CSDN的博客中有这样一篇博客点击打开链接,是关于TCP的socket编程的,我想基于我的理解解释一下,毕竟原文只给出了纯粹的代码,
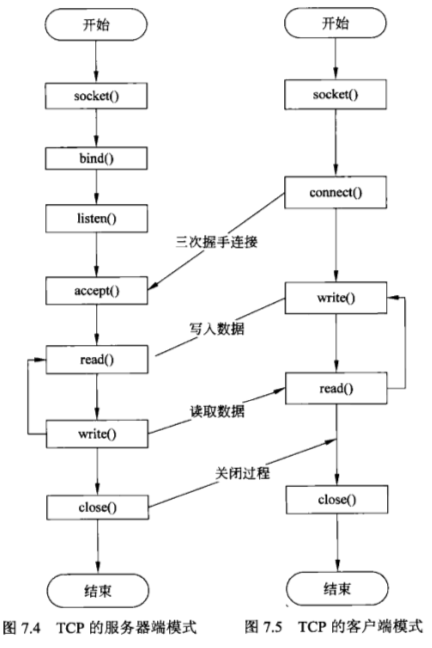
我们知道上图是它们之间的工作模式,基本编程的规则也是按照上面来的
下面是服务器端的代码,但插入的代码本应该是C的,但是CSDN中插入的代码选项却没有C的,比较让人困扰
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <ctype.h>
char host_name[20];
int port = 8000;
int main()
{
struct sockaddr_in sin,pin; //以太网套接字的地址结构,是协议族AF_INET对应的结构
int sock_descriptor,temp_sock_descriptor,address_size;
int i , len , on=1;
char buf[16384];
sock_descriptor = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0);//通过socket(int domain,int type,int protocol)的函数原型创建AF_INIT协议族的流//类型的socket,当然type除了流socket的之外还有SOCKET_RAW,据说这种类型的socket甚至可以伪装数据包,如果阅读这篇文章的大神对其很了解的话,希望能够私信//发给我关于它的资料或网址。
bzero(&sin,sizeof(sin));//将变量sin置0
sin.sin_family = AF_INET; //指定协议族
sin.sin_addr.s_addr = INADDR_ANY;
sin.sin_port = htons(port);//地址结构的端口地址,port是主机字节序,通过htons()进行字节序转换成网络字节序
if(bind(sock_descriptor,(struct sockaddr *)&sin,sizeof(sin)) == -1)//将sin的地址和socket文件描述符绑定到一起,绑定是数据接收和发//送的前提
{
perror("call to bind");
exit(1);
}
if(listen(sock_descriptor,100) == -1)//监听用来初始化服务器可连接队列,因为一次只能处理一个连接请求,当收到多个请求,将会存储在队列中,///先到先得
{
perror("call to listem");
exit(1);
}
printf("Accpting connections...\n");
while(1)
{
address_size = sizeof(pin);
temp_sock_descriptor = accept(sock_descriptor,(struct sockaddr *)&pin,&address_size);//前面提到,当收到多个连接请求时//后面未处理请求会被排在队列中,而accept()返回一个新的socket文件描述符来表示来自客户端的连接
if(temp_sock_descriptor == -1)
{
perror("call to accept");
exit(1);
}
if(recv(temp_sock_descriptor,buf,16384,0) == -1)//该描述符是接收端的套接字,buf是用来存储接收到的数据,16384是buf的长度
{
perror("call to recv");
exit(1);
}
inet_ntop(AF_INET,&pin.sin_addr,host_name,sizeof(host_name));
printf("received from client(%s):%s\n",host_name,buf);
len = strlen(buf);
for(i = 0 ; i < len ; i++)
{
buf[i] = toupper(buf[i]);
}
if(send(temp_sock_descriptor,buf,len+1,0) == -1)
{
perror("call to send");
exit(1);
}
close(temp_sock_descriptor);
}
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <sys/socket.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <arpa/inet.h>
#include <netinet/in.h>
#include <errno.h>
#include <strings.h>
#include <ctype.h>
char * host_name = "127.0.0.1";
int port = 8000;
int main(int argc , char * argv[])
{
char buf[8192];
//char message[256];
int socket_descriptor;
struct sockaddr_in pin;
char * str ="A default test string";
if(argc < 2)
{
printf("we will send a default test string.\n");
}
else
{
str = argv[1];
if(argc == 3)
{
host_name = argv[2];
}
}
bzero(&pin,sizeof(pin));
pin.sin_family = AF_INET;
inet_pton(AF_INET,host_name,&pin.sin_addr);
pin.sin_port = htons(port);
if((socket_descriptor = socket(AF_INET,SOCK_STREAM,0)) == -1)//与服务器端相对应
{
perror("error opening socket \n");
exit(1);
}
if(connect(socket_descriptor,(struct sockaddr * )&pin,sizeof(pin)) == -1)客户端在建立起套接字之后,不再需要进行地址绑定,可通过connect函数直接连接服务器
{
perror("error connecting to socket \n");
exit(1);
}
printf("sending message %s to server ..\n",str);
if( write(socket_descriptor,str,strlen(str)+1) == -1 )//将string写入socket描述符中
{
perror("error in send \n");
exit(1);
}
printf("..sent message ...wait for message..\n");
if( read(socket_descriptor,buf,8192) == -1 )//从socket描述符中将8192个字符读到buf中
{
perror("error in receiving response from server \n");
exit(1);
}
printf("\nResponse from server:\n\n%s\n",buf);
close(socket_descriptor);
return 1;
}





















 2505
2505

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








