红黑树是一棵二叉搜索树,它在每个节点上增加了一个存储位来表示节点的颜色,可以是Red或Black。
通过对任何一条从根到叶子简单 路径上的颜色来约束,红黑树保证最长路径不超过最短路径的两倍,因而近似于平衡。
红黑树是满足下面红黑性质的二叉搜索树
1. 每个节点,不是红色就是黑色的
1. 每个节点,不是红色就是黑色的
2. 根节点是黑色的
3. 如果一个节点是红色的,则它的两个子节点是黑色的
4. 对每个节点,从该节点到其所有后代叶节点的简单路径上,均包含相同数目的黑色节点。
插入的几种情况
ps:cur为当前节点,p为父节点,g为祖父节点,u为叔叔节点
ps:cur为当前节点,p为父节点,g为祖父节点,u为叔叔节点
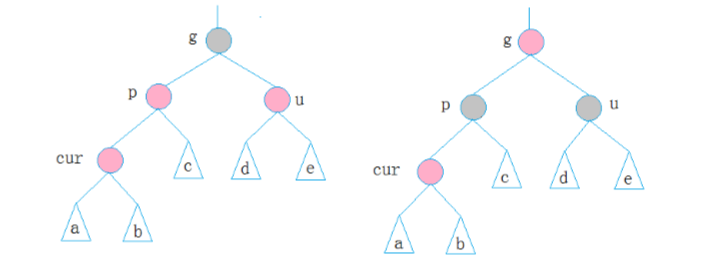
1.第一种情况 cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u存在且为红
则将p,u改为黑,g改为红,然后把g当成cur,继续向上调整。
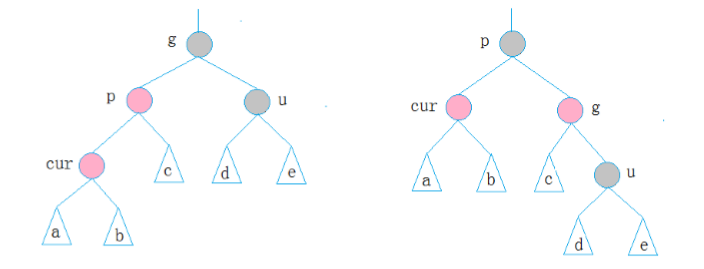
2.第二种情况 cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/u为黑
p为g的左孩子,cur为p的左孩子,则进行右单旋转;
相反,p为g的右孩子,cur为p的右孩子,则进行左单旋转
p、g变色--p变黑,g变红
3.第三种情况
cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/u为黑
cur为红,p为红,g为黑,u不存在/u为黑
p为g的左孩子,cur为p的右孩子,则针对p做左单旋转;
相反,p为g的右孩子,cur为p的左孩子,则针对p做右单旋转
则转换成了情况2

4.第四种情况
为空树或者只有一个根节点
主要代码:
#pragma once
enum Color
{
RED,
BLACK
};
template <typename K, typename V>
struct RBTreeNode
{
K _key;
V _value;
Color _col;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _left;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _right;
RBTreeNode<K, V>* _parent;
RBTreeNode(const K& key, const V& value)
:_key(key)
, _value(value)
, _left(NULL)
, _right(NULL)
, _parent(NULL)
, _col(RED)
{}
};
template<typename K, typename V>
class RBTree
{
typedef RBTreeNode<K,V> Node;
public:
RBTree()
:_root(NULL)
{}
pair<Node* ,bool> Insert(const K& key, const V& value)
{
if (_root == NULL)
{
_root = new Node(key, value);
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(_root,true);
}
Node* cur = _root;
Node* parent = NULL;
while (cur)
{
if (key < cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_left;
}
else if (key>cur->_key)
{
parent = cur;
cur = cur->_right;
}
else
{
return make_pair(cur, false);
}
}
cur = new Node(key, value);
if (parent->_key < key)
{
parent->_right = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
}
else
{
parent->_left = cur;
cur->_parent = parent;
} //到这块表示插入完成,然后进行调整
Node* newcur = cur;
while (parent && parent->_col == RED)
{
Node* grandparent = parent->_parent;
if (grandparent->_left == parent)
{
Node* uncle = grandparent->_right;
//1.
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;
grandparent->_col = RED;
cur = grandparent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else // 2,3 (2为单旋,3为双旋)
{
if (cur == parent->_left)
{
//右单旋
RotateR(grandparent);
}
else
{
//左右双旋
RotateLR(grandparent);
swap(parent, cur);
}
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandparent->_col = RED;
break;
}
}
else
{
Node* uncle = grandparent->_left;
if (uncle && uncle->_col == RED)
{
uncle->_col = parent->_col = BLACK;
grandparent->_col = RED;
cur = grandparent;
parent = cur->_parent;
}
else // 2,3 (2为单旋,3为双旋)
{
if (cur == parent->_right)
{
//右单旋
RotateL(grandparent);
}
else
{
//左右双旋
RotateRL(grandparent);
swap(parent, cur);
}
parent->_col = BLACK;
grandparent->_col = RED;
break;
}
}
}
_root->_col = BLACK;
return make_pair(newcur, true);
}
V& operator[](const K& key)
{
pair<Node*, bool> ret;
ret = Insert(key,V());
return ret.first->_value;
}
bool IsRBTree()
{
if (_root && _root->_col == RED)
return false;
size_t k = 0;
size_t num = 0;
Node* cur = _root;
while (cur)
{
if (cur->_col == BLACK)
++k;
cur = cur->_left;
}
return CheckColor(_root) && CheckBlackNum(_root, k, num);
}
protected:
bool CheckColor(Node* root)
{
if (root == NULL)
return true;
if (root->_col == RED && root->_parent->_col == RED)
return false;
return CheckColor(root->_left) && CheckColor(root->_right);
}
bool CheckBlackNum(Node* root, const size_t k, size_t num)
{
if (root == NULL)
{
return k == num;
}
if (root->_col == BLACK)
num++;
return CheckBlackNum(root->_left, k, num) && CheckBlackNum(root->_right, k, num);
}
void RotateL(Node* grandparent) //左单旋
{
Node* subR = grandparent->_right;
Node* subRL = subR->_left;
grandparent->_right = subRL;
if (subRL)
subRL->_parent = grandparent;
subR->_left = grandparent;
Node* ppNode = grandparent->_parent;
grandparent->_parent = subR;
subR->_parent = ppNode;
if (ppNode == NULL)
{
_root = subR;
}
else
{
if (ppNode->_left == grandparent)
{
ppNode->_left = subR;
}
else
{
ppNode->_right = subR;
}
}
}
void RotateR(Node* grandparent) //右单旋
{
Node* subL = grandparent->_left;
Node* subLR = subL->_right;
grandparent->_left = subLR;
if (subLR)
subLR->_parent = grandparent;
subL->_right = grandparent;
Node* ppNode = grandparent->_parent;
grandparent->_parent = subL;
subL->_parent = ppNode;
if (ppNode == NULL)
{
_root = subL;
}
else
{
if (ppNode->_left == grandparent)
{
ppNode->_left = subL;
}
else
{
ppNode->_right = subL;
}
}
}
void RotateRL(Node* grandparent)
{
RotateR(grandparent->_right);
RotateL(grandparent);
}
void RotateLR(Node* grandparent)
{
RotateL(grandparent->_left);
RotateR(grandparent);
}
private:
Node* _root;
};





















 901
901

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








