一、红黑树可以保证:在每次插入或删除操作之后的重平衡过程中,全书的拓扑结构的更新仅涉及常数个节点。尽管最坏情况下需要多达O(logN)个节点重染色,但就分摊意义而言仅为O(1)!
二、 红黑树的性质(定义):
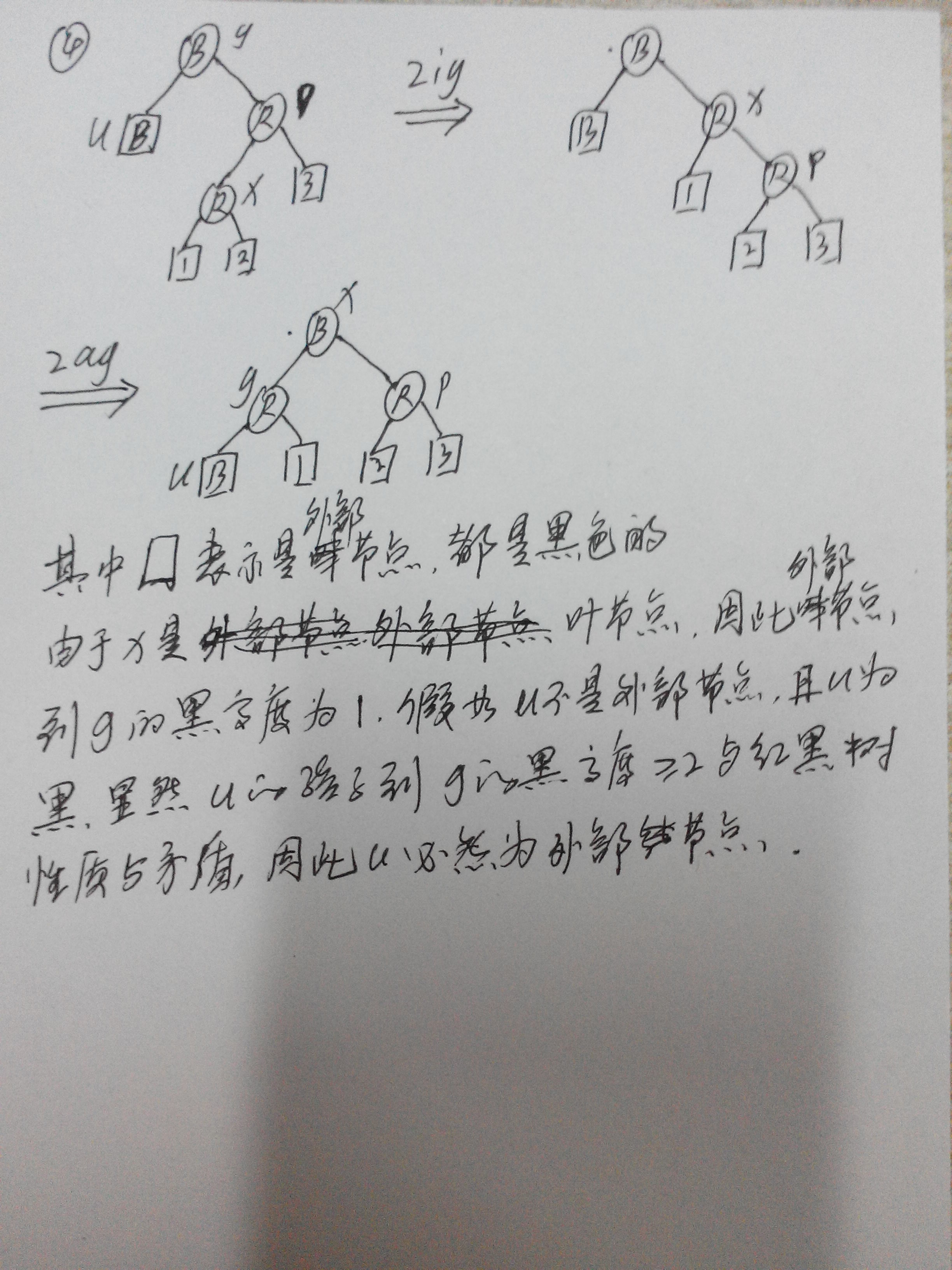
性质1.所有节点不是红色就是黑色
性质2. 根是黑色。
性质3. 所有外部节点都是黑色(有些地方也叫叶子节点,是NIL节点)。
性质4. 每个红色节点必须有两个黑色的子节点。(从每个外部节点到根的所有路径上不能有两个连续的红色节点。)
性质5. 从任一节点到其每个外部节点的所有简单路径都包含相同数目的黑色节点。
三、插入新节点后的平衡性:
情况一、插入节点的父亲是黑色节点:不需要进行校正,直接插入即可
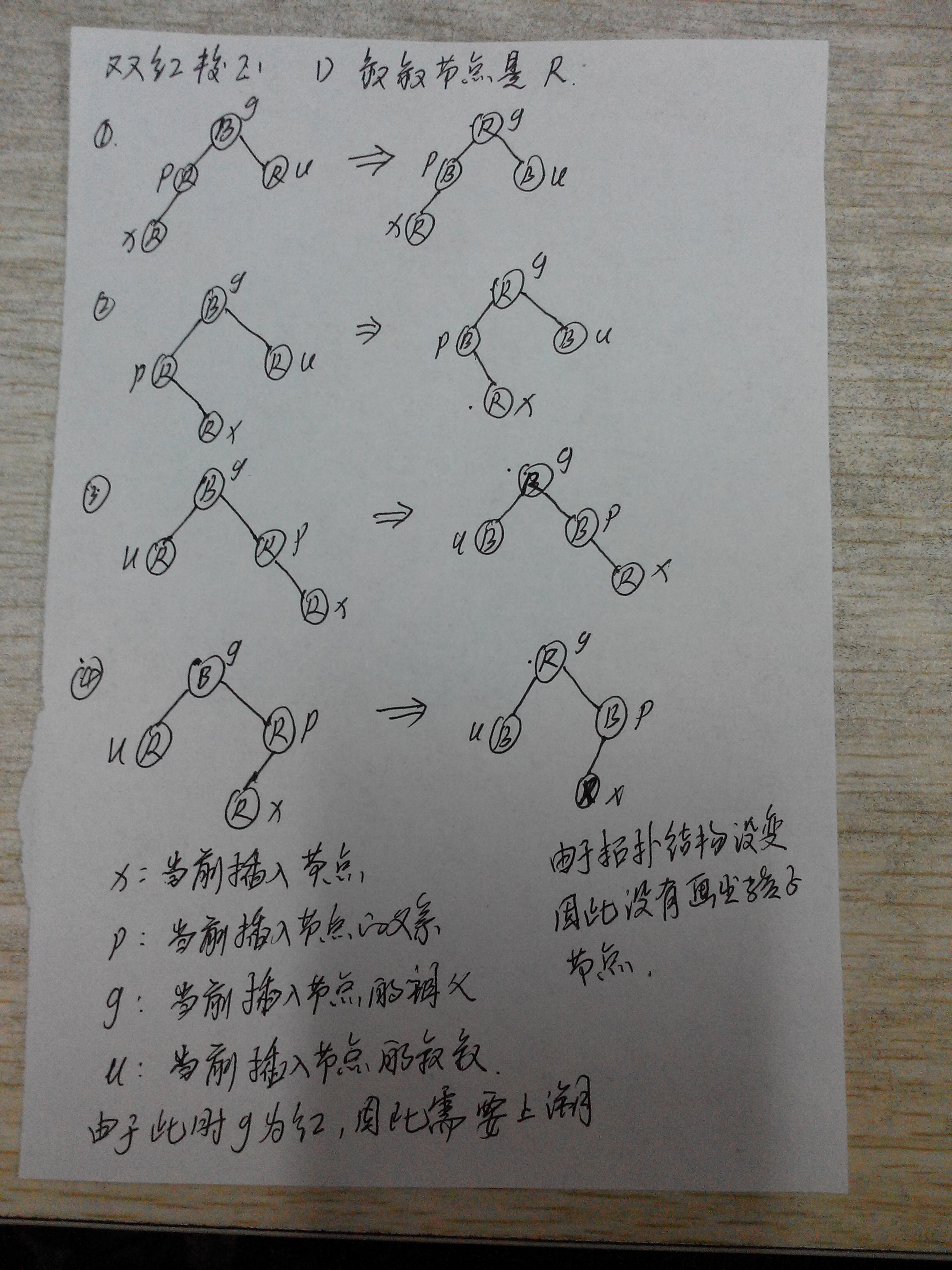
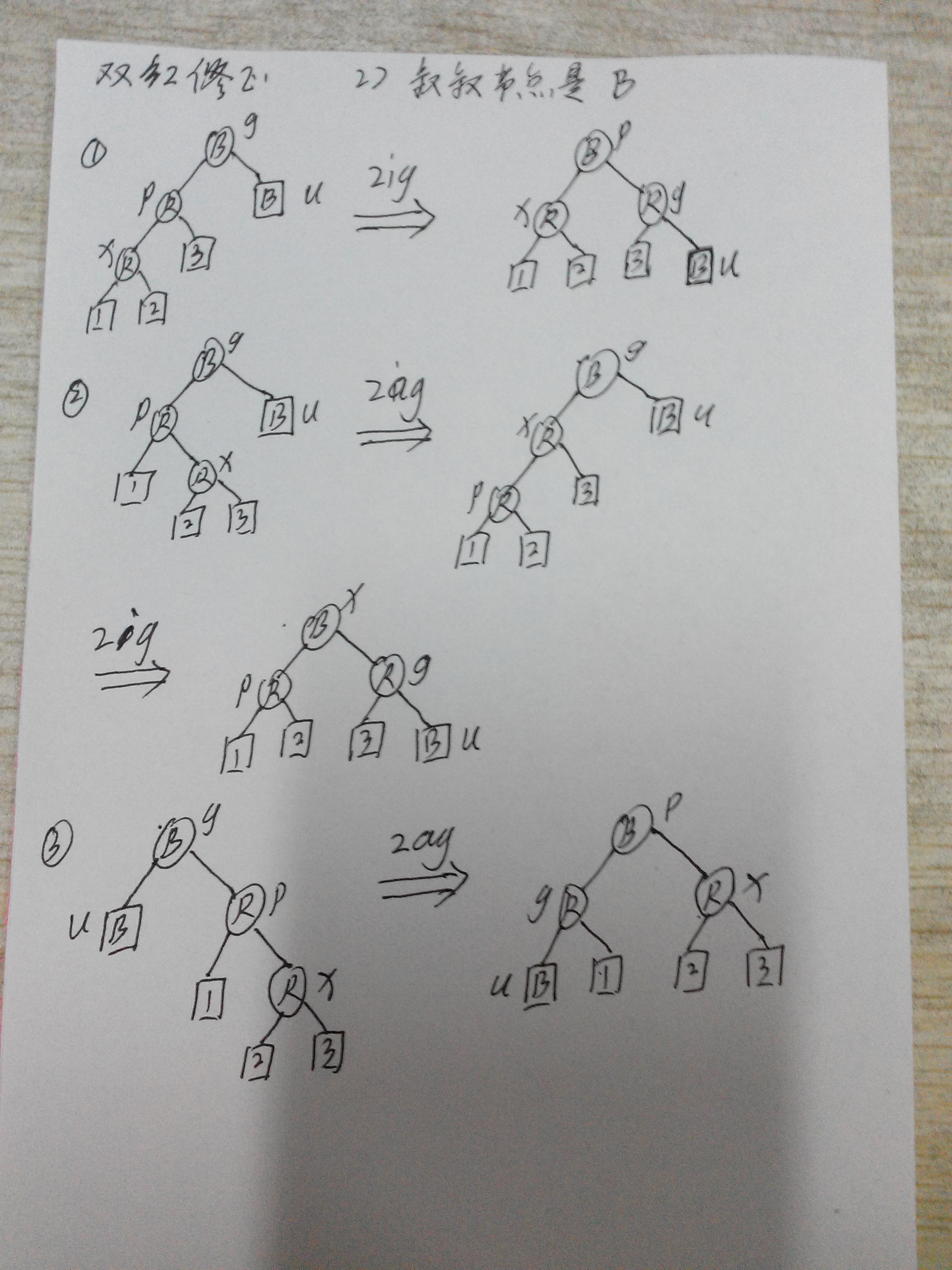
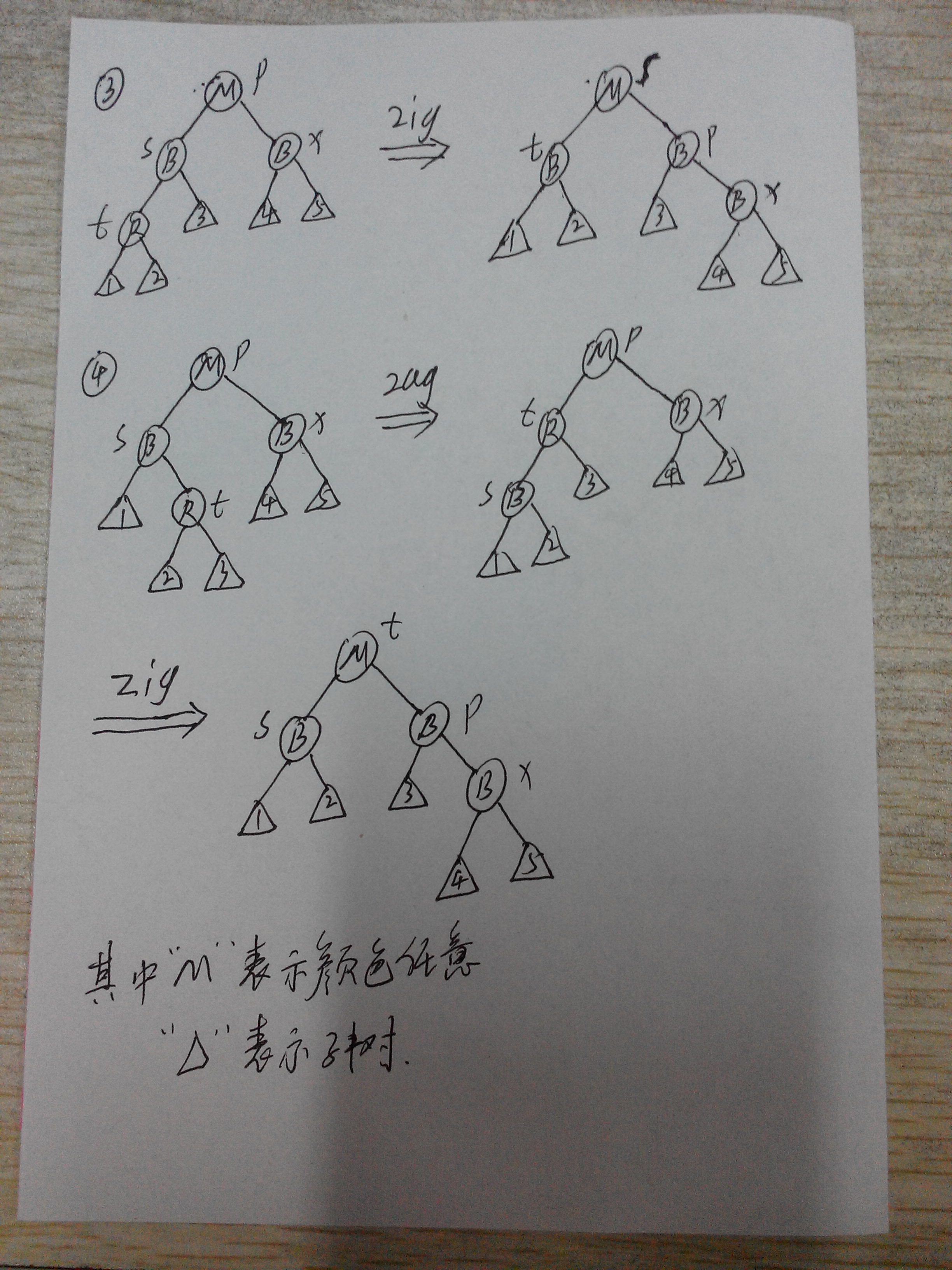
情况二、插入节点的父亲是红色,而刚插入的节点必然也是红色,这样就违反了性质4,即红色节点的子节点必须是黑色,因此需要双红校正。
双红校正1):叔叔节点是红色R
双红校正2):叔叔节点是黑色B
四、删除节点后的平衡
情况一、删除节点(此处表示的是当前将要被删除的节点的替代节点)的颜色是红色,直接删除即可。
情况二、删除节点(同上)的颜色是黑色,但是其替代节点(删除节点的替代节点的替代节点)的颜色是红色,直接删除,并且把替代节
点颜色染黑。
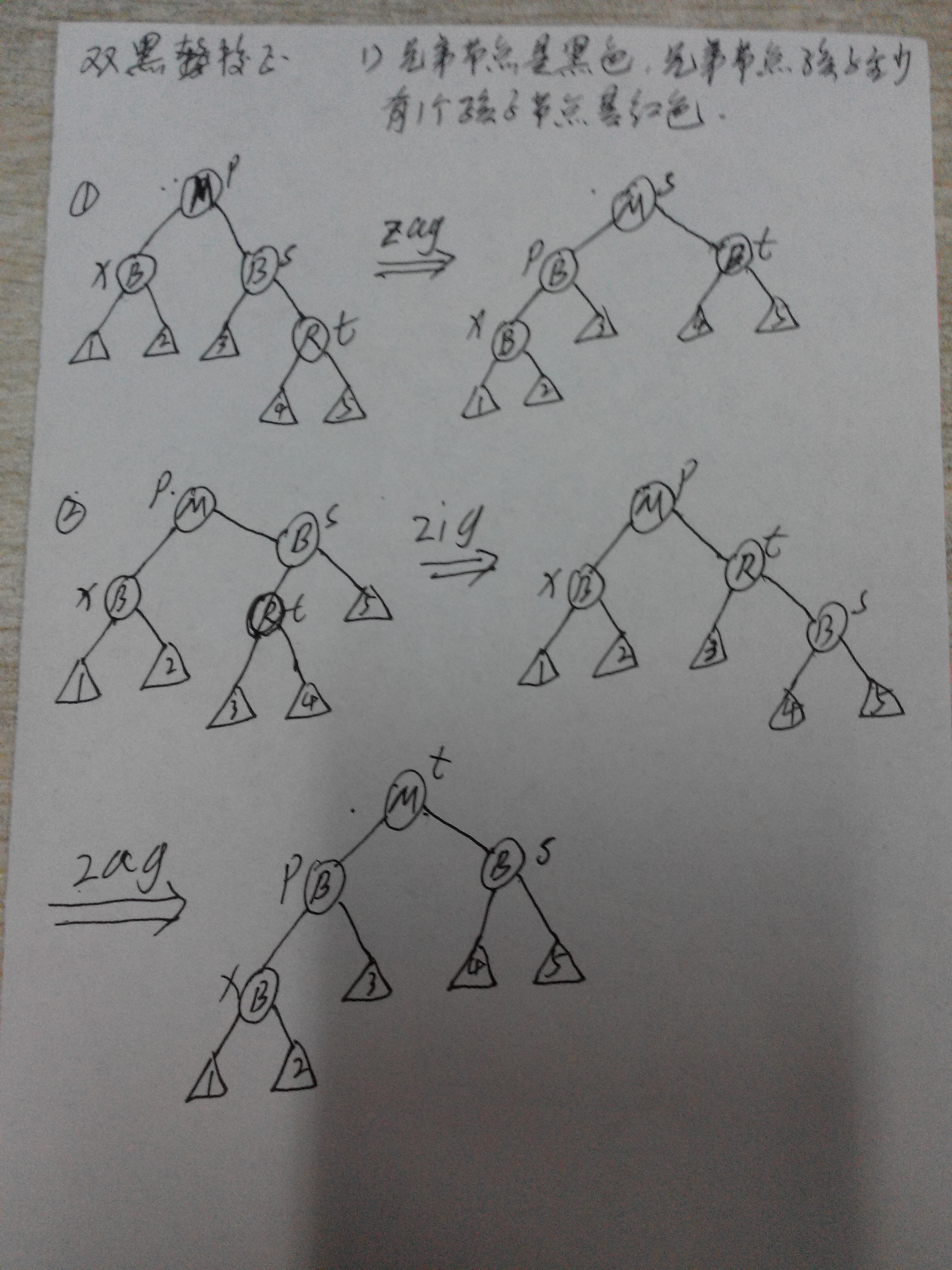
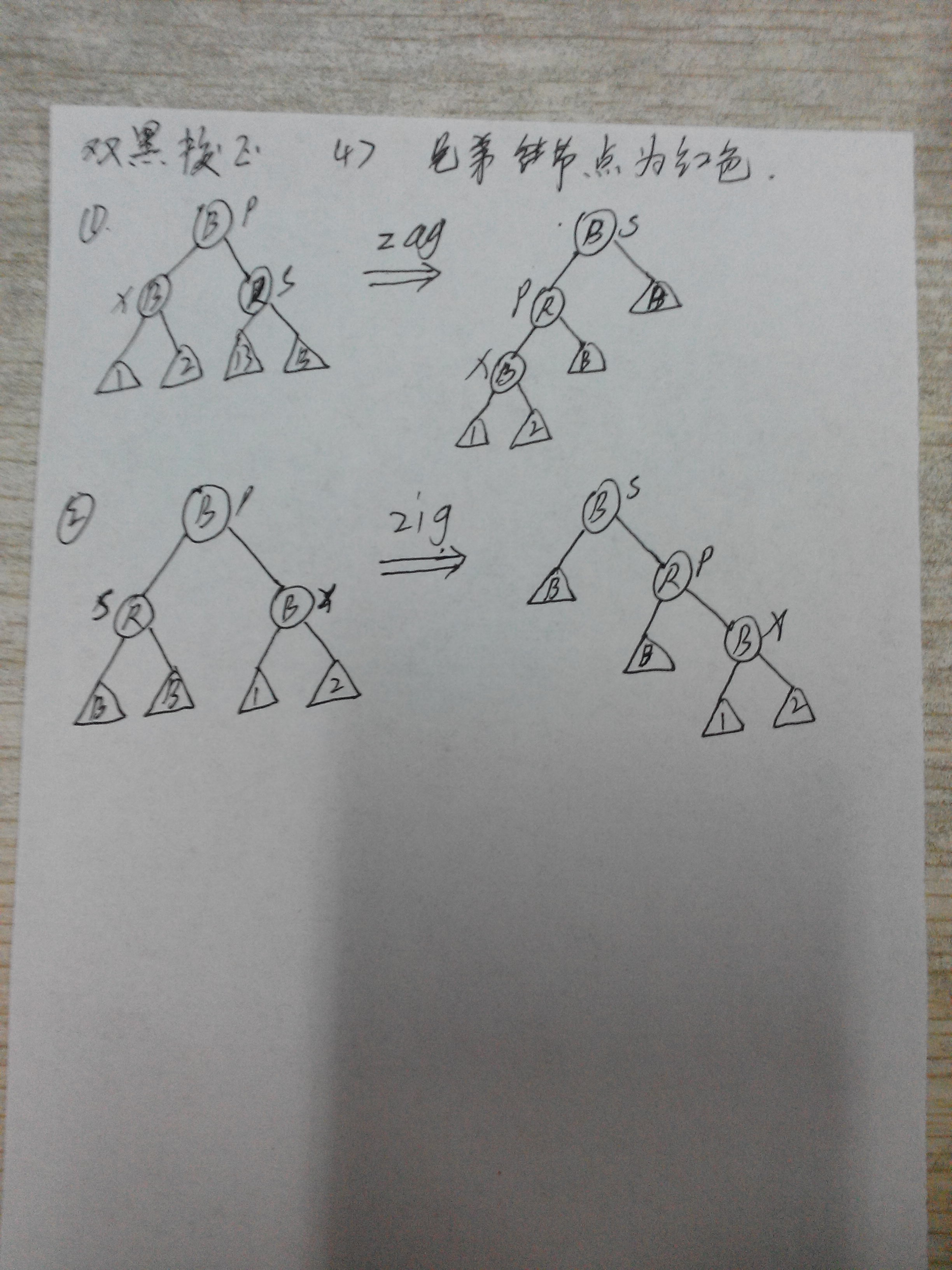
情况三、删除节点(同上)的颜色是黑色,其替代节点(同上)的颜色也是黑色,此时由于删除了一个黑色节点,因此需要进行双黑校正
双黑校正1):兄弟节点是黑色,且兄弟节点的孩子节点至少有一个节点是红色
双黑校正2):兄弟节点是黑色,且兄弟节点的孩子节点也是黑色,父节点为红色
双黑校正3):兄弟节点是黑色,且兄弟节点的孩子节点也是黑色,父节点为黑色
双黑校正4):兄弟节点为红色
五、代码
1)普通BST的代码:BST.h和BST.cpp
//<span style="font-size:14px;">BST</span>.h
#ifndef _BST_
#define _BST_
struct Node
{
int data;
Node *parent;
Node *lChild;
Node *rChild;
enum RBColor{RED,BLACK};
RBColor color;
Node(int d=0,Node* p=nullptr,Node *l=nullptr,Node *r=nullptr):data(d),parent(p),lChild(l),rChild(r),color(RED){}
~Node();
};
class BST
{
protected:
Node *root;
Node *hot;
void clear(Node *root);
void transPlant(Node *pa,Node *child);
public:
BST(Node *r=nullptr):root(r){}
Node *getRoot()
{
return root;
}
Node *nextNode(Node *curr);
void insert(int val);
Node *erase(int val);
void preOrderTraverse(Node *root);
void inOrderTraverse(Node *root);
void postOrderTraverse(Node *root);
Node *search(int val);
~BST();
};
#endif //<span style="font-size:14px;">BST</span>.cpp
#include"bst.h"
#include<iostream>
#include<stack>
using namespace std;
Node::~Node()
{
std::cout<<data<<"析构"<<std::endl;
}
void BST::insert(int val)
{
if(root==nullptr)
root=new Node(val);
Node *curr=root;
Node *p=root;
bool left;
while(curr!=NULL)
{
left=false;
p=curr;
if(val<curr->data)
{
left=true;
curr=curr->lChild;
}
else if(val>curr->data)
curr=curr->rChild;
else
return ;//表示当前value已经存在
}
if(left==true)
p->lChild=new Node(val,p);
else
p->rChild=new Node(val,p);
}
void BST::clear(Node *root)
{
if(root==NULL)
return ;
clear(root->lChild);
clear(root->rChild);
delete root;
cout<<"析构"<<endl;
}
Node * BST::search(int val)
{
Node *curr=root;
hot=root;
while(curr!=NULL)
{
hot=curr;
if(val>curr->data)
curr=curr->rChild;
else if(val<curr->data)
curr=curr->lChild;
else
return curr;
}
return nullptr;
}
BST::~BST()
{
clear(root);
}
Node * BST::nextNode(Node *curr)
{
if(curr==root && root->rChild==nullptr)//保证下面每个节点都有父节点
return nullptr;
if(curr->rChild==nullptr && curr==curr->parent->lChild)
return curr->parent;
if(curr->rChild!=nullptr)
{
Node *temp=curr->rChild;
while(temp->lChild!=nullptr)
temp=temp->lChild;
return temp;
}
if(curr==curr->parent->rChild)
{
while(curr->parent!=nullptr && curr==curr->parent->rChild)
curr=curr->parent;
return curr->parent;
}
}
void BST::transPlant(Node *curr,Node *child)
{
if(curr->parent==nullptr)
root=child;
else if(curr==curr->parent->lChild)
curr->parent->lChild=child;
else
curr->parent->rChild=child;
if(child!=nullptr)
child->parent=curr->parent;
}
Node * BST::erase(int val)
{
Node *curr=search(val);
hot=curr->parent;
Node *v=nullptr;
if(curr==nullptr)
return v;
if(curr->lChild==nullptr)//左孩子为空,则用右孩子代替
{
v=curr->rChild;
transPlant(curr,curr->rChild);
}
else if(curr->rChild==nullptr)//右孩子为空,则用左孩子代替
{
v=curr->lChild;
transPlant(curr,curr->lChild);
}
else//两个孩子都不为空
{
Node *next=nextNode(curr);
if(next->parent!=curr)//如果下一个元素不是curr的右孩子,需要维护curr的右子树
{
transPlant(next,next->rChild);
next->rChild=curr->rChild;
next->rChild->parent=next;
}
//如果下一个元素是curr的右孩子,则用右孩子代替curr节点,同时维护curr的左子树
transPlant(curr,next);
next->lChild=curr->lChild;
next->lChild->parent=next;
v=next;
}
if(v)
hot=v->parent;
delete curr;
return v;
}
void BST::preOrderTraverse(Node *root)
{
if(root==nullptr)
return ;
stack<Node *> s;
s.push(root);
while(!s.empty())
{
Node *temp=s.top();
cout<<temp->data<<endl;
s.pop();
if(temp->rChild!=nullptr)
s.push(temp->rChild);
if(temp->lChild!=nullptr)
s.push(temp->lChild);
}
}
void BST::inOrderTraverse(Node *root)
{
if(root==nullptr)
return ;
stack<Node *> s;
Node *curr=root;
while(curr!=nullptr)
{
s.push(curr);
curr=curr->lChild;
}
while(!s.empty())
{
curr=s.top();
cout<<curr->data<<endl;
s.pop();
if(curr->rChild!=nullptr)
{
curr=curr->rChild;
while(curr!=nullptr)
{
s.push(curr);
curr=curr->lChild;
}
}
}
}
void BST::postOrderTraverse(Node *root)
{
if(root==nullptr)
return ;
stack<Node *> s;
Node *prev=nullptr;//保存前一时刻访问的节点
Node *curr=root;
while(curr!=nullptr)
{
s.push(curr);
curr=curr->lChild;
}
while(!s.empty())
{
curr=s.top();
if(curr->rChild==prev)
{
cout<<curr->data<<endl;
s.pop();
prev=curr;
}
else
{
curr=curr->rChild;
while(curr!=nullptr)
{
s.push(curr);
curr=curr->lChild;
}
prev=nullptr;
}
}
}
//RBTree.h
#ifndef __RBTree__
#define __RBTree__
#include"BST.h"
class RBTree:public BST
{
void solveDoubleRed(Node *x);
void solveDoubleBlack(Node *x);
Node* rotateAt(Node *x);
Node* connect34(Node *a,Node *b,Node *c,Node *T0,Node *T1,Node *T2,Node *T3);
public:
RBTree()
{
root=nullptr;
}
Node *getRoot()
{
return root;
}
Node *insert(int e);
bool remove(int e);
};
#endif//RBTree.cpp
#include"RBTree.h"
Node *RBTree::insert(int e)
{
Node *v=search(e);
if(v)
return v;
Node *x=new Node(e,hot);
if(hot==nullptr)
root=x;
else if(hot->data>e)
hot->lChild=x;
else
hot->rChild=x;
solveDoubleRed(x);
return x;
}
void RBTree::solveDoubleRed(Node *x)
{
if(x==root)
{
x->color=Node::BLACK;
return ;
}
if(x->parent->color==Node::BLACK)
return ;
Node *p=x->parent;
Node *g=p->parent;//既然p为红,则其必然有父亲
Node *uncle=(p==g->lChild)?g->rChild:g->lChild;
if(uncle==nullptr || uncle->color==Node::BLACK)
{
if((x==p->lChild && p==g->lChild) || (x==p->rChild && p==g->rChild))//x与p同侧
p->color=Node::BLACK;
else//x与p异侧
x->color=Node::BLACK;
g->color=Node::RED;
Node *gg=g->parent;
bool left=false;
if(gg && g==gg->lChild)
left=true;
Node *r=rotateAt(x);//这里已经把p,g,x的拓扑结构都改变了
// r->parent=gg;//这个在rotateAt函数中已经做过了
if(gg==nullptr)
root=r;
else if(left)
gg->lChild=r;
else
gg->rChild=r;
}
else
{
uncle->color=Node::BLACK;
g->color=Node::RED;
x->parent->color=Node::BLACK;
x=g;
solveDoubleRed(x);
}
}
Node *RBTree::rotateAt(Node *x)
{
Node *p=x->parent,*g=p->parent;
if(p==g->lChild)
{
if(x==p->lChild)//zig
{
p->parent=g->parent;
return connect34(x,p,g,x->lChild,x->rChild,p->rChild,g->rChild);
}
else//zag-zig
{
x->parent=g->parent;
return connect34(p,x,g,p->lChild,x->lChild,x->rChild,g->rChild);
}
}
else
{
if(x==p->rChild)//zag
{
p->parent=g->parent;
return connect34(g,p,x,g->lChild,p->lChild,x->lChild,x->rChild);
}
else//zag-zig
{
x->parent=g->parent;
return connect34(g,x,p,g->lChild,x->lChild,x->rChild,p->rChild);
}
}
}
Node* RBTree::connect34(Node *a,Node *b,Node *c,Node *T0,Node *T1,Node *T2,Node *T3)
{
a->lChild=T0;
a->rChild=T1;
if(a->lChild) a->lChild->parent=a;
if(a->rChild) a->rChild->parent=a;
c->lChild=T2;
c->rChild=T3;
if(c->lChild) c->lChild->parent=c;
if(c->rChild) c->rChild->parent=c;
b->lChild=a;
b->rChild=c;
a->parent=b;
c->parent=b;
return b;
}
bool RBTree::remove(int e)
{
Node *x=search(e);//保存当前节点的颜色
if(!x)
return false;//不存在e
Node::RBColor oldColor=x->color;
Node *r=erase(e);//保存删除x后替代x的节点
if(root==nullptr)
return true;
if(!hot)//hot保存r的父节点
{
root=r;
root->color=Node::BLACK;
return true;
}
if(oldColor==Node::RED)
return true;//直接删除,不需要修正
else
{
if(r && r->color==Node::RED)
{
r->color=Node::BLACK;
}
else//如果r为NULL或者r为黑色
solveDoubleBlack(r);
}
return true;
}
void RBTree::solveDoubleBlack(Node *r)
{
Node *p=r?r->parent:hot;
if(!p)//p为空则r必然为根节点
return ;
Node *s=(r==p->lChild)?p->rChild:p->lChild;
if(s->color==Node::BLACK)
{
Node *t=nullptr;
if(s->lChild!=nullptr && s->lChild->color==Node::RED)
t=s->lChild;
else if(s->rChild!=nullptr && s->rChild->color==Node::BLACK)
t=s->rChild;
if(t)//s至少有一个红孩子
{
Node::RBColor oldColor=p->color;
Node *gg=p->parent;
bool left=false;
if(gg && p==gg->lChild)
left=true;
Node *b=rotateAt(t);
if(gg==nullptr)
root=b;
else if(left)
gg->lChild=b;
else
gg->rChild=b;
b->lChild->color=Node::BLACK;
b->rChild->color=Node::BLACK;
b->color=oldColor;
}
else//s只有黑孩子
{
s->color=Node::RED;
if(p->color==Node::BLACK)
solveDoubleBlack(p);
else
p->color=Node::BLACK;
}
}
else//s是红色的
{
p->color=Node::RED;
s->color=Node::BLACK;
//注意:t必然不是外部节点,即s的两个孩子都非空!!如果有一个为空,则另一个必然为空,
//这样从p到外部节点的黑高度为1,而从p到r的黑高度也是1,因此就不存在双黑修正的问题了
Node *t=(s==p->lChild)?s->lChild:s->rChild;
Node *gg=p->parent;
bool left=false;
if(gg && p==gg->lChild)
left=true;
Node *b=rotateAt(t);
if(gg==nullptr)
root=b;
else if(left)
gg->lChild=b;
else
gg->rChild=b;
solveDoubleBlack(r);
}
}
#include<iostream>
#include"BST.h"
#include"RBTree.h"
using namespace std;
int main()
{
RBTree rbt;
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++)
rbt.insert(i);
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++)
rbt.remove(i);
system("pause");
return 0;
}























 1184
1184

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








