本篇为在复习过程中发现应该掌握的java基础知识。
try-catch用来捕获异常(checked异常)。适用于:在某个类的方法中会抛出异常(这应该在spec中声明好)。那么当其父类或其他类调用这个方法时,就要预测这个方法在某种情况下会抛出这个异常。将它捕获并进行处理。
例子如下:
FileReader reader = null;
try {
// constructor may throw FileNotFoundException
reader = new FileReader("someFile");
int i=0;
while(i != -1){
//reader.read() may throw IOException
i = reader.read();
System.out.println((char) i);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}在调用对象reader的构造方法时、read()方法时,都可能会抛出checked异常。抛出异常会使程序终止,但这个异常是我们能预测到、并且可以规避的异常,所以我们不能任由他发生,而是使用try-catch将其捕获,并在catch后对其进行处理。
需要注意的是,try-catch并不是类似if-else的关系。
1.try和catch块内部的代码是相对独立的,也就是说在try中创建的对象、声明的变量的生命周期在try结束后也就随之结束了;
2.若在try中代码运行的过程中没有发生任何异常,那么catch中的代码就完全不会运行。
try-catch是捕获异常的过程,finally相当于是对它们两个的“收尾工作”。
int x;
try {
x = 1 / 0;
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("这里有个异常");
} finally {
System.out.println("没有异常,或异常被捕获");
}程序运行结果如下图:

我们修改try中的代码,规避掉这个异常:
int x;
try {
x = 312;
System.out.println("这里有个数字是312");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("这里有个异常");
} finally {
System.out.println("没有异常,或异常被捕获");
}代码运行结果:

综上,try-catch运行结束之后,不管是否捕获到异常,总要执行finally中的程序。
但在try-catch-finally中存在return语句时,需要格外注意:
public class herscore{
public static int extest(){
int x=0;
try {
x = 312;
System.out.println("这里有个数字是312");
return x;
} catch (Exception e) {
x=123;
System.out.println("这里有个异常123");
return x;
} finally {
x=321;
System.out.println("没有异常,或异常被捕获321");
System.out.println();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println(herscore.extest());
}
}如图,在try-catch中均有return x语句,否则程序不能通过编译器检查;但这在finally中却不是必要的。
而且,finally执行的时间发生在try-catch中return发生之前,并且finally中x=321这句代码并没有覆盖return x中x的值。
综上,try-catch中代码运行到return语句时,首先把将要返回的结果临时存储起来,然后去执行finally中的代码,最后又将存储的返回值取出,执行return语句。这是try-catch-finally中大致的执行顺序。
观察上述程序的运行结果:
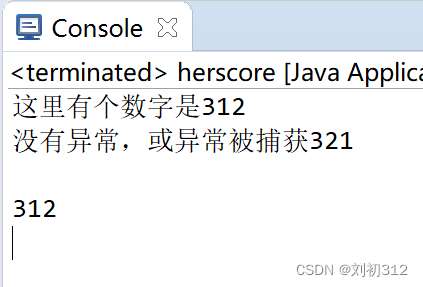
修改try中代码,使其发生异常,进入catch块:
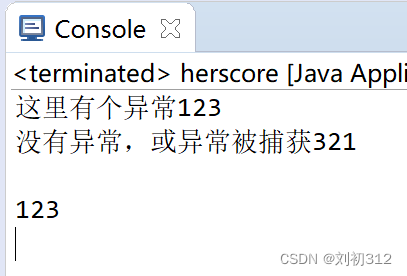
另一种情况,就是当finally中也有return语句,此时程序仍然通过了检查,并能正常运行。
public static int extest(){
int x=0;
try {
x = 1 / 0;
System.out.println("这里有个数字是312");
return x;
} catch (Exception e) {
x=123;
System.out.println("这里有个异常123");
return x;
} finally {
x=321;
System.out.println("没有异常,或异常被捕获321");
System.out.println();
return x;
}
}运行结果如下:
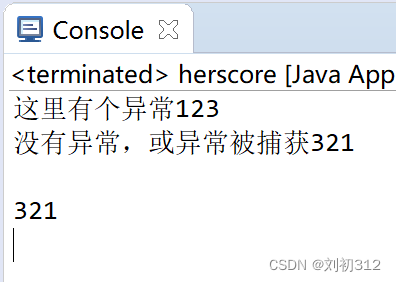
所以,当fianlly中也存在return语句时,在try/catch中将要return的返回值会被finally中的return的返回值覆盖。
另外需要注意的是,当这样编程时,IDE会产生warning:
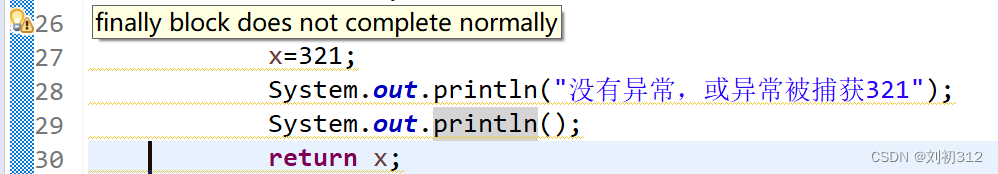
需要添加注释:























 3万+
3万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








