一、目的
在我们编写Java代码的过程中,Map是我们常用的存储数据的类型,因为他的查询效率非常的高。如果想要遍历Map的话,是使用keySet()方法,是entrySet()方法,是迭代器,是forEach呢?
下面通过实验说明:建议使用entrySet(),最好是forEach.
二、测试过程
下面是测试Map遍历的代码:
/**
* Licensed to the Apache Software Foundation (ASF) under one or more
* contributor license agreements. See the NOTICE file distributed with
* this work for additional information regarding copyright ownership.
* The ASF licenses this file to You under the Apache License, Version 2.0
* (the "License"); you may not use this file except in compliance with
* the License. You may obtain a copy of the License at
*
* http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
*
* Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
* distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
* WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
* See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
* limitations under the License.
*
*/
package com.tompai.common.utils;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Map.Entry;
import org.apache.commons.lang3.RandomStringUtils;
/**
* @desc: snow
* @name: MapTest.java
* @author: tompai liinux@qq.com
* @createTime: 2019年11月24日 下午10:13:40
* @history:
* @version: v1.0
*/
public class MapTest {
/**
* @author: tompai
* @createTime: 2019年11月24日 下午10:13:40
* @history:
* @param args void
*/
public static void main(String[] args) {
int initialCapacity=16;
int aHundredMillion = 10000000;
Map<String, String> hm = new HashMap<String, String>(initialCapacity);
for(int i=0;i<aHundredMillion;i++) {
String sts=RandomStringUtils.random(6, true, true);
hm.put(String.valueOf(i), sts);
}
// 1. keySet
Instant start=Instant.now();
for (String key : hm.keySet()) {
//System.out.println(key + ": " + hm.get(key));
}
Instant end=Instant.now();
System.out.println("KeySet Time use:"+Duration.between(start, end).toMillis());
// 2. entrySet
start=Instant.now();
for (Entry<String, String> entry : hm.entrySet()) {
//System.out.println(entry.getKey() + ": " + entry.getValue());
}
end=Instant.now();
System.out.println("EntrySet Time use:"+Duration.between(start, end).toMillis());
// 3. forEach
start=Instant.now();
hm.forEach((key, value) -> {
//System.out.println(key + ": " + value);
});
end=Instant.now();
System.out.println("Map forEach Time use:"+Duration.between(start, end).toMillis());
}
}
三、测试结果
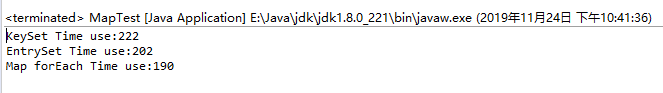
从上面的测试结果表可以看出,key_value键值对在数量较少的情况下,keySet和entrySet遍历的效率差别不大,但是数量在10000K时,keySet遍历花费了222ms;entrySet遍历只花费了202ms,可见entrySet比keySet遍历的效率高很多,forEach遍历集合是在Java8中出现的,其效率更190ms高。我建议需要遍历Map时,使用entrySet遍历,JDK8+使用forEach。
四、结果分析
1)keySet():
返回的是只存放key值的Set集合,使用迭代器方式遍历该Set集合,在迭代器中再使用get方法获取每一个键对应的值。使用get方法获取键对应的值时就需要遍历Map集合,主要的差异就在此处。
2)entrySet():
返回的是存放了映射关系的Set集合(一个映射关系就是一个键-值对),就是把(key-value)作为一个整体一对一对地存放到Set集合当中的。然后使用迭代器方式遍历该Set集合就可以取出Map中存放的键值对。
3)Iterator遍历 :
你也可以在keySet和values上应用同样的方法。该种方式看起来冗余却有其优点所在。首先,在老版本java中这是惟一遍历map的方式。另一个好处是,你可以在遍历时调用iterator.remove()来删除entries,另两个方法则不能。根据javadoc的说明,如果在for-each遍历中尝试使用此方法,结果是不可预测的。从性能方面看,该方法类同于for-each遍历的性能。
4)forEach:【jdk8+】
返回的是存放了映射关系的Set集合(一个映射关系就是一个键-值对),就是把(key-value)作为一个整体一对一对地存放到Set集合当中的。然后使用迭代器方式遍历该Set集合就可以取出Map中存放的键值对。





 本文通过实验分析了Java中Map遍历的三种常见方式——keySet、entrySet和forEach的性能,发现当键值对数量较大时,entrySet和forEach在效率上优于keySet,尤其在10000K数据量下,entrySet和forEach分别用时202ms和190ms。建议在遍历Map时优先选择entrySet,对于JDK8及更高版本,推荐使用forEach。
本文通过实验分析了Java中Map遍历的三种常见方式——keySet、entrySet和forEach的性能,发现当键值对数量较大时,entrySet和forEach在效率上优于keySet,尤其在10000K数据量下,entrySet和forEach分别用时202ms和190ms。建议在遍历Map时优先选择entrySet,对于JDK8及更高版本,推荐使用forEach。
















 1万+
1万+










