题目描述:
输入一课二叉树和一个整数,打印出二叉树中结点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。从树的根结点开始往下一直到叶结点所经过的结点形成一条路径。
解题思路:
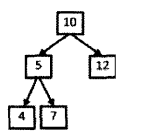
先模拟一下过程:树的结构如下所示,期待路径的和为22
10→5→4是一条路径,它们的和不是22。所以下一条路径10→5→7,(这是一种回溯的方法),它们的和22,然后回溯,下一条路径10→12。这里我们只有到叶子结点才有必要判断和是否等于期待的数值。
首先需要选择一种遍历方式,一定是深度优先,进一步要先访问根结点,所以选择先序遍历。
然后是选择一种数据结构保存路径,因为回溯的话肯定是要知道之前的结点的。一般采用栈结构,但是这里注意一点就是题目中要求打印路径,而打印栈中的元素是要出栈的,所以我们可以用普通的链表模仿栈的行为。
代码如下:
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
public class FindPathTest {
static class Node{
int key;
Node left;
Node right;
Node(int key){
this.key = key;
}
}
public static void findPath(Node root, int expect){
if(root == null){
return;
}
List<Node> path = new LinkedList<Node>();
int currentSum = 0;
findPath(root, expect, path, currentSum);
}
private static void findPath(Node node, int expect, List<Node> path,
int currentSum) {
currentSum += node.key;
path.add(node);
if(node.left == null && node.right == null && currentSum == expect){
System.out.println("A path is found : ");
for(Node n : path){
System.out.print(n.key + " ");
}
System.out.println("");
}
if(node.left != null){
findPath(node.left, expect, path, currentSum);
}
if(node.right != null){
findPath(node.right, expect, path, currentSum);
}
path.remove(path.size() - 1);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Node root = new Node(8);
Node node8 = new Node(8);
Node node7 = new Node(7);
root.left = node8;
root.right = node7;
Node node9 = new Node(9);
node8.left = node9;
Node node2 = new Node(2);
node8.right = node2;
Node node4 = new Node(4);
Node node72 = new Node(7);
node2.left = node4;
node2.right = node72;
findPath(root, 15);
}
}






















 1488
1488

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








