转载于:http://blog.csdn.net/jsagacity/article/details/78531819
前段时间,公司利用 ESP8266 这个WiFi模块,做了好多小产品。从手机 APP 直连这个 ESP8266 进行通讯,再到实现远程控制。中间实现过程磕磕碰碰,虽然这方面已经做得非常成熟,但是网上的资料少之又少。现在把实现方式展示出来,同时也算是做一个笔记。
首先这里要实现的是Android端的APP直连ESP8266进行双向通讯。
首先我们来说一下这个ESP8266,这个在淘宝上非常便宜,10块左右,安信可的产品。这个WiFi模块已经做得非常的成熟,下面介绍一下它的基本使用,首先这个模块有三种模式:
1:STA 模式:ESP8266模块通过路由器连接互联网,手机或电脑通过互联网实现对设备的远程控制。
2:AP 模式:ESP8266模块作为热点,实现手机或电脑直接与模块通信,实现局域网无线控制。
3:STA+AP 模式:两种模式的共存模式,即可以通过互联网控制可实现无缝切换,方便操作。
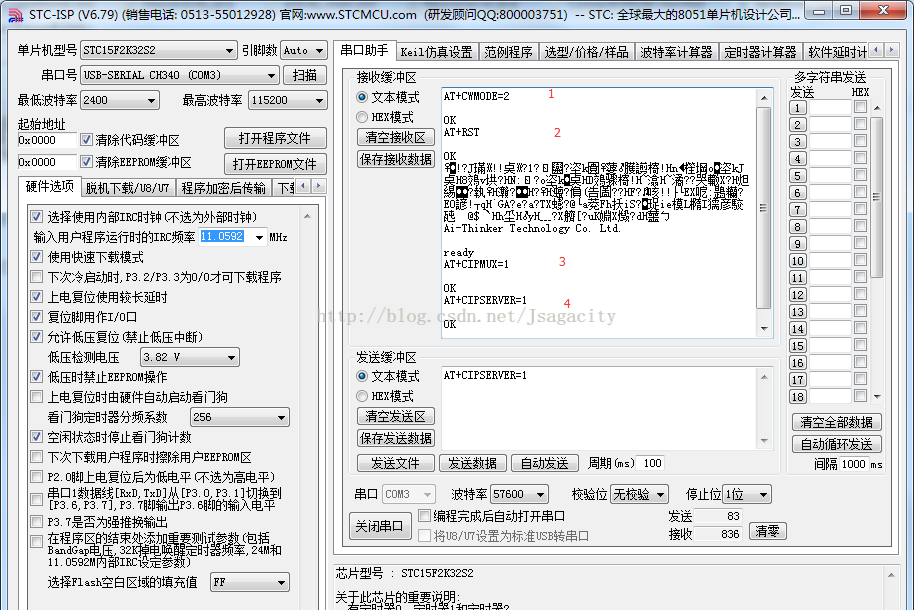
今天的实现用AP模式就够了,指令有下面这几个就够了:
1、设置wifi模式:AT+CWMODE=2
2、重启生效:AT+RST
3、启动多连接:AT+CIPMUX=1
4、建立server:AT+CIPSERVER=1
另外还有非常多的指令可以修改这个模块的参数,甚至还可以修改里面的程序重新烧录,更多的详情就参考安信可的官网。这个就需要电子比较厉害的人才会适合了,我是Android开发的,所以这方面不太了解,还望海涵。
这是设备:
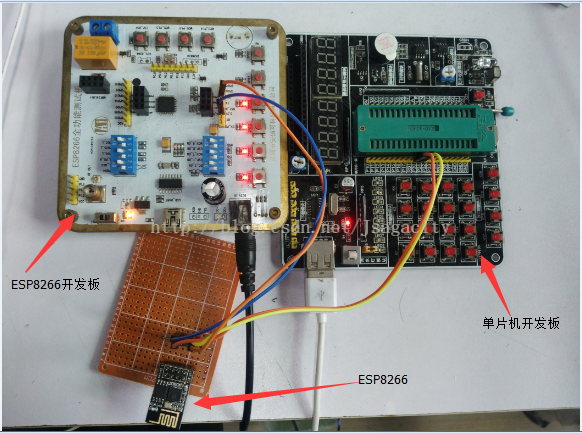
接下来通过串口发送指令开启ESP8266的WiFi:
发送完这四个指令之后,打开手机就可以看到相应的WiFi开启了(这个WiFi名给我改过):
好了,硬件准备完毕,接下来我们准备APP软件,针对Android端的。新建一个Android项目,项目结构:
添加一个异步处理类:
- /**
- * Created by Layne_Yao on 2017/5/12.
- * CSDN:http://blog.csdn.net/Jsagacity
- */
- public class SendAsyncTask extends AsyncTask<String, Void, Void> {
- //这里是连接ESP8266的IP和端口号,IP是通过指令在单片机开发板查询到,而端口号可以自行设置,也可以使用默认的,333就是默认的
- private static final String IP = "192.168.4.1";
- private static final int PORT = 333;
- private Socket client = null;
- private PrintStream out = null;
- @Override
- protected Void doInBackground(String... params) {
- String str = params[0];
- try {
- client = new Socket(IP, PORT);
- client.setSoTimeout(5000);
- // 获取Socket的输出流,用来发送数据到服务端
- out = new PrintStream(client.getOutputStream());
- out.print(str);
- out.flush();
- if (client == null) {
- return null;
- } else {
- out.close();
- client.close();
- }
- } catch (IOException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- return null;
- }
- }
在手机端建立一个作为接受ESP8266发送的消息的服务器:
- public class MobileServer implements Runnable {
- private ServerSocket server;
- private DataInputStream in;
- private byte[] receice;
- private Handler handler = new Handler();
- public MobileServer() {
- }
- public void setHandler(Handler handler) {
- this.handler = handler;
- }
- @Override
- public void run() {
- try {
- //5000是手机端开启的服务器的端口号,ESP8266进行TCP连接时使用的端口,而IP也是通过指令查询的联入设备的IP
- server = new ServerSocket(5000);
- while (true) {
- Socket client = server.accept();
- in = new DataInputStream(client.getInputStream());
- receice = new byte[50];
- in.read(receice);
- in.close();
- Message message = new Message();
- message.what = 1;
- message.obj = new String(receice);
- handler.sendMessage(message);
- }
- } catch (IOException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- try {
- server.close();
- } catch (IOException e) {
- e.printStackTrace();
- }
- }
- }
布局文件:
- <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
- xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="match_parent"
- tools:context="com.itman.connectesp8266.MainActivity" >
- <TextView
- android:id="@+id/tv_content"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="25dp"
- android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
- android:layout_marginTop="10dp"
- android:background="#fe9920"
- android:gravity="center"
- android:text="接收的内容" />
- <Button
- android:id="@+id/bt_send"
- android:layout_width="match_parent"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_below="@id/tv_content"
- android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
- android:layout_marginTop="40dp"
- android:text="发送" />
- <TextView
- android:id="@+id/tv_send_text"
- android:layout_width="wrap_content"
- android:layout_height="wrap_content"
- android:layout_below="@id/bt_send"
- android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
- android:layout_marginTop="33dp"
- android:text="发送的内容" />
- </RelativeLayout>
最后是MainActivity:
- public class MainActivity extends ActionBarActivity implements OnClickListener {
- private TextView tv_content, tv_send_text;
- private Button bt_send;
- @Override
- protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
- super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
- setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
- InitView();
- //开启服务器
- MobileServer mobileServer = new MobileServer();
- mobileServer.setHandler(handler);
- new Thread(mobileServer).start();
- }
- private void InitView() {
- tv_content = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_content);
- tv_send_text = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tv_send_text);
- bt_send = (Button) findViewById(R.id.bt_send);
- bt_send.setOnClickListener(this);
- }
- @Override
- public void onClick(View v) {
- switch (v.getId()) {
- case R.id.bt_send:
- String str = "Sent to the ESP8266";
- new SendAsyncTask().execute(str);
- tv_send_text.setText(str);
- break;
- }
- }
- Handler handler = new Handler() {
- @Override
- public void handleMessage(Message msg) {
- switch (msg.what) {
- case 1:
- tv_content.setText("WiFi模块发送的:" + msg.obj);
- Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "接收到信息", Toast.LENGTH_LONG)
- .show();
- }
- }
- };
- }
最后不要忘了添加网路权限:
- <uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET"/>
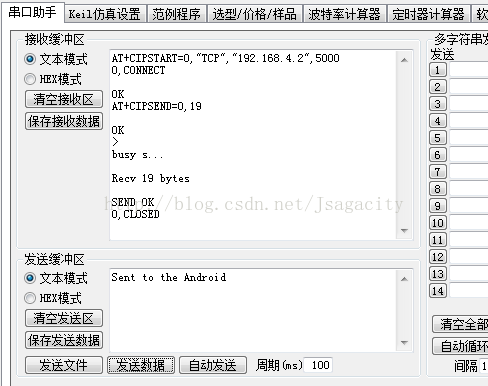
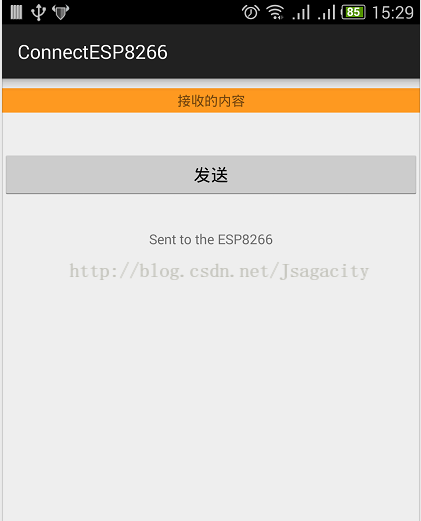
运行到真机,确保手机连接上ESP8266的WiFi, 就可以进行手机发送信息到ESP8266了 。手机APP发送过去的:
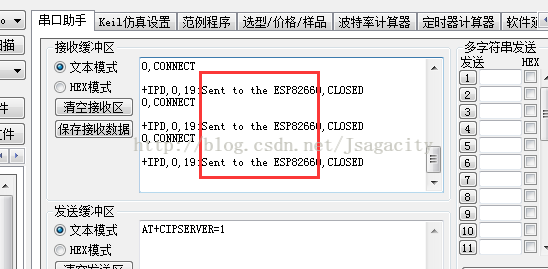
ESP8266接收到的:
接下来是ESP8266发送数据到APP。首先ESP要使用到的指令有:
1、建立TCP连接:AT+CIPSTART=0,"TCP","192.168.4.2",5000
2、确定发送数据的长度:AT+CIPSEND=0,19
3、发送信息:Sent to the Android
操作指令:
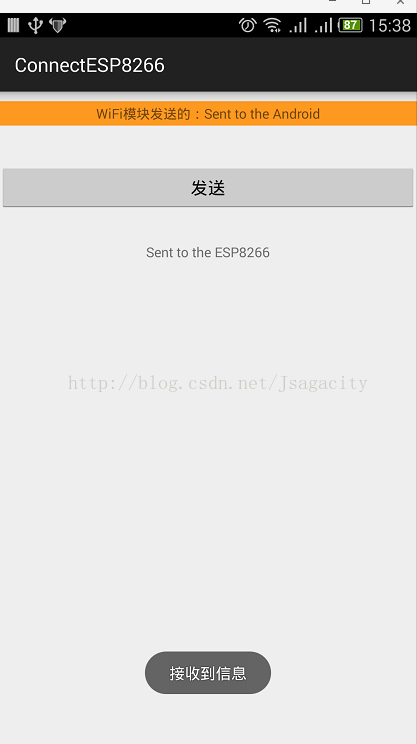
APP端接受到的信息:
以上是简单的实现APP和ESP8266直连通讯的实现。
如果想要实现远程控制,过程是比较繁杂的,但是并不复杂。
这里只简单的说明一下大致的实现方式:
1、要实现远程控制就必须得租用一个服务器,当然自己电脑也可以作为服务器,就是需要配置。最简单的方式是租用云服务器,比如阿里云的ECS,如果是学生,还有学生价。
2、接下来是最麻烦的步骤:
1)手机发数据到云服务器,这个不用多说了,使用json数据的网络通信;
2)接着就是云服务器继续把手机发送过来的转发的ESP8266,而云服务器和ESP8266之间的通讯是需要使用TCP长连接的。因为ESP8266这边的IP是会变化的所以只能使用长连接;
3)ESP8266发数据到云服务器就不用再多说了,就第2点中的长连接。但是云服务器怎么推送数据到APP呢?答案也是长连接的,这里可以使用别人集成好的框架mina。
以上就是远程控制的大致过程要点,想要实现就各自去完成了。当初我还是在别的平台问人问到的实现方案,网上根本没有相应的资料,或者是方案。以上的实现方案虽然有点繁杂,但是并不复杂,慢慢实现是没有很大难度的。








 本文介绍如何使用ESP8266 WiFi模块与Android APP进行直连双向通讯,包括设置ESP8266的工作模式、通过串口发送指令、APP端的实现代码等,并给出了实现远程控制的基本思路。
本文介绍如何使用ESP8266 WiFi模块与Android APP进行直连双向通讯,包括设置ESP8266的工作模式、通过串口发送指令、APP端的实现代码等,并给出了实现远程控制的基本思路。
















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








