android sparseArray源码解析
step1:背景
今天偶然看到了sparseArray,发现其主要是针对<(Integer,obj>的类型进行了优化,何为sparse?是稀疏的意思。指的是对稀疏数组情况的讨论
所谓稀疏数组:
* 就是数组中大部分的内容值都未被使用(或都为零),在数组中仅有少部分的空间使用。因此造成内存空间的浪费,为了节省内存空间,并且不影响数组中原有的内容值,我们可以采用一种压缩的方式来表示稀疏数组的内容。
step2:上源码
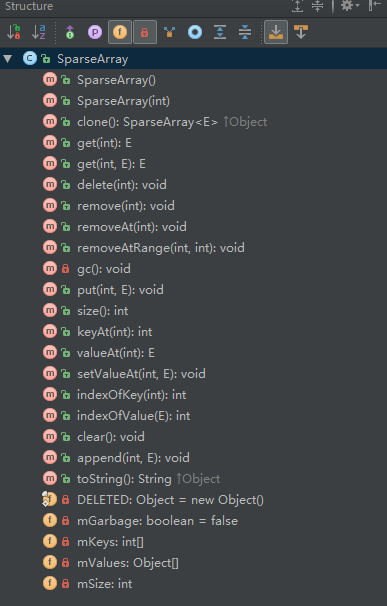
- 类结构图
- 构造函数
SparseArray(int)可以指定容量
public SparseArray(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity == 0) {
mKeys = EmptyArray.INT;
mValues = EmptyArray.OBJECT;
} else {
mValues = ArrayUtils.newUnpaddedObjectArray(initialCapacity);
mKeys = new int[mValues.length];
}
mSize = 0;
}- 它有两个方法可以添加键值对
- 1.put(int key, E value)
/**
* 朝map里面加入key,value的数据,如果key存在,替换操作
*/
public void put(int key, E value) {
//二分查找,具体看step3
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
if (i >= 0) {
mValues[i] = value;//找到,说明之前存在
} else {
i = ~i;//为负说明没找到
if (i < mSize && mValues[i] == DELETED) {
mKeys[i] = key;
mValues[i] = value;//添加key位置的value被删除了
return;
}
//需要gc或者是当前数组大小越界了
if (mGarbage && mSize >= mKeys.length) {
gc();//gc()
// gc后index变化了,需要重新查找
i = ~ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
}
//插入key和value到指定位置
mKeys = GrowingArrayUtils.insert(mKeys, mSize, i, key);//
mValues = GrowingArrayUtils.insert(mValues, mSize, i, value);
mSize++;//当前大小+1
}
}* 2.append(int key, E value)
public void append(int key, E value) {
if (mSize != 0 && key <= mKeys[mSize - 1]) {
put(key, value);
return;
}
if (mGarbage && mSize >= mKeys.length) {
gc();
}
mKeys = GrowingArrayUtils.append(mKeys, mSize, key);
mValues = GrowingArrayUtils.append(mValues, mSize, value);
mSize++;
}- 有四个方法可以执行删除操作:
- 1.delete(int key)
/**
* 移除指定key的value
*/
public void delete(int key) {
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
if (i >= 0) {
if (mValues[i] != DELETED) {
mValues[i] = DELETED;//标记为DELETED
mGarbage = true;
}
}
}* 2.remove(int key)
public void remove(int key) {
delete(key);
}* 3. removeAt(int index)
/**
* Removes the mapping at the specified index.
*/
public void removeAt(int index) {
if (mValues[index] != DELETED) {
mValues[index] = DELETED;
mGarbage = true;
}
}* 4.removeAtRange(int index, int size)
//移除index之后的size个元素
public void removeAtRange(int index, int size) {
final int end = Math.min(mSize, index + size);
for (int i = index; i < end; i++) {
removeAt(i);
}
}step3:Util函数支持
put(int key, E value) 中出现了3个函数,现在我们一一解析
1)ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
2)gc();
3)GrowingArrayUtils.insert(mKeys, mSize, i, key);
* ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
static int binarySearch(int[] array, int size, int value) {
int lo = 0;
int hi = size - 1;
//说明array是排号序的,那么他们在哪里排序,在insert的时候排的
while (lo <= hi) {
final int mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
final int midVal = array[mid];
if (midVal < value) {
lo = mid + 1;
} else if (midVal > value) {
hi = mid - 1;
} else {
return mid; // value found
}
}
return ~lo; // value not present
}- GrowingArrayUtils.insert(mKeys, mSize, i, key);
public static int[] insert(int[] array, int currentSize, int index, int element) {
assert currentSize <= array.length;
if (currentSize + 1 <= array.length) {//增加一个不越界的情况
System.arraycopy(array, index, array, index + 1, currentSize - index);
array[index] = element;
return array;
}
int[] newArray = ArrayUtils.newUnpaddedIntArray(growSize(currentSize));//数组扩容
System.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, index);
newArray[index] = element;
System.arraycopy(array, index, newArray, index + 1, array.length - index);
return newArray;
}- 3)gc
private void gc() {
// Log.e("SparseArray", "gc start with " + mSize);
int n = mSize;
int o = 0;
int[] keys = mKeys;
Object[] values = mValues;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Object val = values[i];
if (val != DELETED) {
if (i != o) {
keys[o] = keys[i];
values[o] = val;
values[i] = null;//value置空
}
o++;
}
}
mGarbage = false;
mSize = o;
// Log.e("SparseArray", "gc end with " + mSize);
}总结:
SparseArray是android里为(Interger,Object)这样的Hashmap而专门写的类,目的是提高内存效率,其核心是折半查找函数(binarySearch)。注意内存二字很重要,因为它仅仅提高内存效率,而不是提高执行效率,所以也决定它只适用于android系统(内存对android项目有多重要,地球人都知道)。SparseArray有两个优点:1.避免了自动装箱(auto-boxing),2.数据结构不会依赖于外部对象映射。我们知道HashMap 采用一种所谓的“Hash 算法”来决定每个元素的存储位置,存放的都是数组元素的引用,通过每个对象的hash值来映射对象。而SparseArray则是用数组数据结构来保存映射,然后通过折半查找来找到对象。但其实一般来说,SparseArray执行效率比HashMap要慢一点,因为查找需要折半查找,而添加删除则需要在数组中执行,而HashMap都是通过外部映射。但相对来说影响不大,最主要是SparseArray不需要开辟内存空间来额外存储外部映射,从而节省内存。






















 326
326

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








