看标题,有人会问,这是啥子怪需求? 艺术源于生活,同理, 标题来源于需求。
需求
- 捕获class所有的方法(同步 + 异步)的异常,
- 并能给出异常上下文, 比如业务类别。
运行时,class的方法出现异常,可能导致整个程序都运行不了,如果能捕获,至少能保障整个程序还Ok。
比如如下代码, 能捕获 staticMethod 和 testMethod 两个方法
class TestClass {
private name: string = 'name';
public static staticName: string = 'staticName';
static staticMethod() {
console.log('this === TestClass:', this === TestClass);
console.log("staticName:", this.staticName);
throw new Error("test staticMethod error");
}
async testMethod(data: any) {
console.log("this.name", this.name);
throw new Error("test error");
}
}
(new TestClass()).testMethod({ name: "test" });
console.log("----------------------------------")
TestClass.staticMethod();
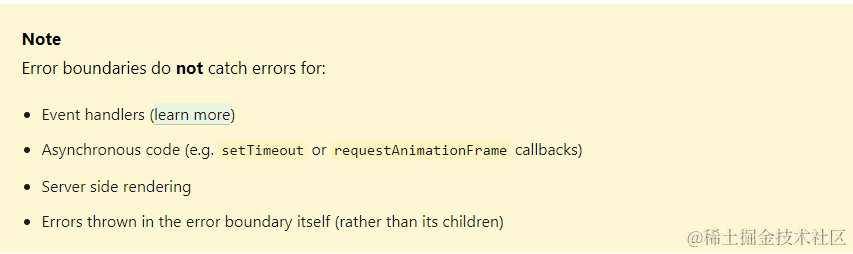
提一下react, 虽然有 Error Boundaries 能捕获错误,但是其中最常见的事件处理是不在名单中的,
思路
交给最后一道屏障
在浏览器中,如果想捕获这些错误倒是不难,内置了同步和异步方法异常的捕获能力。
window.onerror = function (event, source, lineno, colno, error) {
console.log("onerror", event, source, lineno, colno, error)
}
window.addEventListener("error", ev => {
console.log("error:", ev);
})
window.addEventListener("unhandledrejection", ev => {
console.log("unhandledrejection:", ev);
})
但是现在的代码一般都是混淆压缩后的,提供的信息可能不尽人意。
比如想知道报错的方法信息,业务类别等等。
AST
直接编译层面去处理。 但是可能也需要开发者去配合设置一些信息。 不失为一种手段。
装饰器
装饰器 分为好几种
- 类
- 类的属性
- 类的方法
- 属性存取器(accessor)
如果每个方法都要去加上一个装饰器,不友好,工作量也不小。
如果仅仅需要添加一个类装饰器,这个代价是可以接受的。
其他
- 嗯,没错,其他
基于类装饰器的实现
整个实现过程中主要有两点略微复杂一点
- 识别同步方法和异步方法
- 如何通过class装饰器获取和监听静态方法和实例方法
识别同步方法和异步方法
事情的发生都会存在 事前, 事中, 事后。 方法的调用也是如此,所以方法的识别也是如此。
- 调用前识别
一种简单的方式就是利用Object.prototype.toString
const f = async function(){}
Object.prototype.toString.call(f) === '[object AsyncFunction]' // true
完善的识别,可以参考 is-async-function
- 调用后识别,如果方法返回后的值是一个Promise的实例,那么该方法就是异步方法。
简单的逻辑:
const f = async function(){}
f() instanceof Promise // true
完整的识别可以参考 p-is-promise
通过class装饰器获取静态方法和实例方法
装饰器的语法有新旧版本,旧版本只能说一言难尽,新版本,值得一试。
所以,讲的是新版本,详情参见 阮大神的 类装饰器(新语法)
有一个很重要的规则: 类装饰器可以返回一个新的类,取代原来的类,也可以不返回任何值。。
除此之外有一个重要的逻辑:
class上的非静态方法是本质是原型上的方法,但是方法可以实例化多次,不同实例方法调用的上下文是不一样的,要获取不同实例化的上下文,就要能监听到calss的实例化,即构造过程。
有些同志可能想到去代理 constructor 方法,实际上因为其特殊性,不能被代理。
所以,思路还是 前面提到的重要规则。
通过class装饰器获取静态方法和实例方法
拦截class,返回新的class
这样才具备了,获取class每次实例化的实例对象即this.
class NewClass extends OriClass {
constructor(...args: any[]) {
super(...args);
// 调用的时候this为实例,方法是原型上的方法
const instance = this;
const proto = geOriginalPrototype(instance, OriClass);
proxyInstanceMethods(instance, proto);
}
}
静态方法
对于静态方法来说,还是比较好拦截的:
- 遍历属性,
- 检查白名单
- 代理方法(本质只是调用并拦截错误)
// 静态方法 代理, 代理的是原Class的方法,传递的thisObject是NewClass
context.addInitializer(function () {
dataStore.updateClassConfig(OriClass, config);
// 静态方法
Reflect.ownKeys(OriClass).filter(name => {
// 白名单检查
const isInWhitelist = checkIsInWhitelist(name, whiteList);
return !isInWhitelist && typeof OriClass[name] === 'function'
}).forEach(name => {
const method = OriClass[name] as Function;
// 监听调用和捕获异常
tryProxyMethod(method, name, OriClass, OriClass, NewClass, creatorOptions, () => {
// 存储相关信息
dataStore.updateStaticMethodConfig(OriClass, method, {
config: {
isStatic: true
}
});
})
})
});
非静态方法
这里的proxyInstanceMethods要结合之前的重写class的代码一起看,其是在构造函数中执行的。
// 原型(非静态)方法
function proxyInstanceMethods(instance: any, proto: any) {
Reflect.ownKeys(proto).filter(name => {
// 白名单
const isInWhitelist = checkIsInWhitelist(name, whiteList);
return !isInWhitelist && typeof proto[name] === 'function'
}).forEach(name => {
const method = proto[name] as Function;
// 监听调用和捕获异常
tryProxyMethod(method, name, proto, OriClass, instance, creatorOptions, () => {
//存储相关信息
dataStore.updateMethodConfig(OriClass, method, {
config: {
isStatic: false
}
});
})
})
}
完整的装饰器代码
function autoCatchMethods(
OriClass: any,
context: ClassDecoratorContext<any>,
creatorOptions: CreateDecoratorOptions,
config: ClassCatchConfig
) {
const { dataStore, logger } = creatorOptions;
OriClass[SYMBOL_CLASS_BY_PROXY_FLAG] = true;
class NewClass extends OriClass {
constructor(...args: any[]) {
super(...args);
// 调用的时候this为实例,方法是原型上的方法
const instance = this;
const proto = geOriginalPrototype(instance, OriClass);
proxyInstanceMethods(instance, proto);
}
}
// this: class
// target: class
// context: demo '{"kind":"class","name":"Class的Name"}'
logger.log("classDecorator:", OriClass.name);
const whiteList = METHOD_WHITELIST.concat(... (config.whiteList || []))
// 静态方法 代理, 代理的是原Class的方法,传递的thisObject是NewClass
context.addInitializer(function () {
dataStore.updateClassConfig(OriClass, config);
// 静态方法
Reflect.ownKeys(OriClass).filter(name => {
// 白名单检查
const isInWhitelist = checkIsInWhitelist(name, whiteList);
return !isInWhitelist && typeof OriClass[name] === 'function'
}).forEach(name => {
const method = OriClass[name] as Function;
// 监听调用和捕获异常
tryProxyMethod(method, name, OriClass, OriClass, NewClass, creatorOptions, () => {
// 存储相关信息
dataStore.updateStaticMethodConfig(OriClass, method, {
config: {
isStatic: true
}
});
})
})
});
// 原型(非静态)方法
function proxyInstanceMethods(instance: any, proto: any) {
Reflect.ownKeys(proto).filter(name => {
// 白名单
const isInWhitelist = checkIsInWhitelist(name, whiteList);
return !isInWhitelist && typeof proto[name] === 'function'
}).forEach(name => {
const method = proto[name] as Function;
// 监听调用和捕获异常
tryProxyMethod(method, name, proto, OriClass, instance, creatorOptions, () => {
//存储相关信息
dataStore.updateMethodConfig(OriClass, method, {
config: {
isStatic: false
}
});
})
})
}
return NewClass;
}
export function createClassDecorator(creatorOptions: CreateDecoratorOptions) {
return function classDecorator(config: ClassCatchConfig = DEFAULT_CONFIG): any {
return function (
target: Function,
context: ClassDecoratorContext<any>
) {
const { dataStore, logger } = creatorOptions;
if (context.kind !== "class") {
throw new Error("classDecorator 只能用于装饰class");
}
// this: class
// target: class
// context: demo '{"kind":"class","name":"Class的Name"}'
// 自动捕获 非静态(原型)方法 和 静态方法
if (!!config.autoCatchMethods) {
// 通过Class的继承监听构造函数,会返回新的 Class
const NewClass = autoCatchMethods(target, context, creatorOptions, config)
return NewClass;
} else {
logger.log("classDecorator:", target.name);
context.addInitializer(function () {
const _class_ = target;
dataStore.updateClassConfig(_class_, config);
});
}
};
};
}
实际效果
普通class
import { createInstance } from "../src/index"
const { classDecorator, methodDecorator } = createInstance({
defaults: {
handler(params) {
console.log(`default error handler:: function name : ${params.func?.name}, isStatic: ${params.isStatic}`);
},
}
});
@classDecorator({
autoCatchMethods: true,
handler(params) {
console.log(`classDecorator error handler:: function name : ${params.func?.name}, isStatic: ${params.isStatic}`);
// 返回 false ,表示停止冒泡
return false;
}
})
class TestClass {
private name: string = 'name';
public static staticName: string = 'staticName';
static staticMethod() {
console.log('this === TestClass:', this === TestClass);
console.log("staticName:", this.staticName);
throw new Error("test staticMethod error");
}
async testMethod(data: any) {
console.log("this.name", this.name, data);
throw new Error("test error");
}
}
(new TestClass()).testMethod({ name: "test" });
console.log("----------------------------------")
TestClass.staticMethod();
执行结果:
this.name name { name: 'test' }
----------------------------------
this === TestClass: true
staticName: staticName
classDecorator error handler:: function name : staticMethod, isStatic: true
classDecorator error handler:: function name : testMethod, isStatic: false
class 继承
import { classDecorator, methodDecorator, setConfig } from "../src";
setConfig({
handler(params) {
console.log(`error handler:: function name : ${params.func?.name}, isStatic: ${params.isStatic}`);
}
})
@classDecorator({
autoCatchMethods: true,
chain: true
})
class SuperClass {
private superMethodName = 'superMethodName';
static superStaticMethodName = 'staticMethodName';
superMethod() {
console.log('superMethod superMethodName', this.superMethodName);
throw new Error('superMethod');
}
static superStaticMethod() {
console.log('superStaticMethod superStaticMethodName', this.superStaticMethodName);
throw new Error('superStaticMethod');
}
}
@classDecorator({
autoCatchMethods: true
})
class SubClass extends SuperClass {
private subMethodName = 'subMethodName';
static subStaticMethodName = 'subStaticMethodName';
subMethod() {
console.log('subMethod subMethodName', this.subMethodName);
throw new Error('superMethod');
}
static subStaticMethod() {
console.log('subStaticMethod methodName', this.subStaticMethodName);
throw new Error('superStaticMethod');
}
}
const subClass = new SubClass();
subClass.superMethod();
subClass.subMethod();
try {
SubClass.superStaticMethod();
SubClass.subStaticMethod();
} catch (err: any) {
console.log('SubClass.superStaticMethod: error', err && err.message);
}
执行结果:
superMethod superMethodName superMethodName
error handler:: function name : superMethod, isStatic: false
subMethod subMethodName subMethodName
error handler:: function name : subMethod, isStatic: false
superStaticMethod superStaticMethodName staticMethodName
error handler:: function name : superStaticMethod, isStatic: true
subStaticMethod methodName subStaticMethodName
error handler:: function name : subStaticMethod, isStatic: true
源码
接下来
仔细的同学从上面的输出结果会发现一些问题,按住不表。
这一套class的方法拦截方式是通用,其可以拓展到很多地方。
TODO::
- 完善
- 分离装饰器后面的dataStore,变为通用的装饰器配置存储。
- 实现类似插件的方式,来增强装饰器
- 寻找更多合适的落地场景
写在最后
谢谢观看,你的一评一赞是我更新的最大动力。






















 4910
4910

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








