在生存分析中,Cox 比例风险回归模型(Cox Proportional Hazards Model)是一种常用的统计方法,可用于评估多个变量对生存时间的影响。




本篇博客将介绍如何使用 MATLAB 构造模拟生存数据,并应用 Cox 模型进行分析,包括:
- 生成模拟数据(基于肺癌数据集格式)
- 处理缺失值
- 拟合 Cox 回归模型
- 计算风险评分并进行分组
- 使用 Kaplan-Meier 估计绘制生存曲线
- 进行 Log-Rank 检验
1. 生成模拟生存数据
首先,我们创建一个模拟数据集,包括生存时间(time)、生存状态(status)、年龄(age)以及 ph.ecog 评分(反映患者体能状况)。
数据示例(删除缺失值后的 cleanData):
| time | status | age | ph_ecog |
|---|---|---|---|
| 315.2 | 1 | 65 | 2 |
| 278.4 | 0 | 52 | 1 |
| 322.7 | 1 | 74 | 3 |
2. Cox 回归模型
Cox 模型用于评估 age 和 ph.ecog 对生存时间的影响。 在 MATLAB 中,使用 coxphfit 函数进行拟合。
3. 计算风险评分并分组
Cox 模型的线性预测值(风险评分)计算。
示例数据:
| time | status | age | ph_ecog | risk_score | risk_group |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 315.2 | 1 | 65 | 2 | 0.62 | middle |
| 278.4 | 0 | 52 | 1 | 0.21 | low |
| 322.7 | 1 | 74 | 3 | 1.32 | high |
4. Kaplan-Meier 生存曲线
我们使用 kmplot 自定义函数绘制 Kaplan-Meier 生存曲线,观察不同风险组的生存情况。
figure;
hold on;
groups = categories(cleanData.risk_group);
colors = [0.9 0.5 0; 0.4 0.6 0.2; 0 0.4 0.8]; % 橙、绿、蓝
for i = 1:length(groups)
idx = (cleanData.risk_group == groups{i});
kmplot(time(idx), status(idx),...
'Color', colors(i,:), 'LineWidth', 2, 'DisplayName', groups{i});
end
title('生存分析:低、中、高风险组');
xlabel('时间'); ylabel('生存概率');
legend('Location', 'best'); grid on;
hold off;
kmplot 函数
function [S, T] = kmplot(time, status, varargin)
% 计算生存函数
[S, T] = ecdf(time, 'censoring', ~status, 'function', 'survivor');
% 解析绘图参数
p = inputParser;
addParameter(p, 'Color', [0 0.447 0.741], @isnumeric);
addParameter(p, 'LineWidth', 1.5, @isnumeric);
addParameter(p, 'DisplayName', 'Group', @ischar);
parse(p, varargin{:});
% 绘制阶梯图
stairs(T, S, 'Color', p.Results.Color,...
'LineWidth', p.Results.LineWidth,...
'DisplayName', p.Results.DisplayName);
end
5. Log-Rank 检验
为了检验不同风险组的生存率是否存在显著差异,我们使用 Log-Rank 检验。
6. 结果解读
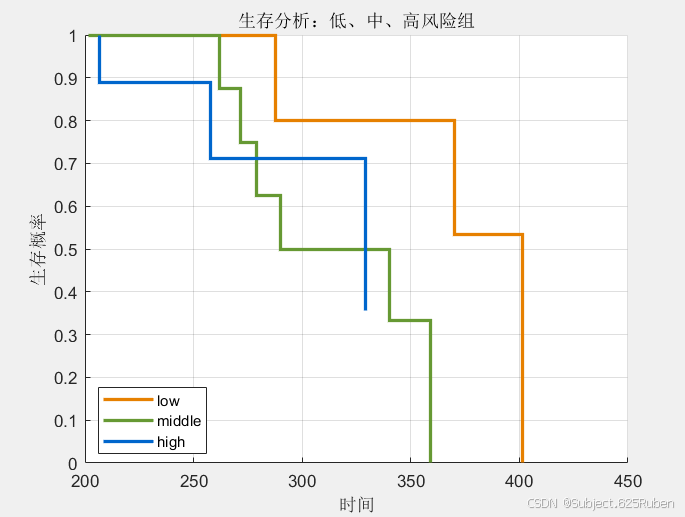
- Cox 模型分析:发现
age和ph.ecog影响生存率,且ph.ecog更显著。 - 生存曲线:风险评分高的患者生存率较低。
- Log-Rank 检验:若 p 值 < 0.05,说明不同风险组之间生存差异显著。
完整代码:
% 生成示例数据(30条记录,格式与lung数据集一致)
rng(1); % 固定随机种子保证可重复性
% 明确创建列向量 (关键步骤)
time_col = abs(randn(30,1)*50 + 300); % 确保时间为正数
status_col = randi([0 1],30,1); % 状态(0=删失,1=事件)
age_col = randi([40,80],30,1); % 年龄(40-80岁)
ph_ecog_col = randi([0,3],30,1); % ph.ecog评分(0-3)
% 水平拼接为矩阵(30行×4列)
dataMatrix = [time_col, status_col, age_col, ph_ecog_col];
% 转换为表格并指定列名
sampleData = array2table(dataMatrix, 'VariableNames', {'time','status','age','ph_ecog'});
% 添加缺失值(模拟真实数据场景)
sampleData.ph_ecog(randi(30,2,1)) = NaN;
sampleData.age(randi(30,1,1)) = NaN;
% 删除缺失值
cleanData = rmmissing(sampleData);
% 提取协变量矩阵和时间-状态数据
X = [cleanData.age, cleanData.ph_ecog];
time = cleanData.time;
status = cleanData.status;
% ========== 关键修复部分 ==========
% 正确指定时间和删失参数
% 语法:coxphfit(X, Time, 'Censoring', Censoring)
[beta, ~, stats] = coxphfit(X, time,...
'Censoring', ~status); % ~status将1(事件)转为0,0(删失)转为1
% 显示模型系数与p值(正确字段为stats.coeff)
fprintf('Cox模型系数:\n');
disp('stats 变量类型:');
disp(class(stats)); % 显示 stats 的数据类型
disp('stats 变量内容:');
disp(stats); % 显示 stats 具体结构
% ================================
% 计算风险评分(线性预测值)
cleanData.risk_score = X * beta;
% 按三分位数分组
quantiles = quantile(cleanData.risk_score, [0, 0.33, 0.66, 1]);
cleanData.risk_group = discretize(cleanData.risk_score, quantiles,...
'categorical', {'low', 'middle', 'high'});
% 绘制生存曲线(需kmplot.m)
figure;
hold on;
groups = categories(cleanData.risk_group);
colors = [0.9 0.5 0; 0.4 0.6 0.2; 0 0.4 0.8]; % 橙、绿、蓝
for i = 1:length(groups)
idx = (cleanData.risk_group == groups{i});
kmplot(time(idx), status(idx),...
'Color', colors(i,:), 'LineWidth', 2, 'DisplayName', groups{i});
end
title('生存分析:低、中、高风险组');
xlabel('时间'); ylabel('生存概率');
legend('Location', 'best'); grid on;
hold off;
% 自定义颜色和参数设置
groupNames = categories(cleanData.risk_group);
colors = [0.9 0.5 0; 0.4 0.6 0.2; 0 0.4 0.8]; % 橙、绿、蓝
confIntAlpha = 0.2; % 置信区间透明度
% ============== 自定义Log-Rank检验函数 ==============
function p = logrank_pvalue(data)
% 改进版Log-Rank检验p值计算
groups = categories(data.risk_group);
if length(groups) < 2
p = NaN;
return;
end
% 提取时间和状态
time = data.time;
status = data.status;
group = data.risk_group;
% 方法1: 优先使用lifetest函数 (需Statistics Toolbox)
try
[~,p] = lifetest(time, group, 'Censoring', ~status, 'Display','off');
% 方法2: 若方法1不可用,使用Cox模型近似
catch
% 将分组变量转换为数值 (例如: low=0, middle=1, high=2)
group_num = double(ordinal(group, {}, categories(group)));
% 拟合Cox模型
[~, ~, stats] = coxphfit(group_num, time, 'Censoring', ~status);
% 正确提取p值 (字段名为p而非coeff)
p = stats.p(1);
end
end
function [S, T] = kmplot(time, status, varargin)
% 简化版Kaplan-Meier曲线绘制函数
% 输入:
% time: 生存时间向量
% status: 事件指示(1=事件,0=删失)
% 可选参数:
% 'Color', 'LineWidth', 'DisplayName' 等绘图属性
% 计算生存函数
[S, T] = ecdf(time, 'censoring', ~status, 'function', 'survivor');
% 解析绘图属性
p = inputParser;
addParameter(p, 'Color', [0 0.447 0.741], @isnumeric);
addParameter(p, 'LineWidth', 1.5, @isnumeric);
addParameter(p, 'DisplayName', 'Group', @ischar);
parse(p, varargin{:});
% 绘制阶梯图
stairs(T, S, 'Color', p.Results.Color,...
'LineWidth', p.Results.LineWidth,...
'DisplayName', p.Results.DisplayName);
end




















 371
371

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








