Description
A rooted tree is a well-known data structure in computer science and engineering. An example is shown below:
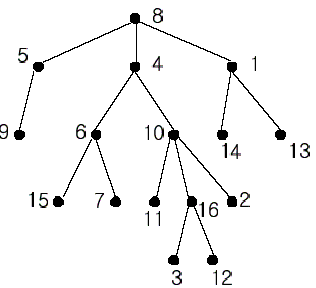
In the figure, each node is labeled with an integer from {1, 2,…,16}. Node 8 is the root of the tree. Node x is an ancestor of node y if node x is in the path between the root and node y. For example, node 4 is an ancestor of node 16. Node 10 is also an ancestor of node 16. As a matter of fact, nodes 8, 4, 10, and 16 are the ancestors of node 16. Remember that a node is an ancestor of itself. Nodes 8, 4, 6, and 7 are the ancestors of node 7. A node x is called a common ancestor of two different nodes y and z if node x is an ancestor of node y and an ancestor of node z. Thus, nodes 8 and 4 are the common ancestors of nodes 16 and 7. A node x is called the nearest common ancestor of nodes y and z if x is a common ancestor of y and z and nearest to y and z among their common ancestors. Hence, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 16 and 7 is node 4. Node 4 is nearer to nodes 16 and 7 than node 8 is.
For other examples, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 2 and 3 is node 10, the nearest common ancestor of nodes 6 and 13 is node 8, and the nearest common ancestor of nodes 4 and 12 is node 4. In the last example, if y is an ancestor of z, then the nearest common ancestor of y and z is y.
Write a program that finds the nearest common ancestor of two distinct nodes in a tree.
Input
The input consists of T test cases. The number of test cases (T) is given in the first line of the input file. Each test case starts with a line containing an integer N , the number of nodes in a tree, 2<=N<=10,000. The nodes are labeled with integers 1, 2,…, N. Each of the next N -1 lines contains a pair of integers that represent an edge –the first integer is the parent node of the second integer. Note that a tree with N nodes has exactly N - 1 edges. The last line of each test case contains two distinct integers whose nearest common ancestor is to be computed.
Output
Print exactly one line for each test case. The line should contain the integer that is the nearest common ancestor.
Sample Input
2
16
1 14
8 5
10 16
5 9
4 6
8 4
4 10
1 13
6 15
10 11
6 7
10 2
16 3
8 1
16 12
16 7
5
2 3
3 4
3 1
1 5
3 5
Sample Output
4
3
题目大意
给出一个树,查询两个节点的最近公共祖先。
解题思路
1. 暴力
记节点i到根节点的深度为depth[i],如果节点u和v的共同祖先是w,那么从下向上u节点需走(depth[u]-depth[w])步,v节点需走(depth[v]-depth[w]步),这样就会到达节点w。因此我们可以先让节点u和节点v距离根节点更远的一方先走|depth[u]-depth[v]|步,然后两个节点再一起向上走,走到的第一个同一个节点即为最近公共祖先。
代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
#define ll long long
#define maxn 10007
bool r[maxn];
vector<int>edge[maxn];
int root ;
int parent[maxn];
int depth[maxn];
void dfs(int v,int p,int d)
{
parent[v]=p;
depth[v]=d;
for(int i=0;i<edge[v].size();i++)
if(edge[v][i]!=p)
dfs(edge[v][i],v,d+1);
}
void init()
{
dfs(root,-1,0);
}
int lca(int u,int v)
{
while(depth[u]>depth[v]) u=parent[u];
while(depth[v]>depth[u]) v=parent[v];
while(u!=v)
{
u=parent[u];
v=parent[v];
}
return u;
}
int main()
{
int T,V;
int a,b;
int s,t;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
for(int i=0;i<maxn;i++)
edge[i].clear();
memset(r,0,sizeof(r));
scanf("%d",&V);
for(int i=0;i<V-1;i++)
{
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
r[b]=1;
edge[a].push_back(b);
}
for(int i=1;i<=V;i++)
if(!r[i]) root=i;
scanf("%d %d",&s,&t);
init();
printf("%d\n",lca(s,t));
}
return 0;
}
2. 基于暴力的二分搜索
预处理出parent[k][v]标记每次向上走
2k
步到达的顶点,不再一步一步的向上走。实现优化。
代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 10007
#define MAX_LOG_V 50
vector<int> edge[maxn];
int root;
bool r[maxn];
int parent[MAX_LOG_V][maxn];
int depth[maxn];
void dfs(int v,int p,int d)
{
parent[0][v]=p;
depth[v]=d;
for(int i=0;i<edge[v].size();i++)
if(edge[v][i]!=p)
dfs(edge[v][i],v,d+1);
}
void init(int V)
{
dfs(root,-1,0);
for(int k=0;k+1<MAX_LOG_V;k++)
{
for(int v=1;v<=V;v++)
{
if(parent[k][v]<0) parent[k+1][v]=-1;
else parent[k+1][v]=parent[k][parent[k][v]];
}
}
}
int lca(int u,int v)
{
if(depth[u]>depth[v]) swap(u,v);
for(int k=0;k<MAX_LOG_V;k++)
{
if((depth[v]-depth[u])>>k&1)
v=parent[k][v];
}
if(u==v) return u;
for(int k=MAX_LOG_V-1;k>=0;k--)
{
if(parent[k][u]!=parent[k][v])
{
u=parent[k][u];
v=parent[k][v];
}
}
return parent[0][u];
}
int main()
{
int T,V;
int a,b;
int s,t;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
for(int i=0;i<maxn;i++)
edge[i].clear();
memset(r,0,sizeof(r));
scanf("%d",&V);
for(int i=0;i<V-1;i++)
{
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
r[b]=1;
edge[a].push_back(b);
}
for(int i=1;i<=V;i++)
if(!r[i]) root=i;
init(V);
scanf("%d %d",&s,&t);
printf("%d\n",lca(s,t));
}
return 0;
}
3. 基于RMQ进行实现
参考《挑战程序设计竞赛》P330 很形象
代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<cstdio>
#include<vector>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define maxn 10007
vector<int>edge[maxn];
int root,k;
int vs[maxn*2-1];
int dp[maxn*2][20];
int depth[maxn*2-1];
int id[maxn];
bool r[maxn];
void rmq_init()
{
for(int i=0; i<k+1; i++)
{
dp[i][0]=i;
}
for(int j=1; (1<<j)<=k; j++)
for(int i=0; i+(1<<j)<=k; i++)
{
dp[i][j]=depth[dp[i][j-1]]<depth[dp[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1]]?dp[i][j-1]:dp[i+(1<<(j-1))][j-1];
}
}
int query(int L,int R)
{
int k=0;
while((1<<(k+1))<=R-L+1) k++;
return depth[dp[L][k]]<depth[dp[R-(1<<k)+1][k]]?dp[L][k]:dp[R-(1<<k)+1][k];
}
void dfs(int v,int p,int d)
{
id[v]=k;
vs[k]=v;
depth[k++]=d;
for(int i=0; i<edge[v].size(); i++)
if(edge[v][i]!=p)
{
dfs(edge[v][i],v,d+1);
vs[k]=v;
depth[k++]=d;
}
}
void init(int V)
{
k=0;
dfs(root,-1,0);
rmq_init();
}
int lca(int u,int v)
{
return vs[query(min(id[u],id[v]),max(id[u],id[v]))];
}
int main()
{
int T,V;
int a,b;
int s,t;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
for(int i=0; i<maxn; i++)
edge[i].clear();
memset(r,0,sizeof(r));
memset(vs,0,sizeof(vs));
memset(depth,0,sizeof(depth));
memset(dp,0,sizeof(dp));
scanf("%d",&V);
for(int i=0; i<V-1; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d",&a,&b);
r[b]=1;
edge[a].push_back(b);
}
for(int i=1; i<=V; i++)
if(!r[i])
{
root=i;
break;
}
init(V);
scanf("%d %d",&s,&t);
printf("%d\n",lca(s,t));
}
return 0;
}
4. Tarjan 算法
算法详解传送门
代码实现
#include<iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cmath>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=10001;
int root;
int r[maxn];
int pre[maxn];
bool vis[maxn];
vector<int> edge[maxn],q[maxn];
int parent[maxn];
int find_pre(int x)
{
int r=pre[x];
while(pre[r]!=r)
r=pre[r];
int i=x,j;
while(i!=r)
{
j=pre[i];
pre[i]=r;
i=j;
}
return r;
}
void join(int x,int y)
{
int fx,fy;
fx=find_pre(x);
fy=find_pre(y);
if(fx!=fy)
pre[fx]=fy;
}
void lca(int u)
{
parent[u]=u;
for(int i=0; i<edge[u].size(); i++)
{
lca(edge[u][i]);
join(u,edge[u][i]);
parent[find_pre(u)]=u;
}
vis[u]=true;
for(int i=0; i<q[u].size(); i++)
if(vis[q[u][i]])
{
printf("%d\n",parent[find_pre(q[u][i])]);
return ;
}
}
int main()
{
int T,V;
int s,t;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d",&V);
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
memset(r,0,sizeof(r));
memset(parent,0,sizeof(parent));
for(int i=1; i<=V; i++)
{
pre[i]=i;
edge[i].clear();
q[i].clear();
}
for(int i=1; i<V; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d",&s,&t);
edge[s].push_back(t);
r[t]=1;
}
for(int i=1; i<=V; i++)
if(!r[i])
{
root=i;
break;
}
scanf("%d %d",&s,&t);
q[s].push_back(t);
q[t].push_back(s);
lca(root);
}
return 0;
}



























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








