|
Language:
Square Destroyer
Description
The left figure below shows a complete 3*3 grid made with 2*(3*4) (=24) matchsticks. The lengths of all matchsticks are one. You can find many squares of different sizes in the grid. The size of a square is the length of its side. In the grid shown in the left figure, there are 9 squares of size one, 4 squares of size two, and 1 square of size three.
Each matchstick of the complete grid is identified with a unique number which is assigned from left to right and from top to bottom as shown in the left figure. If you take some matchsticks out from the complete grid, then some squares in the grid will be destroyed, which results in an incomplete 3*3 grid. The right figure illustrates an incomplete 3*3 grid after removing three matchsticks numbered with 12, 17 and 23. This removal destroys 5 squares of size one, 3 squares of size two, and 1 square of size three. Consequently, the incomplete grid does not have squares of size three, but still has 4 squares of size one and 1 square of size two. 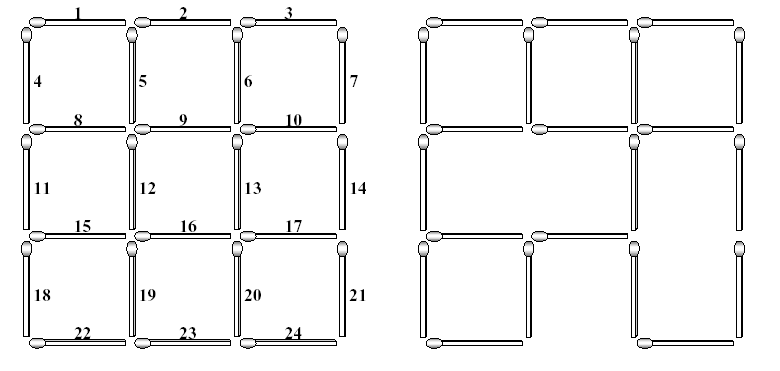
As input, you are given a (complete or incomplete) n*n grid made with no more than 2n(n+1) matchsticks for a natural number 5 <= n . Your task is to compute the minimum number of matchsticks taken out to destroy all the squares existing in the input n*n grid. Input
The input consists of T test cases. The number of test cases (T ) is given in the first line of the input file.
Each test case consists of two lines: The first line contains a natural number n , not greater than 5, which implies you are given a (complete or incomplete) n*n grid as input, and the second line begins with a nonnegative integer k , the number of matchsticks that are missing from the complete n*n grid, followed by k numbers specifying the matchsticks. Note that if k is equal to zero, then the input grid is a complete n*n grid; otherwise, the input grid is an incomplete n*n grid such that the specified k matchsticks are missing from the complete n*n grid. Output
Print exactly one line for each test case. The line should contain the minimum number of matchsticks that have to be taken out to destroy all the squares in the input grid.
Sample Input 2 2 0 3 3 12 17 23 Sample Output 3 3 |
题意:用火叉棒摆成正方形,然后问最少拿掉多少根能拍坏掉所有的正方形
思路:DLX转化成精确覆盖模型,这题麻烦的是如何确定哪根火柴会影响哪个正方形,参考了kuangbin大神的博客,然后就是套模板了
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<string>
#include<cstring>
#include<vector>
#include<cmath>
#include<queue>
#include<stack>
#include<map>
#include<set>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=200;
const int maxm=200;
const int maxnode=maxn*maxm;
const int INF=1000000000;
bool f[maxn];
int b[maxn];
int n,m;
int id[20][20];
int a[20][20][20];
struct DLX
{
int n,m,size;
int U[maxnode],D[maxnode],R[maxnode],L[maxnode];
int H[maxn],S[maxm];
int row[maxnode],col[maxnode];
int ansd,ans[maxn];
bool vis[maxnode];
void init(int N,int M)
{
n=N,m=M;
ansd=INF;
for(int i=0;i<=m;i++)
{
S[i]=0;
U[i]=D[i]=i;
L[i]=i-1;
R[i]=i+1;
}
L[0]=m,R[m]=0;
size=m;
for(int i=0;i<=n;i++)H[i]=-1;
}
void Link(int r,int c)
{
++S[col[++size]=c];
row[size]=r;
D[size]=D[c];
U[size]=c;
U[D[c]]=size;
D[c]=size;
if(H[r]<0)H[r]=R[size]=L[size]=size;
else
{
R[size]=R[H[r]];
L[size]=H[r];
L[R[H[r]]]=size;
R[H[r]]=size;
}
}
void remove(int c)
{
for(int i=D[c];i!=c;i=D[i])
L[R[i]]=L[i],R[L[i]]=R[i];
}
void restore(int c)
{
for(int i=U[c];i!=c;i=U[i])
L[R[i]]=R[L[i]]=i;
}
int f()
{
memset(vis,0,sizeof(vis));
int cnt=0;
for(int i=R[0];i;i=R[i])
{
if(!vis[i])
{
cnt++;vis[i]=1;
for(int j=D[i];j!=i;j=D[j])
for(int k=R[j];k!=j;k=R[k])
vis[col[k]]=1;
}
}
return cnt;
}
void Dance(int d)
{
if(d+f()>=ansd)return;
if(R[0]==0)
{
if(ansd>d)ansd=d;
return;
}
int c=R[0];
for(int i=R[0];i;i=R[i])
if(S[i]<S[c])c=i;
for(int i=D[c];i!=c;i=D[i])
{
remove(i);
for(int j=R[i];j!=i;j=R[j])remove(j);
Dance(d+1);
for(int j=L[i];j!=i;j=L[j])restore(j);
restore(i);
}
}
}dlx;
int main()
{
int T,v;
scanf("%d",&T);
while(T--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
int tot=(2*n+1)*n+n;
for(int i=1;i<=tot;i++)f[i]=true;
scanf("%d",&m);
while(m--)
{
scanf("%d",&v);
f[v]=false;
}
int num=0;
memset(id,-1,sizeof(id));
for(int i=1;i<=n+1;i++)//给每条边编号,一行分为横着的和竖着的
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
id[2*i-1][j]=(++num);
if(i<=n)
{
for(int j=0;j<=n;j++)
id[2*i][j]=(++num);
}
}
int cnt=0;
for(int i=1;i<=tot;i++)//把原图中剩下的重新编号
if(f[i])b[i]=(++cnt);
num=0;
memset(a,-1,sizeof(a));
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)//记录每个小正方形关联的长度为k的正方形编号
{
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
{
for(int k=1;i+k-1<=n&&j+k-1<=n;k++)
{
bool flag=true;
for(int x=0;x<k;x++)
if(!f[id[2*i-1][j+x]]){flag=false;break;}
for(int x=0;x<k;x++)
if(!f[id[2*(i+k-1)+1][j+x]])
{flag=false;break;}
for(int x=0;x<k;x++)
if(!f[id[2*(i+x)][j-1]])
{flag=false;break;}
for(int x=0;x<k;x++)
if(!f[id[2*(i+x)][j+k-1]])
flag=false;
if(!flag)continue;
a[i][j][k]=(++num);
}
}
}
dlx.init(cnt,num);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++)
for(int k=1;i+k-1<=n&&j+k-1<=n;k++)
if(a[i][j][k]!=-1)
{
for(int x=0;x<k;x++)
{
dlx.Link(b[id[2*i-1][j+x]],a[i][j][k]);
dlx.Link(b[id[2*(i+k-1)+1][j+x]],a[i][j][k]);
dlx.Link(b[id[2*(i+x)][j-1]],a[i][j][k]);
dlx.Link(b[id[2*(i+x)][j+k-1]],a[i][j][k]);
}
}
dlx.Dance(0);
printf("%d\n",dlx.ansd);
}
return 0;
}






















 307
307

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








