Modern processor architectures utilize various execution models. Out of these, two are most popular: SIMD (Single Instruction Multiple Data) and SIMT (Single Instruction Multiple Threads). There’s also SMT (Simultaneous Multithreading), but that’s something else we’ll be checking at the end. In this post, we have a look at the SIMD and SIMT processor execution modes and see how they differ from one another.
SIMD: Single Instruction Multiple Data
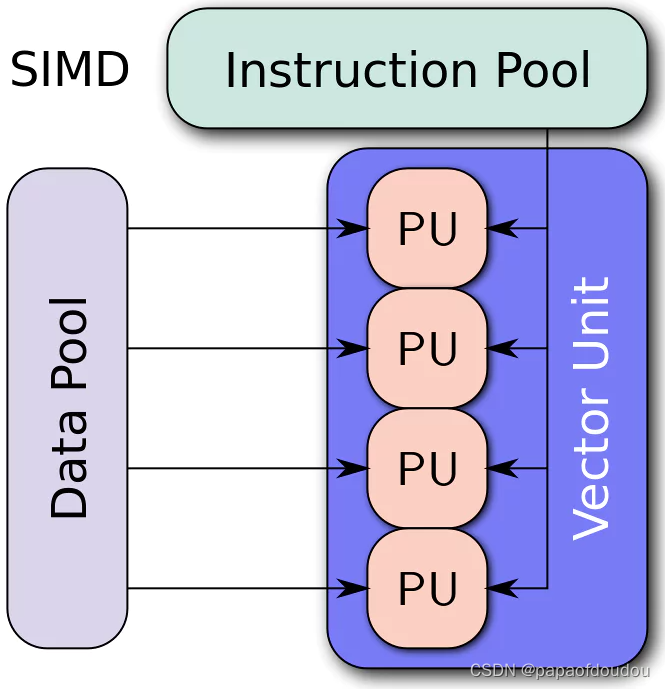
Right off the bat, what is SIMD, and more importantly how does it work? SIMD is an execution model, meaning it’s method employed by processors to queue similar data sets in the pipeline and execute them in parallel. It’s one of the most popular EMs used by modern CPUs and GPUs. Single Instruction Multiple Data. As the name suggests, it works by employing a single instruction on multiple data sets simultaneously.
What that means is: One particular instruction is executed by multiple Execution units on multiple data sets. The EUs may be ALUs (Arithmetic Logic Units) or FPUs (Floating Point Units), but the key point here is that they all receive the same instruction from a shared Control Unit and then execute it on multiple different data sets.
在SIMD指令中,矢量寄存器倍划分为多个通道(lane),每个通道包含矢量中的一个元素。如下图所示,一个128位的矢量寄存器可以分成8个16位的数据通道。

PS:下图展示的是一个计算片段分别在标量计算单元和向量计算单元上不同的编程方法:

This improves data-level parallelism (not instruction level or concurrency) by letting the CPU perform identical tasks on different operands. In the above example, you can see that the lines of code include many functions that require the same operator. In the first column, all four lines basically involve the addition to two different matrices. SIMD allows all four to be executed in the same clock cycle. One important thing to note here is that SIMD uses execution units, not threads or cores.

如上图,指令会并行做4次OP操作,它们分别位于处理器内部的4个数据通道并且是相互独立的,任何一个通道中的溢出或者进位都不会影响其它通道。
SIMD非常适合图像处理的场景,图像常用RGB565,RGBA8888,YUV422等格式的数据,这些格式的数据的特点是一个像素的一个分量(R,G,B,A,Y,U,V)使用一个字节来表示,如果使用传统的处理器做计算,虽然处理器的寄存器是32位或者64位,但是处理这些数据只能使用寄存器的低8位,这浪费了寄存器资源。如果把64位寄存器拆分成8个8位的数据通道,就能同时完成8个操作,计算效率是原来的8倍。

SIMT: Single Instruction Multiple Threads
SIMT is the thread equivalent of SIMD. While the latter uses Execution Units or Vector Units, SIMT expands it to leverage threads. In SIMT, multiple threads perform the same instruction on different data sets. The main advantage of SIMT is that it reduces the latency that comes with instruction prefetching.

SIMD is generally used in CPUs while SIMT is used in GPUs
SIMT is generally used in Super-scalar processors to implement SIMD. So technically, each core is scalar in nature but it still works similarly to an SIMD model by leveraging multiple threads to do the same task on various data sets.
Every time the GPU needs to execute a particular instruction, the data and instructions are fetched from the memory and then decoded and executed. In this case, all the data sets (up to a certain limit) that need the same instruction for execution are prefetched and executed simultaneously using the various threads available to the processor.
SMT: Simultaneous Multi-Threading
SMT or Simultaneous Multithreading allows a CPU core to leverage multiple threads at a time. Although theoretically, you can have up to 8 threads per core via SMT, it’s only feasible to have two. SMT is analogous to having two cargo belts at the airport luggage sorting, and one person sorting them.
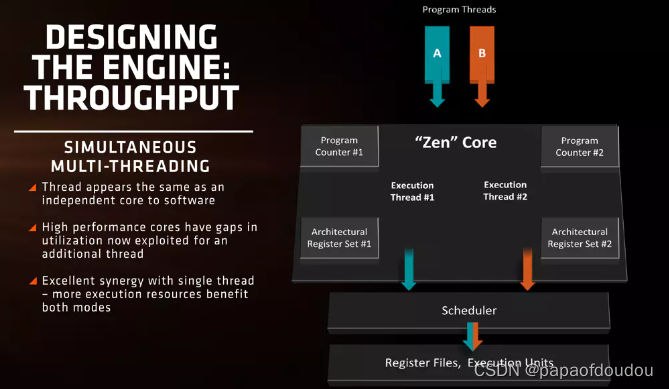
There will be times when one belt is empty but the other still has pending work. In this instance, the person will switch to the other belt and continue sorting till the first belt gets more luggage. This is similar to how SMT operates in CPUs. There are times when there’s a memory delay or a cache miss, at this time, the CPU core would normally stay idle. SMT aims to take advantage of this to fully saturate the CPU time.
The CPU core architecture needs to be modified internally to support SMT. This usually involves increasing the register size (and in some cases the cache size as well) to allow the distribution of resources among the two threads equally, as well as to prevent contention.
Although modern CPUs leverage SMT quite well, there are still times when it’s redundant. That is mostly in latency intensive tasks where there is little to no delay in the pipeline. SMT can even hamper performance in applications that are resource intensive (register and cache). Here the two threads are forced to compete against one another for resources, leading to reduced performance.
总结
- 在SIMD中,在一个vector中的多个element是完全同步并行计算的;
- 在SMT中,多个线程(thread)中的指令是并行执行的;
- 在SIMT中,多个thread共享一条指令并行执行(SMT是各个线程run各自的指令),每个thread处理一个scalar数据,使之看起来像SIMD,但是并不限制同时执行的thread之间的同步性。
可以这样说:SIMT相比SIMD更加灵活,而SMT相比SIMT又更加灵活,SIMD在损失灵活性的前提下提升了运算效率。所以对于灵活性而言,SIMD<SIMT<SMT;而对于计算效率而言,SIMD>SIMT>SMT,但是仅仅在那些SIMD灵活性足以处理的任务中进行比较。
SIMT和SIMD都是通过广播同一条指令到多个执行单元的并行机制。因此多个执行单元可以共享同一套指令装载/指令译码逻辑。
那么,“单指令多线程(SIMT)” 和 “单指令多数据(SIMD)”之间的区别究竟在哪里呢?在NVIDIA GPU的模型里面,有3个特征是SIMD并不具备的:
- 单指令,多套寄存器组(SIMD是并行的元素都在同一个寄存器内);
- 单指令,多个数据访问单元;
- 单指令,多种运算逻辑路径;
- SIMT数据路径独立,访存地址是线程ID的函数,但是SIMD的数据必须按照预先设计的形状分布。
Reference
SIMD<SIMT<SMT: NVIDIA GPU的并行机制_积小流哥的博客-CSDN博客_simd latency and throughput
SIMD < SIMT < SMT: parallelism in NVIDIA GPUs

























 5691
5691











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








