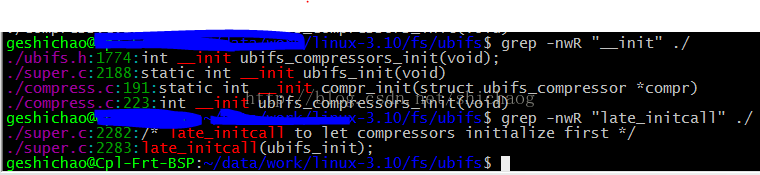
透过上面的两个查找可以知道,UBIFS子系统在加载时会首先执行ubifs_init函数,这很late_initcall在《Linux系统启动那些事—基于Linux 3.10内核》一文提到过其调用的时机,在系统启动时会被调用。
Super.c
static int __init ubifs_init(void)
{
首先申请一个slab分配器,关于slab见《内存管理-之内核内存管理-基于linux3.10》
ubifs_inode_slab = kmem_cache_create("ubifs_inode_slab",
sizeof(struct ubifs_inode), 0,
SLAB_MEM_SPREAD | SLAB_RECLAIM_ACCOUNT,
&inode_slab_ctor);
//将ubifs_shrinker(定义于shrinker.c文件)注册到VM子系统,在cache压力较大时,将会缩小TNC(tree node cache)。
register_shrinker(&ubifs_shrinker_info);
//UBIFS文件系统支持两种压缩格式lzo和zlib,该函数定义于compress.c文件,两种压缩格式在编译时根据宏选定。
err = ubifs_compressors_init();
//注册该文件系统,这个过程见《虚拟文件系统 (VFS)-基于linux3.10》,这里比较感兴趣的是ubifs_fs_type
err = register_filesystem(&ubifs_fs_type);
}mount方法才是最感兴趣的,在《虚拟文件系统 (VFS)-基于linux3.10》里提到文件系统挂载时会调用具体的文件系统的mount方法,这里就来看看它的mount方法。
<super.c>
static struct file_system_type ubifs_fs_type = {
.name = "ubifs",
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.mount = ubifs_mount,
.kill_sb = kill_ubifs_super,
};Mount的函数虽然很重要,但是并没有想象中那么复杂,逻辑结构相对比较明晰。该函数首先调用open_ubi打开一个UBI设备,之所以以只读方式打开是因为这也许是一个新的挂载点,UBI同一时刻只允许有一个读写者。alloc_ubifs_info为描述UBIFS文件系统的结构体struct ubifs_info申请内存,并且初始化自旋锁、互斥锁、链表、树节点等操作。Sget首先在该文件系统中查找超级块,如果没有找到则调用alloc_super创建一个超级块,并初始化超级块的相关成员,该函数并未定义于ubifs文件目录内。然后调用ubifs_fill_super对超级块进行填充,填充的信息源于LEB0,这涉及到UBI和MTD层。由于fill_super()函数在一次打开了UBI,所以这里调用ubi_close_volume将其关闭。最后调用dget返回目录项。
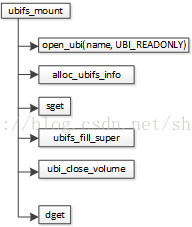
图1.1 UBIFS挂载过程
假设挂载形式如《虚拟文件系统 (VFS)-基于linux3.10》提到的,如:
mount –t ubifs /dev/ubi4_0 /config则open_ubi调用ubi_open_volume_path(“/dev/ubi4_0”,UBI_READONLY)查找UBI卷描述符。
struct ubi_volume_desc *ubi_open_volume_path(const char *pathname, int mode)
{
//该函数分析见《虚拟文件系统 (VFS)-基于linux3.10》
error = kern_path(pathname, LOOKUP_FOLLOW, &path);
inode = path.dentry->d_inode;
mod = inode->i_mode;
//获得主次设备号
ubi_num = ubi_major2num(imajor(inode));
vol_id = iminor(inode) - 1;
path_put(&path);
UBI卷描述符的获取
if (vol_id >= 0 && ubi_num >= 0)
return ubi_open_volume(ubi_num, vol_id, mode);
}ubi_open_volume获取UBI卷描述符,主要依赖前两个参数,第一个参数是UBI主设备号对应的数字,而第二个参数是UBI次设备号对应的数字。由主设备号索引到ubi设备,ubi_devices是一个局部全局的描述ubi设备的数组。
struct ubi_device *ubi;
ubi = ubi_devices[ubi_num];根据ubi设备信息找到UBI卷:
vol = ubi->volumes[vol_id];alloc_ubifs_info主要功能就是slab分配内存,不多解释,有兴趣见《内存管理-之内核内存管理-基于linux3.10》。
sget用于查找并创建超级块
struct super_block *sget(struct file_system_type *type,
int (*test)(struct super_block *,void *),
int (*set)(struct super_block *,void *),
int flags,
void *data)
{
struct super_block *s = NULL;
struct super_block *old;
int err;
retry:
spin_lock(&sb_lock); //获得超级块锁
//这个if语句就是在现有的文件系统中查找超级块是否存在
if (test) { //这个函数在存在,实际上就是sb_test函数。
hlist_for_each_entry(old, &type->fs_supers, s_instances) {
if (!test(old, data))
continue;
if (!grab_super(old))
goto retry;
if (s) {
up_write(&s->s_umount);
destroy_super(s);
s = NULL;
}
down_write(&old->s_umount);
if (unlikely(!(old->s_flags & MS_BORN))) {
deactivate_locked_super(old);
goto retry;
}
return old;
}
}
//如果s == null,则说明上面在ubifs文件系统中没有找到,则需要创建超级块,这里申请内存。
if (!s) {
spin_unlock(&sb_lock);
s = alloc_super(type, flags);
if (!s)
return ERR_PTR(-ENOMEM);
goto retry;
}
//调用set方法,为超级块设置一些内容。
err = set(s, data);
if (err) {
spin_unlock(&sb_lock);
up_write(&s->s_umount);
destroy_super(s);
return ERR_PTR(err);
}
//对超级块的一些其它字段的初始化。
s->s_type = type;
strlcpy(s->s_id, type->name, sizeof(s->s_id));
list_add_tail(&s->s_list, &super_blocks);
hlist_add_head(&s->s_instances, &type->fs_supers);
spin_unlock(&sb_lock);
get_filesystem(type);
register_shrinker(&s->s_shrink);
return s;
}如果sb->s_root为null,则说明还没挂载,该超级块的内容需要从flash上读取。这个任务有ubifs_fill_super实现。
该函数的原型如下:
static int ubifs_fill_super(struct super_block *sb, void *data, int silent)
sb参数是先前创建的超级块,首先将超级块描述ubifs信息的字段单独取出来
struct ubifs_info *c = sb->s_fs_info;
c->vfs_sb = sb;
这里重新打开改UBI设备,注意权限编程的读写,这意味着需要从该设备读写数据了。
c->ubi = ubi_open_volume(c->vi.ubi_num, c->vi.vol_id, UBI_READWRITE);
初始化相关字段,bdi是backing_dev_info简写,其功能是禁止预读,不需要改功能。
c->bdi.name = "ubifs",
c->bdi.capabilities = BDI_CAP_MAP_COPY;
err = bdi_init(&c->bdi);
err = bdi_register(&c->bdi, NULL, "ubifs_%d_%d",
c->vi.ubi_num, c->vi.vol_id);
err = ubifs_parse_options(c, data, 0);
if (err)
goto out_bdi;
//超级块信息初始化
sb->s_bdi = &c->bdi;
sb->s_fs_info = c;
sb->s_magic = UBIFS_SUPER_MAGIC;
sb->s_blocksize = UBIFS_BLOCK_SIZE;
sb->s_blocksize_bits = UBIFS_BLOCK_SHIFT;
sb->s_maxbytes = c->max_inode_sz = key_max_inode_size(c);
if (c->max_inode_sz > MAX_LFS_FILESIZE)
sb->s_maxbytes = c->max_inode_sz = MAX_LFS_FILESIZE;
sb->s_op = &ubifs_super_operations;
mutex_lock(&c->umount_mutex);
//挂载ubifs文件系统。并调用ubifs_read_superblock读取超级块,使能日志功能等
err = mount_ubifs(c);
/*读取根索引节点*/
root = ubifs_iget(sb, UBIFS_ROOT_INO);
将超级块和根索引节点关联
sb->s_root = d_make_root(root);UBIFS文件系统的读写实际上就是UBI层到MTD层的一个过程,其读代码的执行流程如下,
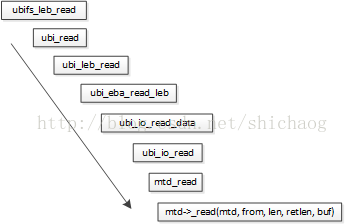
UBIFS接口函数集
Makefile中显示的各个编译后目标的文件提供的函数接口如下:
/* io.c */
void ubifs_ro_mode(struct ubifs_info *c, int err);
int ubifs_leb_read(const struct ubifs_info *c, int lnum, void *buf, int offs,
int len, int even_ebadmsg);
int ubifs_leb_write(struct ubifs_info *c, int lnum, const void *buf, int offs,
int len);
int ubifs_leb_change(struct ubifs_info *c, int lnum, const void *buf, int len);
int ubifs_leb_unmap(struct ubifs_info *c, int lnum);
int ubifs_leb_map(struct ubifs_info *c, int lnum);
int ubifs_is_mapped(const struct ubifs_info *c, int lnum);
int ubifs_wbuf_write_nolock(struct ubifs_wbuf *wbuf, void *buf, int len);
int ubifs_wbuf_seek_nolock(struct ubifs_wbuf *wbuf, int lnum, int offs);
int ubifs_wbuf_init(struct ubifs_info *c, struct ubifs_wbuf *wbuf);
int ubifs_read_node(const struct ubifs_info *c, void *buf, int type, int len,
int lnum, int offs);
int ubifs_read_node_wbuf(struct ubifs_wbuf *wbuf, void *buf, int type, int len,
int lnum, int offs);
int ubifs_write_node(struct ubifs_info *c, void *node, int len, int lnum,
int offs);
int ubifs_check_node(const struct ubifs_info *c, const void *buf, int lnum,
int offs, int quiet, int must_chk_crc);
void ubifs_prepare_node(struct ubifs_info *c, void *buf, int len, int pad);
void ubifs_prep_grp_node(struct ubifs_info *c, void *node, int len, int last);
int ubifs_io_init(struct ubifs_info *c);
void ubifs_pad(const struct ubifs_info *c, void *buf, int pad);
int ubifs_wbuf_sync_nolock(struct ubifs_wbuf *wbuf);
int ubifs_bg_wbufs_sync(struct ubifs_info *c);
void ubifs_wbuf_add_ino_nolock(struct ubifs_wbuf *wbuf, ino_t inum);
int ubifs_sync_wbufs_by_inode(struct ubifs_info *c, struct inode *inode);/* scan.c */
struct ubifs_scan_leb *ubifs_scan(const struct ubifs_info *c, int lnum,
int offs, void *sbuf, int quiet);
void ubifs_scan_destroy(struct ubifs_scan_leb *sleb);
int ubifs_scan_a_node(const struct ubifs_info *c, void *buf, int len, int lnum,
int offs, int quiet);
struct ubifs_scan_leb *ubifs_start_scan(const struct ubifs_info *c, int lnum,
int offs, void *sbuf);
void ubifs_end_scan(const struct ubifs_info *c, struct ubifs_scan_leb *sleb,
int lnum, int offs);
int ubifs_add_snod(const struct ubifs_info *c, struct ubifs_scan_leb *sleb,
void *buf, int offs);
void ubifs_scanned_corruption(const struct ubifs_info *c, int lnum, int offs,
void *buf);/* log.c */
void ubifs_add_bud(struct ubifs_info *c, struct ubifs_bud *bud);
void ubifs_create_buds_lists(struct ubifs_info *c);
int ubifs_add_bud_to_log(struct ubifs_info *c, int jhead, int lnum, int offs);
struct ubifs_bud *ubifs_search_bud(struct ubifs_info *c, int lnum);
struct ubifs_wbuf *ubifs_get_wbuf(struct ubifs_info *c, int lnum);
int ubifs_log_start_commit(struct ubifs_info *c, int *ltail_lnum);
int ubifs_log_end_commit(struct ubifs_info *c, int new_ltail_lnum);
int ubifs_log_post_commit(struct ubifs_info *c, int old_ltail_lnum);
int ubifs_consolidate_log(struct ubifs_info *c);/* journal.c */
int ubifs_jnl_update(struct ubifs_info *c, const struct inode *dir,
const struct qstr *nm, const struct inode *inode,
int deletion, int xent);
int ubifs_jnl_write_data(struct ubifs_info *c, const struct inode *inode,
const union ubifs_key *key, const void *buf, int len);
int ubifs_jnl_write_inode(struct ubifs_info *c, const struct inode *inode);
int ubifs_jnl_delete_inode(struct ubifs_info *c, const struct inode *inode);
int ubifs_jnl_rename(struct ubifs_info *c, const struct inode *old_dir,
const struct dentry *old_dentry,
const struct inode *new_dir,
const struct dentry *new_dentry, int sync);
int ubifs_jnl_truncate(struct ubifs_info *c, const struct inode *inode,
loff_t old_size, loff_t new_size);
int ubifs_jnl_delete_xattr(struct ubifs_info *c, const struct inode *host,
const struct inode *inode, const struct qstr *nm);
int ubifs_jnl_change_xattr(struct ubifs_info *c, const struct inode *inode1,
const struct inode *inode2);/* budget.c */
int ubifs_budget_space(struct ubifs_info *c, struct ubifs_budget_req *req);
void ubifs_release_budget(struct ubifs_info *c, struct ubifs_budget_req *req);
void ubifs_release_dirty_inode_budget(struct ubifs_info *c,
struct ubifs_inode *ui);
int ubifs_budget_inode_op(struct ubifs_info *c, struct inode *inode,
struct ubifs_budget_req *req);
void ubifs_release_ino_dirty(struct ubifs_info *c, struct inode *inode,
struct ubifs_budget_req *req);
void ubifs_cancel_ino_op(struct ubifs_info *c, struct inode *inode,
struct ubifs_budget_req *req);
long long ubifs_get_free_space(struct ubifs_info *c);
long long ubifs_get_free_space_nolock(struct ubifs_info *c);
int ubifs_calc_min_idx_lebs(struct ubifs_info *c);
void ubifs_convert_page_budget(struct ubifs_info *c);
long long ubifs_reported_space(const struct ubifs_info *c, long long free);
long long ubifs_calc_available(const struct ubifs_info *c, int min_idx_lebs);/* find.c */
int ubifs_find_free_space(struct ubifs_info *c, int min_space, int *offs,
int squeeze);
int ubifs_find_free_leb_for_idx(struct ubifs_info *c);
int ubifs_find_dirty_leb(struct ubifs_info *c, struct ubifs_lprops *ret_lp,
int min_space, int pick_free);
int ubifs_find_dirty_idx_leb(struct ubifs_info *c);
int ubifs_save_dirty_idx_lnums(struct ubifs_info *c);/* tnc.c */
int ubifs_lookup_level0(struct ubifs_info *c, const union ubifs_key *key,
struct ubifs_znode **zn, int *n);
int ubifs_tnc_lookup_nm(struct ubifs_info *c, const union ubifs_key *key,
void *node, const struct qstr *nm);
int ubifs_tnc_locate(struct ubifs_info *c, const union ubifs_key *key,
void *node, int *lnum, int *offs);
int ubifs_tnc_add(struct ubifs_info *c, const union ubifs_key *key, int lnum,
int offs, int len);
int ubifs_tnc_replace(struct ubifs_info *c, const union ubifs_key *key,
int old_lnum, int old_offs, int lnum, int offs, int len);
int ubifs_tnc_add_nm(struct ubifs_info *c, const union ubifs_key *key,
int lnum, int offs, int len, const struct qstr *nm);
int ubifs_tnc_remove(struct ubifs_info *c, const union ubifs_key *key);
int ubifs_tnc_remove_nm(struct ubifs_info *c, const union ubifs_key *key,
const struct qstr *nm);
int ubifs_tnc_remove_range(struct ubifs_info *c, union ubifs_key *from_key,
union ubifs_key *to_key);
int ubifs_tnc_remove_ino(struct ubifs_info *c, ino_t inum);
struct ubifs_dent_node *ubifs_tnc_next_ent(struct ubifs_info *c,
union ubifs_key *key,
const struct qstr *nm);
void ubifs_tnc_close(struct ubifs_info *c);
int ubifs_tnc_has_node(struct ubifs_info *c, union ubifs_key *key, int level,
int lnum, int offs, int is_idx);
int ubifs_dirty_idx_node(struct ubifs_info *c, union ubifs_key *key, int level,
int lnum, int offs);
/* Shared by tnc.c for tnc_commit.c */
void destroy_old_idx(struct ubifs_info *c);
int is_idx_node_in_tnc(struct ubifs_info *c, union ubifs_key *key, int level,
int lnum, int offs);
int insert_old_idx_znode(struct ubifs_info *c, struct ubifs_znode *znode);
int ubifs_tnc_get_bu_keys(struct ubifs_info *c, struct bu_info *bu);
int ubifs_tnc_bulk_read(struct ubifs_info *c, struct bu_info *bu);/* tnc_misc.c */
struct ubifs_znode *ubifs_tnc_levelorder_next(struct ubifs_znode *zr,
struct ubifs_znode *znode);
int ubifs_search_zbranch(const struct ubifs_info *c,
const struct ubifs_znode *znode,
const union ubifs_key *key, int *n);
struct ubifs_znode *ubifs_tnc_postorder_first(struct ubifs_znode *znode);
struct ubifs_znode *ubifs_tnc_postorder_next(struct ubifs_znode *znode);
long ubifs_destroy_tnc_subtree(struct ubifs_znode *zr);
struct ubifs_znode *ubifs_load_znode(struct ubifs_info *c,
struct ubifs_zbranch *zbr,
struct ubifs_znode *parent, int iip);
int ubifs_tnc_read_node(struct ubifs_info *c, struct ubifs_zbranch *zbr,
void *node);/* tnc_commit.c */
int ubifs_tnc_start_commit(struct ubifs_info *c, struct ubifs_zbranch *zroot);
int ubifs_tnc_end_commit(struct ubifs_info *c);
/* shrinker.c */
int ubifs_shrinker(struct shrinker *shrink, struct shrink_control *sc);
/* commit.c */
int ubifs_bg_thread(void *info);
void ubifs_commit_required(struct ubifs_info *c);
void ubifs_request_bg_commit(struct ubifs_info *c);
int ubifs_run_commit(struct ubifs_info *c);
void ubifs_recovery_commit(struct ubifs_info *c);
int ubifs_gc_should_commit(struct ubifs_info *c);
void ubifs_wait_for_commit(struct ubifs_info *c);
/* master.c */
int ubifs_read_master(struct ubifs_info *c);
int ubifs_write_master(struct ubifs_info *c);
/* sb.c */
int ubifs_read_superblock(struct ubifs_info *c);
struct ubifs_sb_node *ubifs_read_sb_node(struct ubifs_info *c);
int ubifs_write_sb_node(struct ubifs_info *c, struct ubifs_sb_node *sup);
int ubifs_fixup_free_space(struct ubifs_info *c);
/* replay.c */
int ubifs_validate_entry(struct ubifs_info *c,
const struct ubifs_dent_node *dent);
int ubifs_replay_journal(struct ubifs_info *c);
/* gc.c */
int ubifs_garbage_collect(struct ubifs_info *c, int anyway);
int ubifs_gc_start_commit(struct ubifs_info *c);
int ubifs_gc_end_commit(struct ubifs_info *c);
void ubifs_destroy_idx_gc(struct ubifs_info *c);
int ubifs_get_idx_gc_leb(struct ubifs_info *c);
int ubifs_garbage_collect_leb(struct ubifs_info *c, struct ubifs_lprops *lp);
/* orphan.c */
int ubifs_add_orphan(struct ubifs_info *c, ino_t inum);
void ubifs_delete_orphan(struct ubifs_info *c, ino_t inum);
int ubifs_orphan_start_commit(struct ubifs_info *c);
int ubifs_orphan_end_commit(struct ubifs_info *c);
int ubifs_mount_orphans(struct ubifs_info *c, int unclean, int read_only);
int ubifs_clear_orphans(struct ubifs_info *c);/* lpt.c */
int ubifs_calc_lpt_geom(struct ubifs_info *c);
int ubifs_create_dflt_lpt(struct ubifs_info *c, int *main_lebs, int lpt_first,
int *lpt_lebs, int *big_lpt);
int ubifs_lpt_init(struct ubifs_info *c, int rd, int wr);
struct ubifs_lprops *ubifs_lpt_lookup(struct ubifs_info *c, int lnum);
struct ubifs_lprops *ubifs_lpt_lookup_dirty(struct ubifs_info *c, int lnum);
int ubifs_lpt_scan_nolock(struct ubifs_info *c, int start_lnum, int end_lnum,
ubifs_lpt_scan_callback scan_cb, void *data);
/* Shared by lpt.c for lpt_commit.c */
void ubifs_pack_lsave(struct ubifs_info *c, void *buf, int *lsave);
void ubifs_pack_ltab(struct ubifs_info *c, void *buf,
struct ubifs_lpt_lprops *ltab);
void ubifs_pack_pnode(struct ubifs_info *c, void *buf,
struct ubifs_pnode *pnode);
void ubifs_pack_nnode(struct ubifs_info *c, void *buf,
struct ubifs_nnode *nnode);
struct ubifs_pnode *ubifs_get_pnode(struct ubifs_info *c,
struct ubifs_nnode *parent, int iip);
struct ubifs_nnode *ubifs_get_nnode(struct ubifs_info *c,
struct ubifs_nnode *parent, int iip);
int ubifs_read_nnode(struct ubifs_info *c, struct ubifs_nnode *parent, int iip);
void ubifs_add_lpt_dirt(struct ubifs_info *c, int lnum, int dirty);
void ubifs_add_nnode_dirt(struct ubifs_info *c, struct ubifs_nnode *nnode);
uint32_t ubifs_unpack_bits(uint8_t **addr, int *pos, int nrbits);
struct ubifs_nnode *ubifs_first_nnode(struct ubifs_info *c, int *hght);
/* Needed only in debugging code in lpt_commit.c */
int ubifs_unpack_nnode(const struct ubifs_info *c, void *buf,
struct ubifs_nnode *nnode);
/* lpt_commit.c */
int ubifs_lpt_start_commit(struct ubifs_info *c);
int ubifs_lpt_end_commit(struct ubifs_info *c);
int ubifs_lpt_post_commit(struct ubifs_info *c);
void ubifs_lpt_free(struct ubifs_info *c, int wr_only);
/* lprops.c */
const struct ubifs_lprops *ubifs_change_lp(struct ubifs_info *c,
const struct ubifs_lprops *lp,
int free, int dirty, int flags,
int idx_gc_cnt);
void ubifs_get_lp_stats(struct ubifs_info *c, struct ubifs_lp_stats *lst);
void ubifs_add_to_cat(struct ubifs_info *c, struct ubifs_lprops *lprops,
int cat);
void ubifs_replace_cat(struct ubifs_info *c, struct ubifs_lprops *old_lprops,
struct ubifs_lprops *new_lprops);
void ubifs_ensure_cat(struct ubifs_info *c, struct ubifs_lprops *lprops);
int ubifs_categorize_lprops(const struct ubifs_info *c,
const struct ubifs_lprops *lprops);
int ubifs_change_one_lp(struct ubifs_info *c, int lnum, int free, int dirty,
int flags_set, int flags_clean, int idx_gc_cnt);
int ubifs_update_one_lp(struct ubifs_info *c, int lnum, int free, int dirty,
int flags_set, int flags_clean);
int ubifs_read_one_lp(struct ubifs_info *c, int lnum, struct ubifs_lprops *lp);
const struct ubifs_lprops *ubifs_fast_find_free(struct ubifs_info *c);
const struct ubifs_lprops *ubifs_fast_find_empty(struct ubifs_info *c);
const struct ubifs_lprops *ubifs_fast_find_freeable(struct ubifs_info *c);
const struct ubifs_lprops *ubifs_fast_find_frdi_idx(struct ubifs_info *c);
int ubifs_calc_dark(const struct ubifs_info *c, int spc);/* file.c */
int ubifs_fsync(struct file *file, loff_t start, loff_t end, int datasync);
int ubifs_setattr(struct dentry *dentry, struct iattr *attr);
/* dir.c */
struct inode *ubifs_new_inode(struct ubifs_info *c, const struct inode *dir,
umode_t mode);
int ubifs_getattr(struct vfsmount *mnt, struct dentry *dentry,
struct kstat *stat);
/* xattr.c */
int ubifs_setxattr(struct dentry *dentry, const char *name,
const void *value, size_t size, int flags);
ssize_t ubifs_getxattr(struct dentry *dentry, const char *name, void *buf,
size_t size);
ssize_t ubifs_listxattr(struct dentry *dentry, char *buffer, size_t size);
int ubifs_removexattr(struct dentry *dentry, const char *name);
/* super.c */
struct inode *ubifs_iget(struct super_block *sb, unsigned long inum);
/* recovery.c */
int ubifs_recover_master_node(struct ubifs_info *c);
int ubifs_write_rcvrd_mst_node(struct ubifs_info *c);
struct ubifs_scan_leb *ubifs_recover_leb(struct ubifs_info *c, int lnum,
int offs, void *sbuf, int jhead);
struct ubifs_scan_leb *ubifs_recover_log_leb(struct ubifs_info *c, int lnum,
int offs, void *sbuf);
int ubifs_recover_inl_heads(struct ubifs_info *c, void *sbuf);
int ubifs_clean_lebs(struct ubifs_info *c, void *sbuf);
int ubifs_rcvry_gc_commit(struct ubifs_info *c);
int ubifs_recover_size_accum(struct ubifs_info *c, union ubifs_key *key,
int deletion, loff_t new_size);
int ubifs_recover_size(struct ubifs_info *c);
void ubifs_destroy_size_tree(struct ubifs_info *c);
/* ioctl.c */
long ubifs_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg);
void ubifs_set_inode_flags(struct inode *inode);
#ifdef CONFIG_COMPAT
long ubifs_compat_ioctl(struct file *file, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg);
#endif
/* compressor.c */
int __init ubifs_compressors_init(void);
void ubifs_compressors_exit(void);
void ubifs_compress(const void *in_buf, int in_len, void *out_buf, int *out_len,
int *compr_type);
int ubifs_decompress(const void *buf, int len, void *out, int *out_len,
int compr_type);
























 4878
4878

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










