标准c++中String类非常强大,合理使用,能极大提高编程效率,下面就对string类的用法进行总结。
头文件
#include<string>
String类的构造函数如下:
1) string s; //生成一个空字符串s
2) string s(str) //拷贝构造函数生成str的复制品
3) string s(str,index) //将字符串str内“始于位置index”的部分当作字符串的初值
4) string s(str,index, n) //将字符串str内“始于index且长度顶多n”的部分作为字符串的初值
5) string s(cstr) //将C字符串作为s的初值
6) string s(chars,chars_len) //将C字符串前chars_len个字符作为字符串s的初值。
7) string s(n,c) //生成一个字符串,包含n个c字符
8) string s(str.begin(),str.end()) //以区间begin():end() (不包含end())内的字符作为字符串s的初值
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
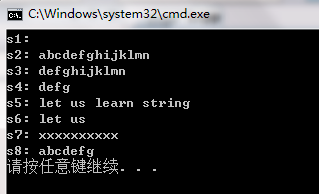
//定义
string s0 ("abcdefghijklmn");
string s1;
string s2 (s0);
string s3(s0,3);
string s4 (s0,3, 4);
string s5 ("let us learn string");
string s6 ("let us learn string",6);
string s7 (10, 'x');
string s8 (s0.begin(), s0.begin()+7);
//输出
cout << "s1: " << s1 << "\ns2: " << s2 << "\ns3: " << s3;
cout << "\ns4: " << s4 << "\ns5: " << s5 << "\ns6: " << s6;
cout << "\ns7: " << s7 << "\ns8: " << s8 << '\n';
return 0;
}
String类常用的操作函数
之后会对相关函数进行讲解,如果不想将下面操作函数全部看完,大伙可以找自己感兴趣的函数看。
1) =,assign() //赋以新值
2) swap() //交换两个字符串的内容
3)+=,append(),push_back() //在尾部添加字符
4) insert() //插入字符
5) erase() //删除字符
6) clear() //删除全部字符
7) replace() //替换字符
8) + //串联字符串
9)==,!=,<,<=,>,>=,compare() //比较字符串
10)size(),length() //返回字符数量
11) max_size() //返回字符的可能最大个数
12) empty() //判断字符串是否为空
13) capacity() //返回重新分配之前的字符容量
14) reserve() //保留一定量内存以容纳一定数量的字符
15) [ ], at() //存取单一字符
16)>>,getline() //从stream读取某值
17) << //将谋值写入stream
18) copy() //将某值赋值为一个C_string
19) c_str() //将内容以C_string返回
20) data() //将内容以字符数组形式返回
21) substr() //返回某个子字符串
22)查找函数
23)begin() end() //提供类似STL的迭代器支持
24) rbegin() rend() //逆向迭代器
25) get_allocator() //返回配置器
字符串添加
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
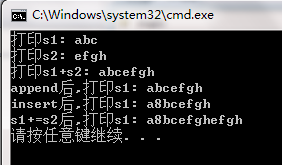
{
string s1;
//尾部插入字符
s1.push_back('a');
s1.push_back('b');
s1.push_back('c');
cout << "打印s1: " << s1 << endl;
char* cArray="efgh";
string s2(cArray);
cout << "打印s2: " << s2 << endl;
//字符串的"+"操作
cout << "打印s1+s2: " << s1 + s2 << endl;
//字符串s1后添加字符串s2
cout << "append后,打印s1: " << s1.append(s2) << endl;
//在s1的第个字符位置前插入字符'8'
s1.insert(s1.begin()+1,'8');
cout << "insert后,打印s1: " << s1 << endl;
//字符串的"+="操作
s1+=s2;
cout << "s1+=s2后,打印s1: " << s1 << endl;
return 0;
}
字符的遍历
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
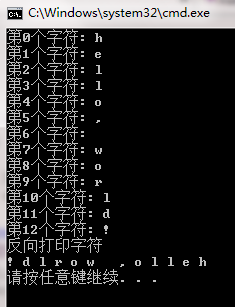
int main(void)
{
char* cArray="hello, world!";
string s(cArray);
//数组方式
for(unsigned int j=0; j< s.size(); j++)
cout << "第" << j << "个字符: " << s[j] << endl;
//迭代器方式
string::reverse_iterator ri;
cout << "反向打印字符" << endl;
for(ri=s.rbegin(); ri!=s.rend(); ri++)
cout << *ri << ' ' ;
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
字符的删除
1)iterator erase(iterator p);//删除字符串中p所指的字符
2)iterator erase(iterator first, iterator last);//删除字符串中迭代器
区间[first,last)上所有字符
3)string& erase(size_t pos = 0, size_t len = npos);//删除字符串中从索引
位置pos开始的len个字符
4)void clear();//删除字符串中所有字符
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
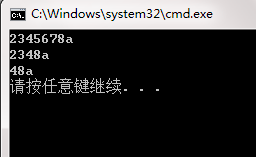
string s("12345678a");
s.erase(s.begin());
cout << s << endl; //打印出:a
s.erase(s.begin()+3, s.end()-2);
cout << s << endl; //打印出:a
s.erase(0,2);
cout << s << endl; //打印出:a
s.clear();
return 0;
}
字符的替换
1)string& replace(size_t pos, size_t n, const char *s);//将当前字符串
从pos索引开始的n个字符,替换成字符串s
2)string& replace(size_t pos, size_t n, size_t n1, char c); //将当前字符串
从pos索引开始的n个字符,替换成n1个字符c
3)string& replace(iterator i1, iterator i2, const char* s);//将当前字符串
[i1,i2)区间中的字符串替换为字符串s
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
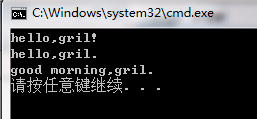
string s("hello,boy!");
s.replace(6,3,"gril"); //boy替换为girl
cout << s << endl; //打印hello gril!
s.replace(10,1,1,'.'); //将"hello gril!"的'!'替换为'.'
cout << s << endl; //打印hello gril.
s.replace(s.begin(),s.begin()+5, "good morning");
cout << s << endl; //打印good morning girl.
return 0;
}
字符的搜索
相关函数较多,下面列举几个常用的:
1)size_t find (constchar* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
//在当前字符串的pos索引位置开始,查找子串s,返回找到的位置索引,
-1表示查找不到子串
2)size_t find (charc, size_t pos = 0) const;
//在当前字符串的pos索引位置开始,查找字符c,返回找到的位置索引,
-1表示查找不到字符
3)size_t rfind (constchar* s, size_t pos = npos) const;
//在当前字符串的pos索引位置开始,反向查找子串s,返回找到的位置索引,
-1表示查找不到子串
4)size_t rfind (charc, size_t pos = npos) const;
//在当前字符串的pos索引位置开始,反向查找字符c,返回找到的位置索引,
-1表示查找不到字符
5)size_tfind_first_of (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
//在当前字符串的pos索引位置开始,查找子串s的字符,返回找到的位置索引,
-1表示查找不到字符
6)size_tfind_first_not_of (const char* s, size_t pos = 0) const;
//在当前字符串的pos索引位置开始,查找第一个不位于子串s的字符,
返回找到的位置索引,-1表示查找不到字符
7)size_t find_last_of(const char* s, size_t pos = npos) const;
//在当前字符串的pos索引位置开始,查找最后一个位于子串s的字符,返回找到的位置索引,-1表示查找不到字符
8)size_tfind_last_not_of (const char* s, size_t pos = npos) const;
//在当前字符串的pos索引位置开始,查找最后一个不位于子串s的字符,返回找到的位置索引,-1表示查找不到子串
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
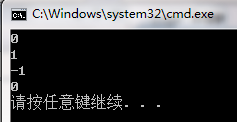
int main(void)
{
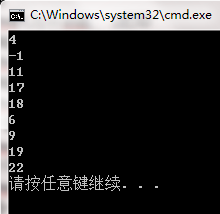
//0123456789012345678901234
string s("dog bird chicken bird cat");
//字符串查找
cout << s.find("bird") << endl; //打印
cout << (int)s.find("pig") << endl; //打印-1
//字符查找
cout << s.find('i',7) << endl; //打印
//从字符串的末尾开始查找字符串
cout << s.rfind("bird") << endl; //打印
//从字符串的末尾开始查找字符
cout << s.rfind('i') << endl; //打印
//查找第个属于某子串的字符
cout << s.find_first_of("13r98") << endl; //找到字符r,打印
//查找第个不属于某字符串的字符
cout << s.find_first_not_of("dog bird 2006") << endl; //找到字符c,打印
//查找最后一个属于某子串的字符
cout << s.find_last_of("13r98") << endl; //字符r,打印
//查找最后一个不属于某字符串的字符
cout << s.find_last_not_of("tea") << endl; //字符c,打印
return 0;
}
字符串的比较
1)int compare (conststring& str) const;//将当前字符串与字符串str比较,
相等返回0,大于str返回1,小于str返回-1
2)int compare (size_tpos, size_t len, const char* s) const; //将当前字符串从
Pos索引位置开始的len个字符构成的字符串与字符串s比较,
相等返回0,大于str返回1,小于str返回-1
3)int compare (constchar* s) const; //直接将当前字符串与字符串s比较,
相等返回0
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main(void)
{
string s1("abcdef");
string s2("abc");
cout << s1.compare("abcdef") << endl; //相等,打印
cout << s1.compare(s2) << endl; //s1 > s2,打印
cout << s1.compare("abyz") << endl; //s1 < "abyz",打印-1
cout << s1.compare(0,3,s2) << endl; //s1的前个字符==s2,打印
return 0;
}
文章为本人原创,转载请注明出处: http://blog.csdn.net/lsh_2013/article/details/46728993
























 1291
1291

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








