上一篇博客中主要介绍了EJB的基本分类,这一篇中总结一下会话EJB中无状态会话Bean和有状态会话Bean的对比。
无状态会话Bean不会受到EJB容器进行管理,也就是对象只创建一次,每次会话都调用这个对象。
有状态会话Bean能够为同义客户端在多次请求直接保存状态信息,EJB容器可以区分不同的客户端,并为不同的客户端保持与其对应的状态信息。也就是每次客户访问都会创建一个新的对象。
无状态会话Bean
接口
<span style="font-family:KaiTi_GB2312;font-size:18px;">package com.roy.ejb;
public interface StateLessEjb {
public void compute(int i);
public int getResult();
}
</span><span style="font-family:KaiTi_GB2312;font-size:18px;">package com.roy.ejb;
import javax.ejb.Remote;
import javax.ejb.Stateless;
@Stateless
@Remote
public class StatelessEjbBean implements StateLessEjb {
private int state;
public void compute(int i) {
state=state+i;
}
public int getResult() {
return state;
}
}
</span>客户端
<span style="font-family:KaiTi_GB2312;font-size:18px;">package com.roy.ejb;
import javax.ejb.EJB;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
public class StateLessClient {
public static void main(String[] arg) throws Exception{
InitialContext ctx=new InitialContext();
//第一次回话
StateLessEjb ejb =(StateLessEjb)ctx.lookup("StatelessEjbBean/remote");
System.out.println(ejb.getResult());
ejb.compute(1);
System.out.println(ejb.getResult());
ejb.compute(1);
System.out.println(ejb.getResult());
ejb.compute(1);
System.out.println(ejb.getResult());
//第二次回话
StateLessEjb ejb2=(StateLessEjb)ctx.lookup("StatelessEjbBean/remote");
ejb2.compute(1);
System.out.println(ejb2.getResult());
ejb2.compute(1);
System.out.println(ejb2.getResult());
ejb2.compute(1);
System.out.println(ejb2.getResult());
}
}
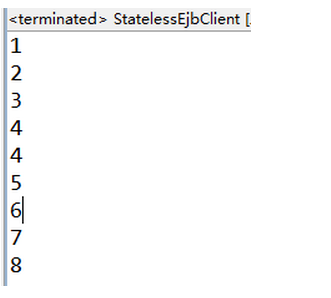
</span>执行状态结果
有状态会话Bean
接口
<span style="font-family:KaiTi_GB2312;font-size:18px;">package com.roy.ejb;
public interface StatefullEjb {
public void compute(int i);
public int getResult();
}</span>实现
<span style="font-family:KaiTi_GB2312;font-size:18px;">package com.roy.ejb;
import javax.ejb.Remote;
import javax.ejb.Stateful;
@Stateful
@Remote
public class StatefullEjbBean implements StatefullEjb {
private int state;
public void compute(int i) {
state=state+i;
}
public int getResult() {
return state;
}
}
</span><span style="font-family:KaiTi_GB2312;font-size:18px;">package com.roy.ejb;
import javax.naming.InitialContext;
import javax.naming.NamingException;
/**
* 有状态的回话BEAN,每次调用服务器都会创建一个实例
* @author yiqing
*
*/
public class StatefullEjbClient {
/**
* @param args
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
InitialContext ctx=new InitialContext();
//第一次回话
StatefullEjb ejb=(StatefullEjb)ctx.lookup("StatefullEjbBean/remote");
System.out.println(ejb.getResult());
ejb.compute(1);
System.out.println(ejb.getResult());
ejb.compute(1);
System.out.println(ejb.getResult());
ejb.compute(1);
System.out.println(ejb.getResult());
//第二次回话
StatefullEjb ejb2=(StatefullEjb)ctx.lookup("StatefullEjbBean/remote");
System.out.println(ejb2.getResult());
ejb2.compute(1);
System.out.println(ejb2.getResult());
ejb2.compute(1);
System.out.println(ejb2.getResult());
ejb2.compute(1);
System.out.println(ejb2.getResult());
} catch (NamingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
</span>执行结果
总结:
有状态会话Bean :每个用户有自己特有的一个实例,Bean随着用户的生命周期一起开启或结束。
无状态会话Bean :只要Bean的生命周期一直存在,无论什么用户调用都只是调用一个Bean。类似于单例模式。























 556
556

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








