给定一个整数数组 A,坡是元组 (i, j),其中 i < j 且 A[i] <= A[j]。这样的坡的宽度为 j - i。
找出 A 中的坡的最大宽度,如果不存在,返回 0 。
双关键字排序
用单调栈维护下标和ans这两个值
建立一个p的单调栈,值+下标双关键字排序
如果值相等就按照下标降序
如果值不相等就按照再nums数组里的大小顺序排序
因为当j如果定下来的话,那么nums上小于nums【p[j]】的在
p数组上位于左边,也就是说j确定了的话,答案i只能在j的左边找
然后求答案的时候从左到右遍历,
class Solution {
public:
int maxWidthRamp(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int>p(nums.size());
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)p[i]=i;
sort(p.begin(),p.end(),[&](int a,int b){
if(nums[a]!=nums[b])return nums[a]<nums[b];
else return a<b;
});
int ans=0;
for(int j=0,i=p[0];j<nums.size();j++){
ans=max(ans , p[j]-i);
i=min(i,p[j]);
}
return ans;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
double get_dist(double x1,double y1,double x2,double y2){
return sqrt((x1-x2)*(x1-x2)+(y1-y2)*(y1-y2));
}
double minAreaFreeRect(vector<vector<int>>& points) {
vector<vector<double>>q;
for(int i=0;i<points.size();i++){
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
double cx=(points[i][0]+points[j][0]);
double cy=(points[i][1]+points[j][1]);
double d=get_dist(points[i][0],points[i][1],points[j][0],points[j][1]);
q.push_back({cx,cy,d,double(i),double(j)});
}
}
sort(q.begin(),q.end());
double ans=1e15;
for(int i=0;i<q.size();i++){
int j=i+1;
while(j<q.size()&&q[i][0]==q[j][0]&&q[i][1]==q[j][1]&&q[i][2]==q[j][2])j++;
//i到j-1这段区间都是中点相等,对角线相等的一对点
//现在要两两取值求答案
for(int a=i;a<j;a++){
double x1=points[q[a][3]][0];
double y1=points[q[a][3]][1];
for(int b=i;b<a;b++){
double x2=points[q[b][3]][0];
double y2=points[q[b][3]][1];
double x3=points[q[b][4]][0];
double y3=points[q[b][4]][1];
double t=get_dist(x1,y1,x2,y2)*get_dist(x1,y1,x3,y3);
ans=min(ans,t);
}
}
i=j-1;
}
if(ans==1e15)ans=0;
return ans;
}
};
给定一个列表 accounts,每个元素 accounts[i] 是一个字符串列表,其中第一个元素 accounts[i][0] 是 名称 (name),其余元素是 emails 表示该账户的邮箱地址。
现在,我们想合并这些账户。如果两个账户都有一些共同的邮箱地址,则两个账户必定属于同一个人。请注意,即使两个账户具有相同的名称,它们也可能属于不同的人,因为人们可能具有相同的名称。一个人最初可以拥有任意数量的账户,但其所有账户都具有相同的名称。
合并账户后,按以下格式返回账户:每个账户的第一个元素是名称,其余元素是 按字符 ASCII 顺序排列 的邮箱地址。账户本身可以以 任意顺序 返回。
来源:力扣(LeetCode)
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/accounts-merge
著作权归领扣网络所有。商业转载请联系官方授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int>p;
int find(int x){
if(p[x]==x)return x;
return p[x]=find(p[x]);
}
vector<vector<string>> accountsMerge(vector<vector<string>>& accounts) {
int n=accounts.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)p.push_back(i);
unordered_map<string,vector<int>>hash;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<accounts[i].size();j++){
hash[accounts[i][j]].push_back(i);
}
}
for(auto& [k,v] : hash){
for(int i=1;i<v.size();i++){
p[find(v[i])]=p[find(v[0])];
}
}
vector<set<string>>res(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<accounts[i].size();j++){
res[find(i)].insert(accounts[i][j]);
}
}
vector<vector<string>>ans;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(res[i].size()){
vector<string>t;
t.push_back(accounts[i][0]);
for(auto s:res[i])t.push_back(s);
ans.push_back(t);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
给定一棵二叉树,你需要计算它的直径长度。一棵二叉树的直径长度是任意两个结点路径长度中的最大值。这条路径可能穿过也可能不穿过根结点。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int ans=0;
int dfs(TreeNode* root){
if(!root)return 0;
int L=dfs(root->left);
int R=dfs(root->right);
ans=max(ans,L+R);
return max(L,R)+1;
}
int diameterOfBinaryTree(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
};
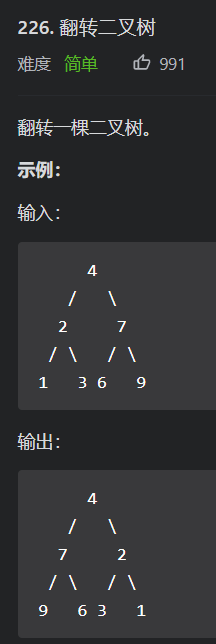
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* invertTree(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)return 0;
swap(root->left , root->right);
invertTree(root->left);
invertTree(root->right);
return root;
}
};

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode* root) {
if(!root)return true;
return dfs(root->left,root->right);
//解决这道题需要两个参数
}
bool dfs(TreeNode* p,TreeNode* q){
if(!p&&!q)return 1;//左右两边都是空的
else if(!p||!q||p->val!=q->val)return 0;
//一边是空的另一边非空或者val不相等返回false
return dfs(p->left,q->right) & dfs(q->left, p->right);
//左子树的左等于右子树的右
//右子树的左等于左子树的右
//取&符号
//很简单,但是很精妙,要好好揣摩消化吸收
}
};

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
bool flipEquiv(TreeNode* root1, TreeNode* root2) {
if(!root1&&!root2)return 1;
else if(!root1||!root2||root1->val!=root2->val)return 0;
return flipEquiv(root1->left, root2->left)&&flipEquiv(root1->right, root2->right) || flipEquiv(root1->left, root2->right)&&flipEquiv(root1->right, root2->left);
}
};

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
int ans=-0x3f3f3f3f;
int maxPathSum(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root);
return ans;
}
int dfs(TreeNode* u){
if(!u)return 0;
int l=max(0,dfs(u->left));
int r=max(0,dfs(u->right));
ans=max(ans,l+ u->val +r);
return u->val+max(l,r);
}
};

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* ans=0;
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
dfs(root,p,q);
return ans;
}
int dfs(TreeNode* root,TreeNode* p,TreeNode* q){
if(!root)return 0;
int state=dfs(root->left,p,q);
if(root==p)state|=1;
else if(root==q)state|=2;
state|=dfs(root->right,p,q);
if(state==3&&!ans)ans=root;
return state;
}
};

DP 时间O(n),空间 O(1)O(1)
class Solution {
public:
int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {
int res = INT_MIN;
for (int i = 0, last = 0; i < nums.size(); i ++ ) {
last = nums[i] + max(last, 0);
res = max(res, last);
}
return res;
}
};
分治 时间O(n),空间O(logn)
class Solution {
public:
struct Node {
int sum, s, ls, rs;
};
Node build(vector<int>& nums, int l, int r) {
if (l == r) {
int v = max(nums[l], 0);
return {nums[l], v, v, v};
}
int mid = l + r >> 1;
auto L = build(nums, l, mid), R = build(nums, mid + 1, r);
Node res;
res.sum = L.sum + R.sum;
res.s = max(max(L.s, R.s), L.rs + R.ls);
res.ls = max(L.ls, L.sum + R.ls);
res.rs = max(R.rs, R.sum + L.rs);
return res;
}
int maxSubArray(vector<int>& nums) {
int res = INT_MIN;
for (auto x: nums) res = max(res, x);
if (res < 0) return res;
auto t = build(nums, 0, nums.size() - 1);
return t.s;
}
};
作者:yxc
链接:https://www.acwing.com/activity/content/code/content/362176/
来源:AcWing
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<int,int>hash;
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
int n=preorder.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)hash[inorder[i]]=i;
return build(preorder,inorder,0,n-1,0,n-1);
}
TreeNode* build(vector<int>&preorder,vector<int>&inorder,int pl,int pr,int il,int ir){
if(pl>pr)return NULL;
auto root=new TreeNode(preorder[pl]);
int k=hash[root->val];
root->left=build(preorder,inorder,pl+1,k-il+pl,il,k-1);
root->right=build(preorder,inorder,k-il+pl+1,pr,k+1,ir);
return root;
}
};

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<int,int>hash;
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
int n=inorder.size();
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)hash[inorder[i]]=i;
return build(inorder,postorder,0,n-1,0,n-1);
}
TreeNode* build(vector<int>&inorder , vector<int>&postorder,int il,int ir,int pl,int pr){
if(pl>pr)return nullptr;
auto root=new TreeNode(postorder[pr]);
int k=hash[root->val];
root->left=build(inorder,postorder,il,k-1,pl,pl+k-1-il);
root->right=build(inorder,postorder,k+1,ir,pr-ir+k,pr-1);
return root;
}
};

/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode() : val(0), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(nullptr), right(nullptr) {}
* TreeNode(int x, TreeNode *left, TreeNode *right) : val(x), left(left), right(right) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
typedef pair<int,int>PII;
public:
//我要写一个cmp排序函数,使得vector按照
//双关键字排序【x,val】
map<int,vector<int>>hash;
unordered_map<int,int>depth;
void dfs(TreeNode* root,int x,int y){
if(!root)return;
depth[root->val]=x;
hash[y].push_back(root->val);
dfs(root->left,x+1,y-1);
dfs(root->right,x+1,y+1);
}
vector<vector<int>> verticalTraversal(TreeNode* root) {
dfs(root,0,0);
vector<vector<int>>ans;
for(auto& [k,v] :hash){
sort(v.begin(),v.end(),[&](int x,int y){
if(depth[x]==depth[y])return x<y;
return depth[x]<depth[y];
});
ans.push_back(v);
}
return ans;
}
};

class Solution {
public:
bool dfs(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* subRoot){
if(!root&&!subRoot)return 1;
else if(!root||!subRoot||root->val!=subRoot->val)return 0;
return dfs(root->left,subRoot->left)&dfs(root->right,subRoot->right);
}
bool isSubtree(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* subRoot) {
if(!root&&subRoot)return 0;
if(!root&&!subRoot)return 1;
//else if(!root||!subRoot||root->val!=subRoot->val)return 0;
//else if(root->val==subRoot->val)return dfs(root->left,subRoot->left)&dfs(root->right,subRoot->right);
return isSubtree(root->left, subRoot)||isSubtree(root->right, subRoot)||dfs(root,subRoot);
}
};
作者:我已经不想再做刺客了
链接:https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/67081/
来源:AcWing
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
这里介绍第二种做法:树上哈希
每棵树的哈希值等于根的val+左子树×质数P+右子树×质数Q
有2个注意事项
1.P和Q不要取太大,P=131,Q=13,mod=1e7+7就好这样就不会溢出
如果设置Q=133331,mod=1e9+7的话就会溢出int的范围
2.如果子树为空,不要返回0,随便发挥一个数字12345就好了
因为返回0的话可能与存在子树val=0的情形相冲突
class Solution {
public:
const int P=131,Q=13,mod=1e7+7;
bool ans=0;
int t=-1;//一开始设置为负数是为了让t等于子树的哈希值
int dfs(TreeNode* root){
if(!root)return 123;
int L=dfs(root->left);
int R=dfs(root->right);
if(t==L||t==R)ans=1;
return ((root->val + L*P %mod + R*Q %mod) %mod+mod)%mod;
}
bool isSubtree(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* subRoot) {
t=dfs(subRoot);
if(t==dfs(root))ans=1;
return ans;
}
};
输入:root = [3,5,1,6,2,0,8,null,null,7,4], target = 5, K = 2
输出:[7,4,1]
解释:
所求结点为与目标结点(值为 5)距离为 2 的结点,
值分别为 7,4,以及 1
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<TreeNode*,vector<TreeNode*>>mp;
vector<int>ans;
void dfs1(TreeNode* root){
if(!root)return;
if(root->left)
mp[root].push_back(root->left),
mp[root->left].push_back(root),
dfs1(root->left);
if(root->right)
mp[root].push_back(root->right),
mp[root->right].push_back(root),
dfs1(root->right);
}
void dfs2(TreeNode* root,TreeNode*father, int k){
if(k==0)ans.push_back(root->val);
else{
for(auto son:mp[root]){
if(son!=father)dfs2(son,root,k-1);
}
}
}
vector<int> distanceK(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* target, int k) {
dfs1(root);
dfs2(target,NULL,k);
return ans;
}
};
上面建的哈希表是指针
下面建的哈希表是节点的值
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int>ans;
unordered_map<int,vector<int>>g;
void dfs1(TreeNode* root){
if(!root)return;
int u=root->val;
if(root->left){
int L=root->left->val;
g[u].push_back(L);
g[L].push_back(u);
dfs1(root->left);
}
if(root->right){
int R=root->right->val;
g[u].push_back(R);
g[R].push_back(u);
dfs1(root->right);
}
}
void dfs2(int u,int fa,int k){
if(k==0)ans.push_back(u);
else{
for(auto t:g[u]){
if(t!=fa)dfs2(t,u,k-1);
}
}
}
vector<int> distanceK(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* target, int k) {
dfs1(root);//建邻接表g
dfs2(target->val,-1,k);
return ans;
}
};
题目描述
给定两个数组,请写一个函数计算它们的交集。
注意:
每个数在结果中出现的次数,需要和它在两个数组中出现的次数相同;
结果可以以任意顺序输出;
思考题:
如果给定的数组已经排好序,你可以怎样优化你的算法?
如果数组nums1的长度小于数组nums2的长度,哪种算法更好?
如果数组nums2存储在硬盘上,然而内存是有限的,你不能将整个数组都读入内存,该怎么做?
样例
给定 nums1 = [1, 2, 2, 1], nums2 = [2, 2],
返回 [2, 2].
算法
(哈希表) O(n+m)O(n+m)
首先先将nums1存入哈希表中,注意这里要用unordered_multiset,而不是unordered_set,因为数组中含有重复元素。
然后遍历nums2,对于每个数 xx,如果 xx 出现在哈希表中,则将 xx 输出,且从哈希表中删除一个 xx。
时间复杂度分析:假设两个数组的长度分别是 n,mn,m。将nums1存入哈希表的计算量是 O(n)O(n),遍历nums2的计算量是 O(m)O(m),所以总时间复杂度是 O(n+m)O(n+m)。
思考题:
如果给定的数组已经排好序,你可以怎样优化你的算法?
答:可以用双指针扫描。这样可以把空间复杂度降为 O(1)O(1),但时间复杂度还是 O(n)O(n);
如果数组nums1的长度小于数组nums2的长度,哪种算法更好?、
答:可以把nums1存入哈希表,然后遍历nums2。这样可以使用更少的内存,但时空复杂度仍是 O(n)O(n);
如果数组nums2存储在硬盘上,然而内存是有限的,你不能将整个数组都读入内存,该怎么做?
答:如果nums1可以存入内存,则可以将nums1存入哈希表,然后分块将nums2读入内存,进行查找;如果两个数组都不能存入内存,可以先将两个数组分别排序,比如可以用外排序,然后用类似于双指针扫描的方法,将两个数组分块读入内存,进行查找。
C++ 代码
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> intersect(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
unordered_multiset<int> S;
vector<int> res;
for (int x : nums1) S.insert(x);
for (int x : nums2)
if (S.count(x))
{
res.push_back(x);
S.erase(S.find(x));
}
return res;
}
};
作者:yxc
链接:https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/372/
来源:AcWing
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<int,int>mp;
vector<int> intersect(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
vector<int>ans;
for(auto c:nums1)mp[c]++;
for(auto c:nums2){
if(mp[c]){
ans.push_back(c);
mp[c]--;
}
}
return ans;
}
};
作者:我已经不想再做刺客了
链接:https://www.acwing.com/solution/content/67123/
来源:AcWing
著作权归作者所有。商业转载请联系作者获得授权,非商业转载请注明出处。

class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<string>> groupAnagrams(vector<string>& strs) {
unordered_map<string,int>hash;
vector<vector<string>>ans;
int idx=0;
for(auto str:strs){
string s=str;
sort(s.begin(),s.end());
if(!hash.count(s)){
hash[s]=idx++;
ans.push_back({str});
}
else ans[hash[s]].push_back(str);
}
return ans;
}
};

class RandomizedSet {
public:
unordered_map<int,int>hash;
vector<int>nums;
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
RandomizedSet() {
}
/** Inserts a value to the set. Returns true if the set did not already contain the specified element. */
bool insert(int val) {
if(!hash.count(val)){
nums.push_back(val);
hash[val]=nums.size()-1;
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
/** Removes a value from the set. Returns true if the set contained the specified element. */
bool remove(int val) {
if(hash.count(val)){
int x=val;
int y=nums.back();
int px=hash[x];
int py=hash[y];
swap(hash[x],hash[y]);
swap(nums[px],nums[py]);
hash.erase(x);
nums.pop_back();
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
/** Get a random element from the set. */
int getRandom() {
return nums[rand()%nums.size()];
}
};
/**
* Your RandomizedSet object will be instantiated and called as such:
* RandomizedSet* obj = new RandomizedSet();
* bool param_1 = obj->insert(val);
* bool param_2 = obj->remove(val);
* int param_3 = obj->getRandom();
*/

哈希表写法
class Solution {
public:
int longestConsecutive(vector<int>& nums) {
unordered_set<int>S;
int ans=0;
for(auto x:nums)S.insert(x);
for(auto x:nums){
if(S.count(x)&&!S.count(x-1)){//这是一个起点,到达dp入口
int y=x+1;
S.erase(x);
while(S.count(y))S.erase(y),y++;
ans=max(ans,y-x);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
并查集写法
class Solution {
public:
unordered_map<int,int> a,b;
int find(int x){
return a.count(x)?a[x]=find(a[x]):x;
}
int longestConsecutive(vector<int>& nums) {
for(auto i:nums)
a[i]=i+1;
int ans=0;
for(auto i:nums){
int y=find(i+1);
ans=max(ans,y-i);
}
return ans;
}
};
class LRUCache {
public:
struct node{
int key,val;
node *left,*right;
node(int key_,int val_):key(key_),val(val_),left(NULL),right(NULL){}
}*L,*R;
unordered_map<int,node*>hash;
int n;
void remove(node *p){
p->left->right=p->right;
p->right->left=p->left;
}
void insert(node *p){
p->left=L;
p->right=L->right;
L->right->left=p;
L->right=p;
}
LRUCache(int capacity) {
n=capacity;
L=new node(0,0);
R=new node(0,0);
L->right=R;
R->left=L;
}
int get(int key) {
if(!hash.count(key))return -1;
auto p=hash[key];
remove(p);
insert(p);
return p->val;
}
void put(int key, int value) {
if(hash.count(key)){
auto p=hash[key];
p->val=value;
remove(p);
insert(p);
}
else{
if(hash.size()==n){
auto p=R->left;
remove(p);
hash.erase(p->key);
delete p;
}
auto p=new node(key,value);
insert(p);
hash[key]=p;
}
}
};
/**
* Your LRUCache object will be instantiated and called as such:
* LRUCache* obj = new LRUCache(capacity);
* int param_1 = obj->get(key);
* obj->put(key,value);
*/


class Solution {
public:
vector<int> largestDivisibleSubset(vector<int>& nums) {
int n=nums.size();
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
vector<int>f(n);
int k=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
for(int j=i-1;j>=0;j--){
if(nums[i]%nums[j]==0)
f[i]=max(f[i],f[j]+1);
}
if(f[k]<f[i])k=i;
}
vector<int>ans(1,nums[k]);
while(f[k]>0){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(nums[k]%nums[i]==0&&f[k]==f[i]+1){
ans.push_back(nums[i]);
k=i;
break;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
class Solution {
public List<Integer> largestDivisibleSubset(int[] nums) {
int n=nums.length;
if(n==0)return new ArrayList<>();
Arrays.sort(nums);
int[] f=new int[n];
Arrays.fill(f,1);
int k=0;
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
if(nums[i]%nums[j]==0)
f[i]=Math.max(f[i] , f[j]+1);
}
if(f[k]<f[i])k=i;
}
//for(int i=0;i<n;i++)System.out.println(f[i]);
List<Integer>ans=new ArrayList<>();
ans.add(nums[k]);
while(f[k]>1){
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(nums[k]%nums[i]==0&&f[k]==f[i]+1){
ans.add(nums[i]);
k=i;
break;
}
}
}
return ans;
}
}

class Solution {
public:
const int mod=1e9+7;
int numDecodings(string s) {
int n=s.length();
vector<int>f(n+1);
f[0]=1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=26;j++){
char a=s[i-1];
//f[i-1]部分
if(j<10){
if(a=='*'||a==j+'0')
f[i]+=f[i-1];
}
//f[i-2]部分
else if(i>=2){
char b=s[i-2];
int shi=j/10;
int ge=j%10;
if((b==shi+'0'||b=='*') &&(a==ge+'0'||a=='*'&&ge))
f[i]+=f[i-2];
}
f[i]%=mod;
}
}
return f[n];
}
};

class Solution {
public:
bool isMatch(string s, string p) {
int n=s.size();
int m=p.size();
s=' '+s;
p=' '+p;
vector<vector<bool>>f(n+1,vector<bool>(m+1));
f[0][0]=1;
//i从0开始就是针对s=”aa”,p=”a*”这样的条件,靠i=0时把f[0][2]设为true,使其符合题意。
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
if(j+1<=m&&p[j+1]=='*')continue;
if(p[j]!='*'&&i)
f[i][j]=f[i-1][j-1]&&(s[i]==p[j]||p[j]=='.');
else if(p[j]=='*')
f[i][j]=f[i][j-2]|| i&&f[i-1][j]&& (s[i]==p[j-1]||p[j-1]=='.');
}
}
return f[n][m];
}
};

class Solution {
public:
bool isMatch(string s, string p) {
int n=s.length();
int m=p.length();
s=' '+s;
p=' '+p;
vector<vector<bool>>f(n+1,vector<bool>(m+1));
f[0][0]=1;
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=m;j++){
if(p[j]!='*'&&i)f[i][j]=f[i-1][j-1]&&(s[i]==p[j]||p[j]=='?');
else if(p[j]=='*')
f[i][j]=f[i][j-1]||i&&f[i-1][j];
}
}
return f[n][m];
}
};

这道题很难
题解放这里
class Solution {
public:
int longestValidParentheses(string s) {
int n=s.length();
int ans=0;
stack<int>stk;
int start=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(s[i]=='(')stk.push(i);
else{
if(stk.empty())start=i+1;
else{
stk.pop();
if(stk.empty())ans=max(ans,i-start+1);
else ans=max(ans,i-stk.top());
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int longestValidParentheses(string s) {
int n=s.length();
int ans1=0;
int start=0;
int val=0;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(s[i]=='(')val++;
else val--;
if(val==0)ans1=max(ans1,i-start+1);
else if(val<0){
val=0;
start=i+1;
}
}
int ans2=0;
start=n-1,val=0;
for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--){
if(s[i]==')')val++;
else val--;
if(val==0)ans2=max(ans2,start-i+1);
else if(val<0){
val=0;
start=i-1;
}
}
return max(ans1,ans2);
}
};

class Solution {
public:
int lengthOfLIS(vector<int>& nums) {
vector<int>q;
for(auto x:nums){
if(q.empty()||x>q.back())q.push_back(x);
else{
if(x<=q[0])q[0]=x;
else *lower_bound(q.begin(),q.end(),x)=x;
}
}
return q.size();
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int maxEnvelopes(vector<vector<int>>& nums) {
int n=nums.size();
sort(nums.begin(),nums.end());
vector<int>q(n);
int ans=1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
q[i]=1;
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
if(nums[i][0]>nums[j][0] && nums[i][1]>nums[j][1]){
q[i]=max(q[i],q[j]+1);
ans=max(ans,q[i]);
}
}
}
return ans;
}
};

class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& a) {
int n=a.size();
int buy=1000000;
int mai=0;
for(auto x:a){
mai=max(mai,x-buy);
buy=min(buy,x);
}
return mai;
}
};

class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int>& a) {
int n=a.size();
vector<vector<int>>f(n,vector<int>(2));
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)f[i][0]=f[i][1]=-0x3f3f3f3f;
f[0][0]=0;
f[0][1]=-a[0];
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
f[i][0]=max(f[i-1][0] , f[i-1][1]+a[i]);
f[i][1]=max(f[i-1][1] , f[i-1][0]-a[i]);
}
return f[n-1][0];
}
};

class Solution {
public:
int f[100001][10][2];
int k=2;
int maxProfit(vector<int>& a) {
int n=a.size();
memset(f,-0x3f,sizeof f);
f[0][0][0]=0;
f[0][0][1]=-a[0];
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
for(int j=k;j>=0;j--){
if(j==0)f[i][j][0]=f[i-1][j][0];
else f[i][j][0]=max(f[i-1][j][0] , f[i-1][j-1][1]+a[i]);
f[i][j][1]=max(f[i-1][j][1] , f[i-1][j][0]-a[i]);
}
}
int ans=0;
for(int t=0;t<=k;t++)ans=max(ans , f[n-1][t][0]);
return ans;
}
};

这道题很精妙
class Solution {
public:
bool canJump(vector<int>& nums) {
int n=nums.size();
for(int i=0,j=0;i<n;i++){
if(i>j)return 0;
j=max(j,i+nums[i]);
}
return 1;
}
};
在代码中,j表示你在i的位置能挑到的最远位置
i是一个逐渐右移的指针,如果i>j也就是说i能追上j的话
那就失败,不能跳到这么远
则当i到第n个下标的时候,j从第n-1这个点能跳到的最远路径>i
return True

class Solution {
public:
int jump(vector<int>& nums) {
int n=nums.size();
vector<int>f(n);
for(int i=1,j=0;i<n;i++){
while(j+nums[j]<i)j++;
f[i]=f[j]+1;
}
return f[n-1];
}
};

class Solution {
public:
int minCut(string s) {
int n=s.length();
s=' '+s;
vector<vector<bool>>g(n+1,vector<bool>(n+1));
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
for(int i=1;i<=j;i++){
if(i==j)g[i][j]=1;
else if(s[i]==s[j]){
if(i+1>=j)g[i][j]=1;
else g[i][j]=g[i+1][j-1];
}
}
}
vector<int>f(n+1,1e9);
//f[i]表示将s[1~i]分成几部分
f[0]=0;
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
for(int i=1;i<=j;i++){
if(g[i][j])
f[j]=min(f[j],f[i-1]+1);
}
}
return f[n]-1;
}
};























 559
559











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








