So Easy!
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)Total Submission(s): 899 Accepted Submission(s): 244
Problem Description
A sequence S
n is defined as:
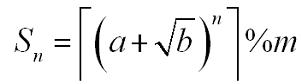
Where a, b, n, m are positive integers.┌x┐is the ceil of x. For example, ┌3.14┐=4. You are to calculate S n.
You, a top coder, say: So easy!

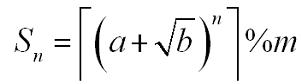
Where a, b, n, m are positive integers.┌x┐is the ceil of x. For example, ┌3.14┐=4. You are to calculate S n.
You, a top coder, say: So easy!

Input
There are several test cases, each test case in one line contains four positive integers: a, b, n, m. Where 0< a, m < 2
15, (a-1)
2< b < a
2, 0 < b, n < 2
31.The input will finish with the end of file.
Output
For each the case, output an integer S
n.
Sample Input
2 3 1 2013 2 3 2 2013 2 2 1 2013
Sample Output
4 14 4
Source
Recommend
zhoujiaqi2010
这可一点都不so easy啊,注意取模的时候可能为负!
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
__int64 mod;
struct matrix {
__int64 a[2][2];
matrix operator * (matrix num)const
{
int i,j,k;
matrix temp;
for(i=0;i<2;i++)
{
for(j=0;j<2;j++)
{
temp.a[i][j]=0;
for(k=0;k<2;k++)
{
temp.a[i][j]+=a[i][k]*num.a[k][j]%mod;
temp.a[i][j]%=mod;
}
}
}
return temp;
}
};
int main()
{
__int64 a,b,n,m;
matrix start,original,temp;
while(scanf("%I64d%I64d%I64d%I64d",&a,&b,&n,&m)!=EOF)
{
mod=m;
if(n==1)
{
printf("%I64d\n",2*(a%m)%m);
continue;
}
else if(n==2)
{
printf("%I64d\n",(2*(a%m)*(a%m)+2*(b%m)%m));
continue;
}
n=n-2;
a=a%m,b=b%m;
start.a[0][0]=2*a%m;
start.a[0][1]=1;
start.a[1][0]=(b-a*a%m+m)%m;
start.a[1][1]=0;
original.a[0][0]=1,original.a[1][1]=1;
original.a[1][0]=0,original.a[0][1]=0;
temp.a[0][0]=(2*a*a%m+2*b%m)%m;temp.a[0][1]=2*a%m;
temp.a[1][0]=0,temp.a[1][1]=0;
while(n)
{
if(n&1)
original=original*start;
n=n>>1;
start=start*start;
}
temp=temp*original;
printf("%I64d\n",temp.a[0][0]%m);
}
return 0;
}

























 506
506

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








