2.4设置语音刷抖音守护进程,实现开机自启动且在后台长期运行
前言
学术竞赛想用香橙派&语音模块实现语音刷抖音 项目成果先预览
学术竞赛想用香橙派&语音模块实现语音刷抖音解放双手
一 香橙派Zero2&语音模块实现语音刷抖音
1.1 配置语音模块官网SDK参数
进入智能公元官网,注册后使用微信登录,选择SU-03T 模块,选择RGB灯,找到语音模块支持的sdk配置官网,配置唤醒词及输出指令。
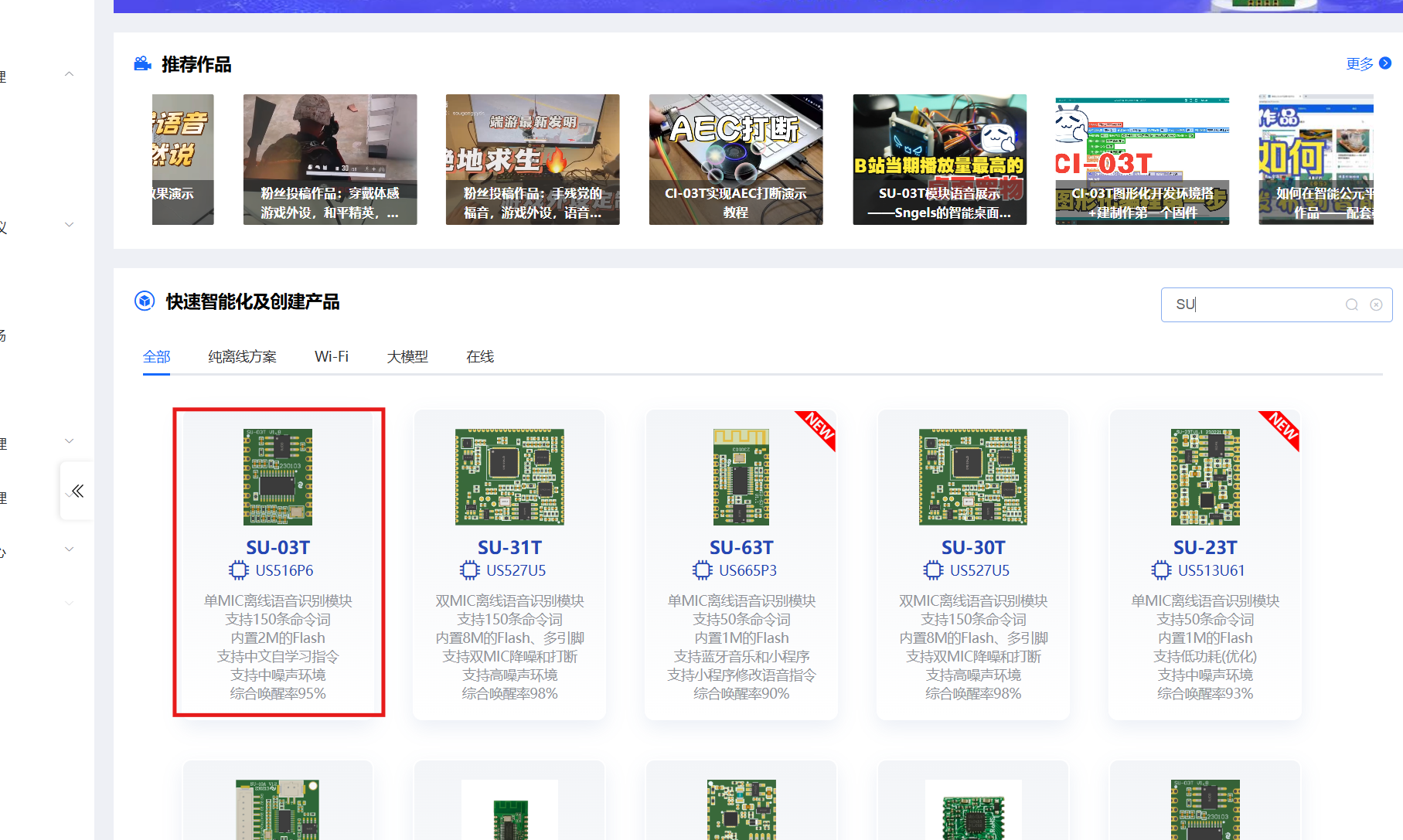

下一步 设置TX RX


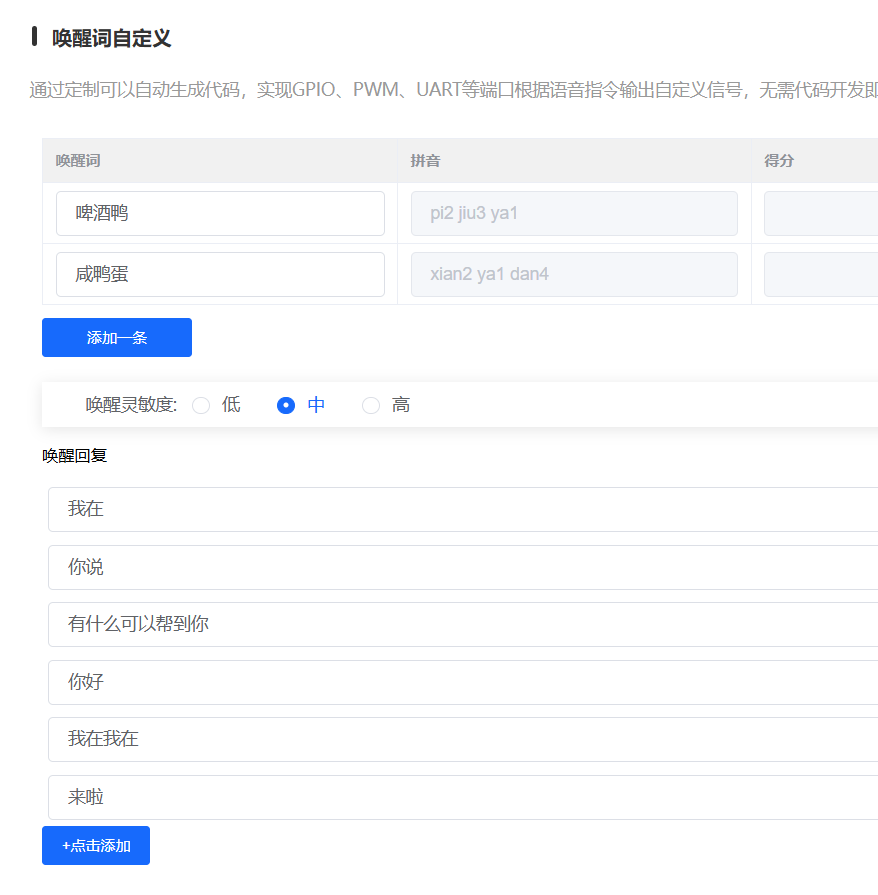
下一步,自定义唤醒词和回答,我这里设置了啤酒鸭和咸鸭蛋,这里的唤醒词就跟小爱音响的唤醒词 小爱同学 一样。
下一步,选择想要的实现的功能,设置相应的命令词和行为。

下一步,根据行为首字母的ASSIC 来配置动作参数,首个参数是98,第二个参数是16进制的首字母的ASSIC。
ASSIC对照表图片来源:CSDN:Little Grey Bear
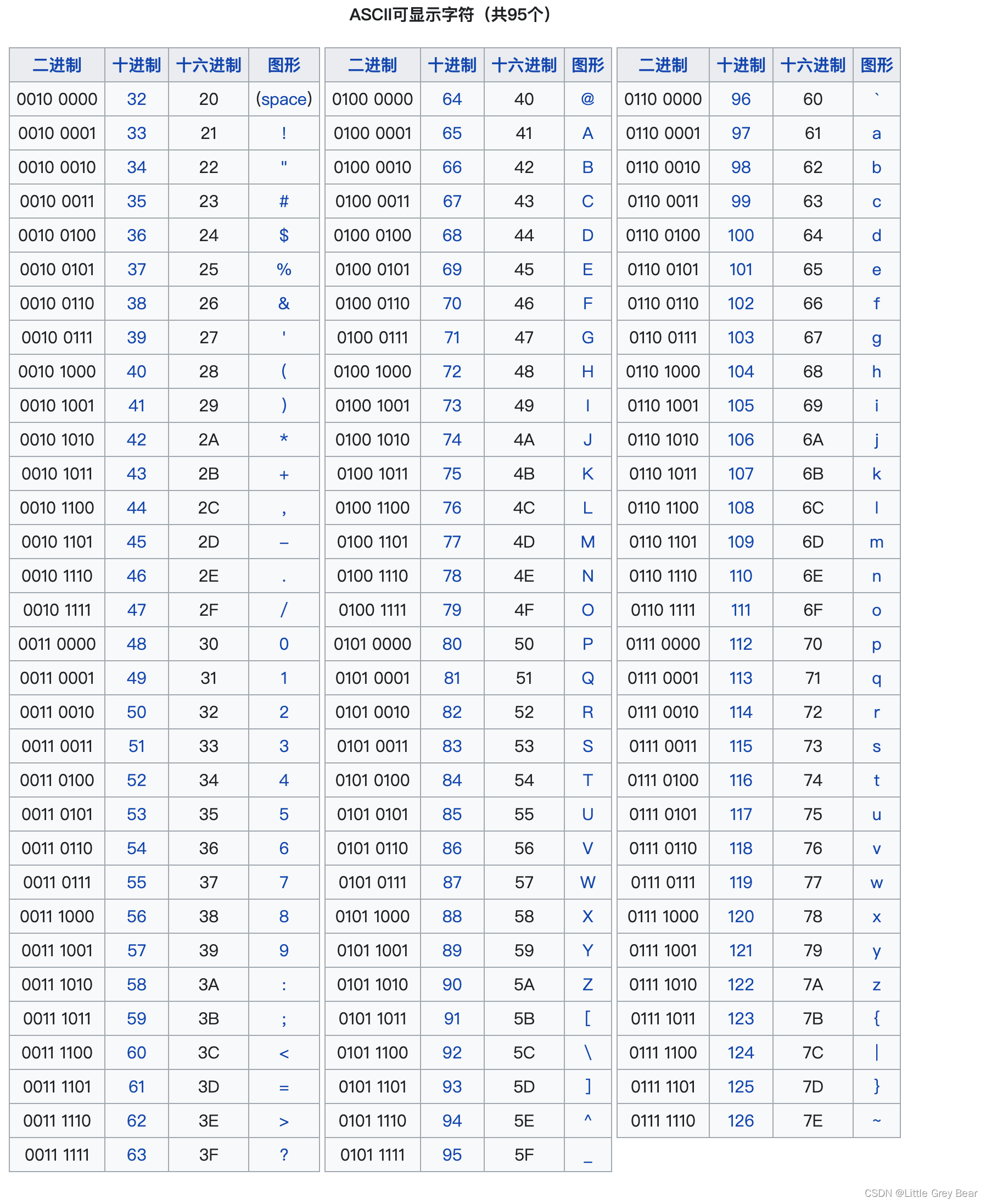
下一步,在命令词自定义界面选择控制详情后对命令词进行配置参数。98后面的16进制数对应的是命令行为的首字母对应的ASSIC。

添加免唤醒提示词
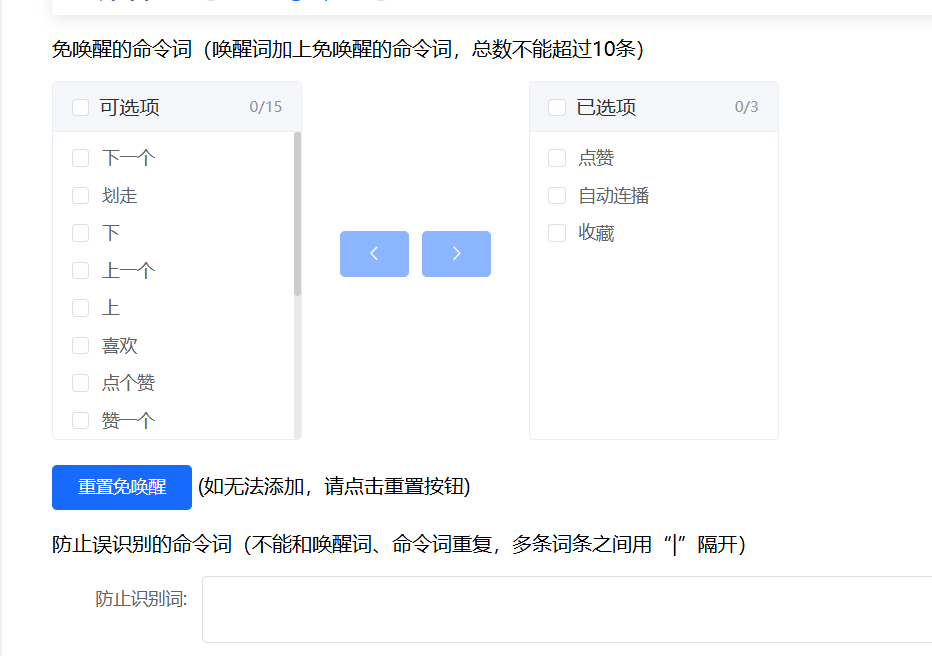
选择发音人,配置音量。可以自配声音,但是每段声音都要录,挺折磨人的,懒人都选择直接用现成的。

设置开机播报

找到右上角,选择发布版本。

1.2 下载sdk固件
(已经上传至文末交流群群文件里)



注意:存放SDK和固件的路径中不能有中文。
E:\Project\uni_hb_m_solution-52848-20250513\uni_hb_m_solution\image_demo\Hummingbird-M-Update-Tool 
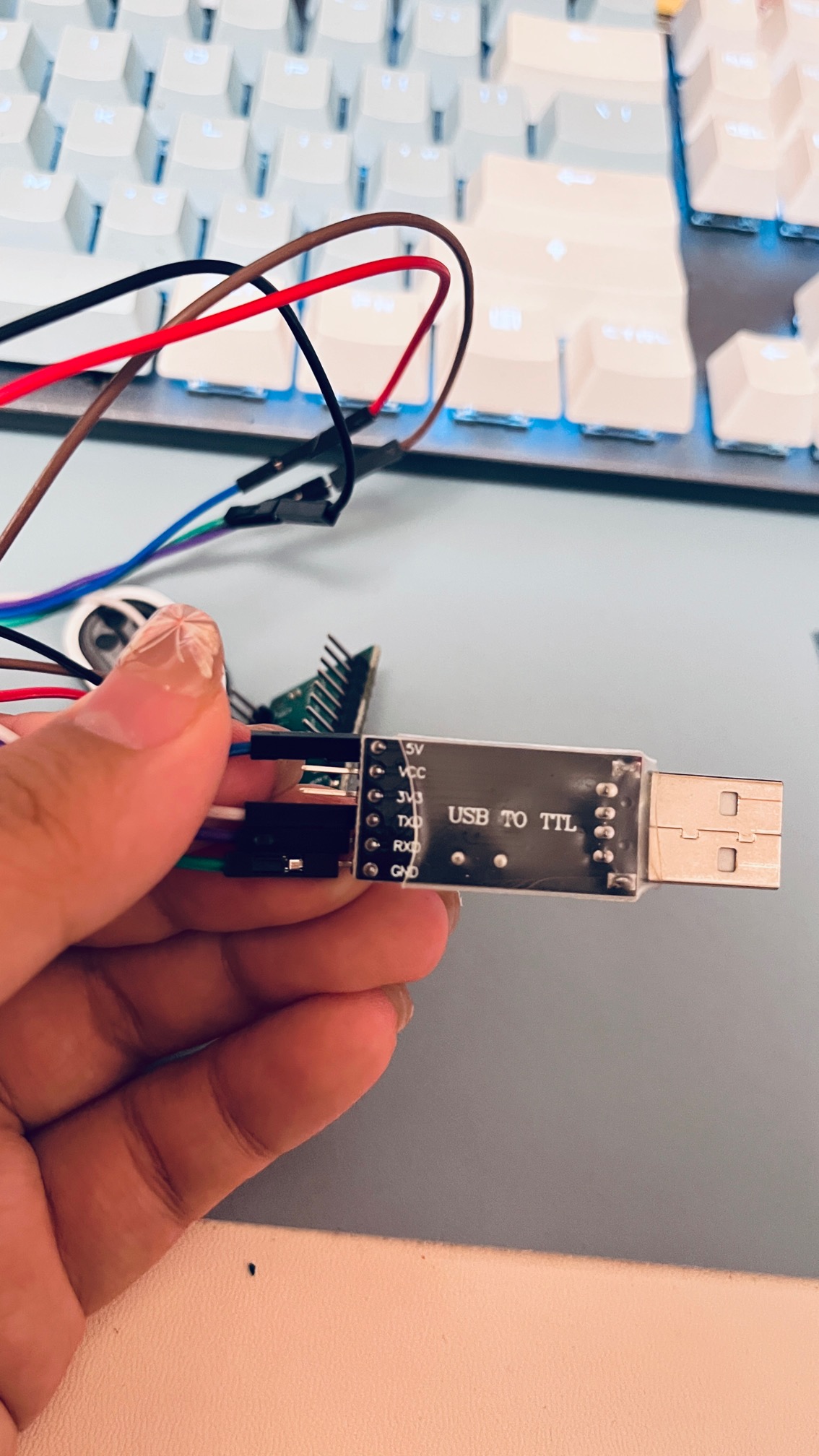
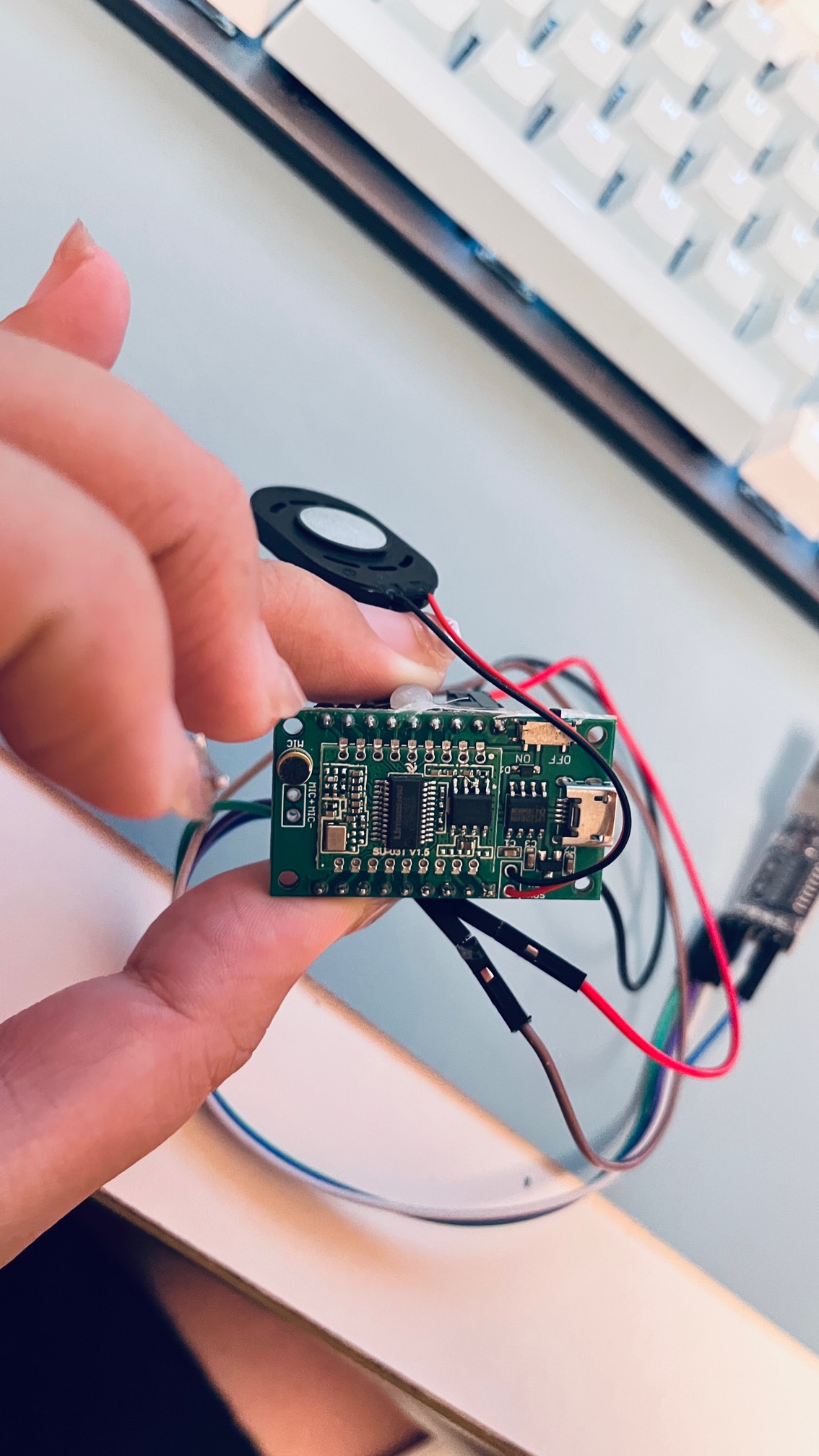
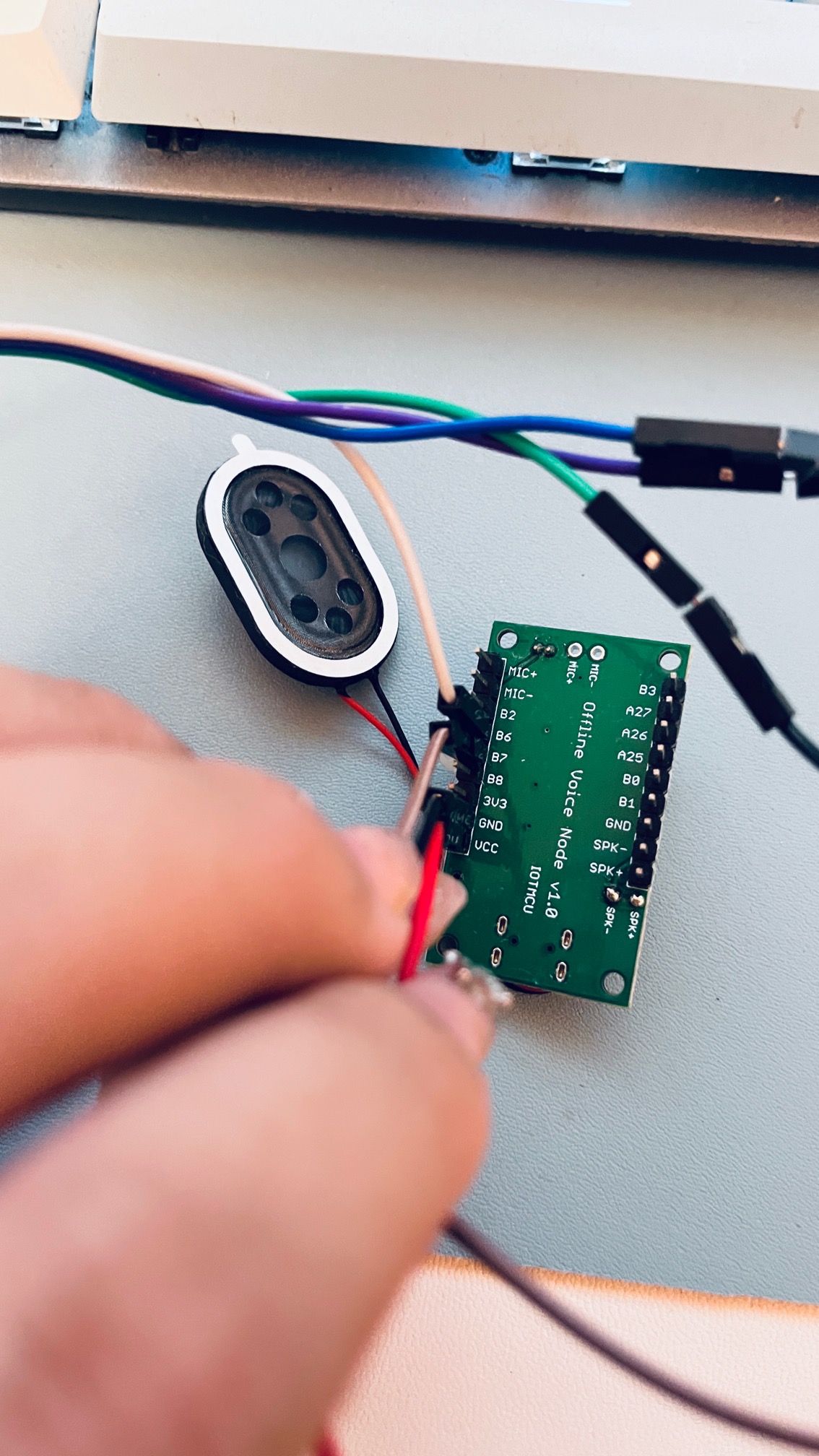
1.3连接SU-03T语音识别模块与USB转TTL模块
连接SU-03T语音识别模块和USB转TTL模块(注意TX和RX要交叉连接)
VCC连到USB转TTL模块的VCC(5V)
GND连到USB转TTL模块的GND
查看芯片手册,B7口是TX,连接USB转TTL的RX;
B6口是RX,连接USB转TTL的TX;

图片来源:CSDN博主 特纳斯电子

1.4烧录离线语音固件包
确认香橙派的COM口号
博主的是COM7(经常会变化)


使用云知声烧录工具(文末交流群群文件里有) 烧录固件包(选择release_update.bin文件)
注意:如果有两个串口同时被识别出但是其中一个为空,烧录工具会卡住,此时需要把空串口在设备管理器里禁用。
注意首先保持SU-03T语音识别模块关闭,再点击烧录,等到所在COM口变黄后再开机,稍等片刻(进度条到100%)即可烧录完成。
烧录成功后重启有开机播报。
烧录完成后将SU-03T的TX和RX口与香橙派的TX和RX口交叉相连,VCC与GND也对应连好,VCC选择5V的。
1.5 调试语音模块
douyin.c
//author:回眸&啤酒鸭
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "uartTool.h"
int fd;
void* readSerial()
{
char cmd;
while (1)
{
memset(cmd,'\0',sizeof(cmd));
cmd = mySerialGetchar(fd);
printf("GET -> 0x%s\n",cmd);
}
}
void* sendSerial()
{
char buffer[32];
while (1)
{
memset(buffer,'\0',sizeof(buffer));
scanf("%s",buffer);
mySerialSendString(fd,buffer);
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char deviceName[32] = {'\0'};
pthread_t readt;
pthread_t sendt;
if(argc < 2)
{
printf("usage:%s /dev/ttyS?\n",argv[0]);
return -1;
}
strcpy(deviceName,argv[1]);
fd = mySerialOpen(deviceName,115200);
if( fd == -1)
{
printf("open %s error\n",deviceName);
return -1;
}
pthread_create(&readt,NULL,readSerial,NULL);
pthread_create(&sendt,NULL,readSerial,NULL);
while (1)
{
sleep(10);
}
}uartTool.c
//author:回眸&啤酒鸭
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int mySerialOpen (const char *device, const int baud)
{
struct termios options ;
speed_t myBaud ;
int status, fd ;
switch (baud)
{
case 9600: myBaud = B9600 ; break ;
case 115200: myBaud = B115200 ; break ;
default:
return -2 ;
}
if ((fd = open (device, O_RDWR | O_NOCTTY | O_NDELAY | O_NONBLOCK)) == -1)
return -1 ;
fcntl (fd, F_SETFL, O_RDWR) ;
// Get and modify current options:
tcgetattr (fd, &options) ;
cfmakeraw (&options) ;
cfsetispeed (&options, myBaud) ;
cfsetospeed (&options, myBaud) ;
options.c_cflag |= (CLOCAL | CREAD) ;
options.c_cflag &= ~PARENB ;
options.c_cflag &= ~CSTOPB ;
options.c_cflag &= ~CSIZE ;
options.c_cflag |= CS8 ;
options.c_lflag &= ~(ICANON | ECHO | ECHOE | ISIG) ;
options.c_oflag &= ~OPOST ;
options.c_cc [VMIN] = 0 ;
options.c_cc [VTIME] = 100 ; // Ten seconds (100 deciseconds)
tcsetattr (fd, TCSANOW, &options) ;
ioctl (fd, TIOCMGET, &status);
status |= TIOCM_DTR ;
status |= TIOCM_RTS ;
ioctl (fd, TIOCMSET, &status);
usleep (10000) ; // 10mS
return fd ;
}
int mySerialGetString (const int fd,char *buffer)
{
int nread;
nread = read(fd,buffer,32);
return nread;
}
void mySerialSendString (const int fd, const char *s)
{
int ret;
ret = write (fd, s, strlen (s));
if (ret < 0)
printf("Serial Puts Error\n");
}
char mySerialGetchar (const int fd)
{
char x ;
if (read (fd, &x, 1) != 1)
return -1 ;
return (x) ;
}
uartTool.h
//author:回眸&啤酒鸭
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
int mySerialOpen (const char *device, const int baud);
int mySerialGetString (const int fd,char *buffer);
void mySerialSendString (const int fd, const char *s);
char mySerialGetchar (const int fd);
预期结果:能够识别为字符串指令且与预设指令一致,但是有一些乱码。
gcc uartTool.c douyin.c -lpthread
sudo ./a.out /dev/ttyS5

1.6 改进代码使串口能识别出字符串,并且打印设置的指令
douyin2.c
//author:回眸&啤酒鸭
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "uartTool.h"
int fd;
void* readSerial()
{
char cmd;
while (1)
{
memset(&cmd,'\0',sizeof(cmd));
cmd = mySerialGetchar(fd);
//printf("GET -> 0x%c\n",&cmd);
switch (cmd)
{
case 'N':
printf("Next\n");
break;
case 'P':
printf("Previous\n");
break;
case 'L':
printf("Like\n");
break;
case 'O':
printf("Off\n");
break;
case 'A':
printf("Auto\n");
break;
case 'F':
printf("Favourite\n");
break;
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char deviceName[32] = {'\0'};
pthread_t readt;
if(argc < 2)
{
printf("usage:%s /dev/ttyS?\n",argv[0]);
return -1;
}
strcpy(deviceName,argv[1]);
fd = mySerialOpen(deviceName,115200);
if( fd == -1)
{
printf("open %s error\n",deviceName);
return -1;
}
pthread_create(&readt,NULL,readSerial,NULL);
while (1)
{
sleep(10);
}
}gcc uartTool.c douyin2.c -lpthread
sudo ./a.out /dev/ttyS5
1.7改进代码加入手机操作指令
因为安卓手机调试起来较为方便,所以选择调试连接安卓手机
使用搜索引擎搜索所用的安卓机怎么进入开发者模式,每个手机的方式会有一些区别。博主在这里使用的是专门打游戏的红米手机。
dmesg
安装adb工具
sudo apt-get install adb

adb shell报错:
error: no devices/emulators found
查询原因:没有开启USB调试 ,设置USB调试之后,博主还要在USB调试界面设置显示点击坐标等等,然后重新插拔安卓机,进入开发者 USB调试模式,手机保持解锁。
cd /etc/udev/rules.d/
sudo vim 51-android.rules
这个.rules文件名字可以自己取
在文件中添加内容 SUBSYSTEM=="usb", ENV{DEVTYPE}=="usb_device", MODE="0666"

adb devices
adb shell


退出后在树莓派界面调试
adb shell input swipe 540 1300 540 500 100 //下滑一段距离
adb shell input swipe 540 500 540 1300 100 //上滑一段距离
adb shell input tap 998 1396 //点击指定坐标
adb shell input tap 998 1733 //点击指定坐标
adb shell input touchscreen swipe 544 1305 544 1305 1000 //长按指定坐标
adb shell input swipe 540 1300 540 500 100 //下滑一段距离
adb shell input swipe 904 1931 968 1919 //滑动一小段指定距离
adb shell input keyevent 26 //锁屏建议先调试至能够正常运行再整合入代码。
douyin3.c
//author:回眸&啤酒鸭
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <stdarg.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <termios.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/ioctl.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include "uartTool.h"
int fd;
void* readSerial()
{
char cmd;
while (1)
{
memset(&cmd,'\0',sizeof(cmd));
cmd = mySerialGetchar(fd);
printf("GET -> 0x%s\n",&cmd);
switch (cmd)
{
case 'N':
printf("Next\n");
system("adb shell input swipe 540 1300 540 500 100");
break;
case 'P':
printf("Previous\n");
system("adb shell input swipe 540 500 540 1300 100");
break;
case 'L':
printf("Like\n");
system("adb shell input tap 998 1396");
break;
case 'O':
printf("Off\n");
system("adb shell input keyevent 26");
break;
case 'A':
printf("Auto\n");
system("adb shell input touchscreen swipe 544 1305 544 1305 1000");
system("adb shell input swipe 540 1300 540 500 100");
sleep(1);
system("adb shell input swipe 904 1931 968 1919");
break;
case 'F':
printf("Favourite\n");
system("adb shell input tap 998 1733");
break;
}
}
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
char deviceName[32] = {'\0'};
pthread_t readt;
if(argc < 2)
{
printf("usage:%s /dev/ttyS?\n",argv[0]);
return -1;
}
strcpy(deviceName,argv[1]);
fd = mySerialOpen(deviceName,115200);
if( fd == -1)
{
printf("open %s error\n",deviceName);
return -1;
}
pthread_create(&readt,NULL,readSerial,NULL);
while (1)
{
sleep(10);
}
}gcc uartTool.c douyin3.c -lpthread
sudo ./a.out /dev/ttyS5 
实物预览
学术竞赛想用香橙派&语音模块实现语音刷抖音解放双手
二 Linux热拔插udev机制
Linux内核 图片来源:网络

2.1udev机制
udev 是一个设备管理工具, udev 以 守护进程 的形式运行。 udev 在用户空间运行,而不在内核空间运行。它能够根据系统中的硬件设备的状态动态更新设备文件,包括设备文件的创建,删除等。设备文件通常放在/dev 目录下。使用 udev 后,在 /dev 目录下就只包含系统中真正存在的设备。
2.2守护进程
Linux Daemon (守护进程)是运行在后台的一种特殊进程。它独立于控制终端并且周期性地执行某种任务或等待处理某些发生的事件。它不需要用户输入就能运行而且提供某种服务,不是对整个系统就是对某个用户程序提供服务。 常见的守护进程包括系统日志进程syslogd 、 web 服务器 httpd 等。守护进程的名称通常以 d 结尾。
查询进程:全格式显示所有进程
ps -ef

筛选 udev进程,除去grep进程
ps -elf |grep udev |grep -v grep

2.3 查询时间守护进程
timedaemon.c
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
// C 库函数 char *asctime(const struct tm *timeptr) 返回一个指向字符串的指针,它代表了结构
// struct timeptr 的日期和时间。
// C 库函数 struct tm *localtime(const time_t *timer) 使用 timer 的值来填充 tm 结构。
// timer 的值被分解为 tm 结构,并用本地时区表示。
/*
struct tm {
int tm_sec; 秒,范围从 0 到 59
int tm_min; 分,范围从 0 到 59
int tm_hour; 小时,范围从 0 到 23
int tm_mday; 一月中的第几天,范围从 1 到 31
int tm_mon; 月份,范围从 0 到 11
int tm_year; 自 1900 起的年数
int tm_wday; 一周中的第几天,范围从 0 到 6
int tm_yday; 一年中的第几天,范围从 0 到 365
int tm_isdst; 夏令时
};
*/
static bool flag = true;
void handler(int sig)
{
printf("I got a signal %d\nI'm quitting.\n", sig);
flag = false;
}
int main()
{
time_t t;
int fd;
// 创建守护进程
if (-1 == daemon(0, 0))
{
printf("daemon error\n");
exit(1);
}
// 设置信号处理函数
struct sigaction act;
act.sa_handler = handler;
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
act.sa_flags = 0;
if (sigaction(SIGQUIT, &act, NULL))
{
printf("sigaction error.\n");
exit(0);
}
// 进程工作内容
while (flag)
{
fd = open("/home/orangepi/daemon.log", O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_APPEND,
0644);
if (fd == -1)
{
printf("open error\n");
}
t = time(0);
char *buf = asctime(localtime(&t));
write(fd, buf, strlen(buf));
close(fd);
sleep(10);
}
return 0;
}
去home目录下看是否生成了daemon.log 的log信息。
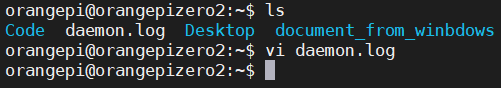
查看daemon.log 现在的时间应该是23点27左右,但是显示是15.27,这是正常的,因为获取到的时间是格林威治时间


gcc timedaemon.c -o tdaemon筛选守护进程 tdaemon(除去grep进程)
ps -ef |grep tdaemon |grep -v grep



2.4设置语音刷抖音守护进程,实现开机自启动且在后台长期运行
ps.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(){
FILE *file;
char buffer[128] = {'\0'};
char *cmd = "ps -elf |grep douyin|grep -v grep";
file = popen(cmd,"r");
fgets(buffer,128,file);
if (strstr(buffer,"douyin") != NULL){
printf("douyin is running\n");
}
else
{
printf("douyin is not running\n");
}
printf("Buffer:%s\n",buffer);
}
ls /home/orangepi/Code/douyin/douyin
daemon.c 给抖音写守护进程
#include <unistd.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <string.h>
static bool flag = true;
void handler(int sig)
{
printf("I got a signal %d\nI'm quitting.\n", sig);
flag = false;
}
int jud()
{
FILE *file;
char buffer[128] = {'\0'};
char *cmd = "ps -elf |grep douyin|grep -v grep";
file = popen(cmd,"r");
fgets(buffer,128,file);
if (strstr(buffer,"douyin") != NULL){
printf("douyin is running\n");
}
else
{
printf("douyin is not running\n");
}
printf("Buffer:%s\n",buffer);
}
int main()
{
time_t t;
int fd;
// 创建守护进程
if (-1 == daemon(0, 0))
{
printf("daemon error\n");
exit(1);
}
// 设置信号处理函数
struct sigaction act;
act.sa_handler = handler;
sigemptyset(&act.sa_mask);
act.sa_flags = 0;
if (sigaction(SIGQUIT, &act, NULL))
{
printf("sigaction error.\n");
exit(0);
}
// 进程工作内容
while (flag)
{
if (jud() == -1){
system("/home/orangepi/Code/douyin/douyin /dev/ttyS5 &");
}
sleep(10);
}
return 0;
}
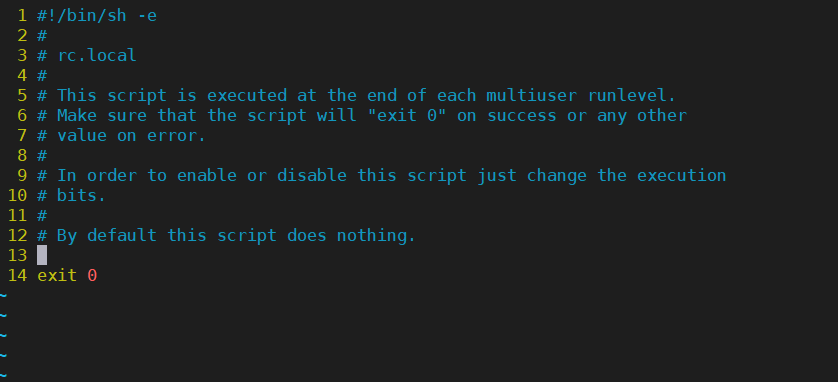
sudo vi /etc/rc.local
将抖音进程和抖音的守护进程写入开机自启动配置文件

重启后就可以看到后台一直在运行抖音和抖音守护进程了。
注意SU-03T模块也需要打开。
后记
这篇博文超级长!





























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










