One day Petya was solving a very interesting problem. But although he used many optimization techniques, his solution still got Time limit exceeded verdict. Petya conducted a thorough analysis of his program and found out that his function for finding maximum element in an array of n positive integers was too slow. Desperate, Petya decided to use a somewhat unexpected optimization using parameter k, so now his function contains the following code:
int fast_max(int n, int a[]) {
int ans = 0;
int offset = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if (ans < a[i]) {
ans = a[i];
offset = 0;
} else {
offset = offset + 1;
if (offset == k)
return ans;
}
return ans;
}
That way the function iteratively checks array elements, storing the intermediate maximum, and if after kconsecutive iterations that maximum has not changed, it is returned as the answer.
Now Petya is interested in fault rate of his function. He asked you to find the number of permutations of integers from 1 to n such that the return value of his function on those permutations is not equal to n. Since this number could be very big, output the answer modulo 109 + 7.
The only line contains two integers n and k (1 ≤ n, k ≤ 106), separated by a space — the length of the permutations and the parameter k.
Output the answer to the problem modulo 109 + 7.
5 2
22
5 3
6
6 3
84
Permutations from second example:
[4, 1, 2, 3, 5], [4, 1, 3, 2, 5], [4, 2, 1, 3, 5], [4, 2, 3, 1, 5], [4, 3, 1, 2, 5], [4, 3, 2, 1, 5].
设dp[i]表示以 i 结尾的,满足题目要求的1~i排列。显然若i<=k+1,则dp[i]=0。
我们考虑i-1在这个排列当中的位置。当i-1和i之间的数字超过k个时,显然成立,此时共有(i-k-1)*(i-2)!种序列;否则,i-1的下标 j >= i-k, 把序列的前 j 个数字离散化为1到 j 之后,这些数字组成的排列一定是以 j 结尾,满足题目要求的序列,共有dp[j]个,因为后面的数字少于k个,不可能满足要求。dp[j]是离散化之后的结果,离散化之前的结果共有dp[j]*C(i-2,j-1)*(i-j-1)!=dp[j]*(i-2)!/(j-1)!个(先在剩下i-2个数当中取j-1个排在下标1~j-1的位置,下标 j 之后到最后一个元素之前的位置随意排列)。这样,
提取出(i-2)!,后面一项就可以利用前缀和求出。阶乘的乘除可以利用逆元求出。
dp[n]是以n结尾的序列个数。我们把n排在不同的位置h,把n下标之前的数离散化到1~h-1,同上面一样,我们得到答案为

#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <map>
#include <queue>
#include <deque>
#include <vector>
#include <set>
#include <algorithm>
#include <math.h>
#include <cmath>
#include <stack>
#include <iomanip>
#define mem0(a) memset(a,0,sizeof(a))
#define meminf(a) memset(a,0x3f,sizeof(a))
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
typedef long double ld;
typedef double db;
const int maxn=1000005,inf=0x3f3f3f3f;
const ll llinf=0x3f3f3f3f3f3f3f3f,mod=1e9+7;
const ld pi=acos(-1.0L);
ll inv[maxn],fac[maxn],dp[maxn],sum[maxn];
ll fastpow(ll base,ll index) {
ll sum=base,ans=1;
ll i=index;
while (i) {
if (i%2) ans=(ans*sum)%mod;
sum*=sum;
sum=sum%mod;
i/=2;
}
return ans;
}
int main() {
ll n,k,ans=0,i;
cin >> n >> k;
if (n<=k+1) {
printf("0\n");return 0;
}
fac[0]=1;
for (i=1;i<=n;i++) {
fac[i]=(fac[i-1]*i)%mod;
}
inv[n]=fastpow(fac[n],mod-2);
for (i=n-1;i>=0;i--) {
inv[i]=inv[i+1]*(i+1);
inv[i]%=mod;
}
mem0(dp);mem0(sum);
for (i=k+2;i<=n;i++) {
dp[i]=(i-k-1+(sum[i-1]-sum[i-k-1]+mod)%mod)%mod;
dp[i]=(dp[i]*fac[i-2])%mod;
sum[i]=sum[i-1]+(dp[i]*inv[i-1])%mod;
sum[i]%=mod;
ans+=(((dp[i]*fac[n-1])%mod)*inv[i-1])%mod;
ans%=mod;
}
cout << ans;
return 0;
}










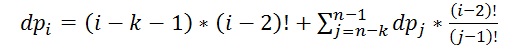














 1290
1290

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








