1.简述
组建iscsi网络三种target工具,分别为tgt,iscsi_tgt和targetcli ,之前已经介绍过targetcli 组装iscsi方法,此文重点介绍tgtadm的配置方法。
2.安装服务
#1.安装和配置网络存储服务器tgtadm
yum install scsi-target-utils
#2.启动tgtd服务
service tgtd start
3.基本配置
#1.创建tgtadm
tgtadm --lld iscsi --op new --mode target --tid 2 -T iqn.2021-10.com.happynas.alilu:iscsi-1
#2.查看tgtadm
tgtadm --lld iscsi --op show --mode target
#3.添加磁盘到
tgtadm --lld iscsi --op new --mode logicalunit --tid 1 --lun 1 -b /dev/sdb1
tgtadm --lld iscsi --op new --mode logicalunit --tid 1 --lun 2 -b /dev/sdc1
tgtadm --lld iscsi --op new --mode logicalunit --tid 1 --lun 3 -b /dev/md0_vg/zfg_lv
#4.授权一个网段可以访问
tgtadm --lld iscsi --op bind --mode target --tid 1 -I 192.168.80.0/24
#所有设备都可访问
tgtadm -L iscsi -o bind -m target -t 1 -I ALL
#5.其他配置
#查看服务 chkconfig
#启动tgtd 暂停iptables
chkconfig tgtd on
chkconfig iptables off
#将设置保存到配置文件
tgt-admin --dump > /etc/tgt/targets.conf
#查看保存的配置
cat /etc/tgt/targets.conf
#关闭防火墙
service iptables stop
#查看配置
tgt-admin -dump
#6.删除
tgtadm --lld iscsi --op delete --mode logicalunit --tid 1 --lun 1
#7.设置为只读
tgtadm --lld iscsi --mode logicalunit --op update --tid 1 --lun 2 --paramsreadonly=0
#8.把任意访问的授权去掉
tgtadm --lld iscsi --op unbind --mode target --tid 1 -l ALL
#9.设置一个ip访问
tgtadm --lld iscsi --op bind --mode target --tid 1 -l 192.168.80.200

4.CHAP访问
#建立新账号
tgtadm --lld iscsi --op new --mode account --user totosun --password 1qaz@WSX#EDC
#显示账户信息
tgtadm --lld iscsi --op show --mode account
#一个账户和一个target邦定 (bind)
tgtadm --lld iscsi --op bind --mode account --tid 1 --user totosun
#删除账号
tgtadm --lld iscsi --mode account --op delete --user totosun
5.重启生效
编辑/etc/tgt/targets.conf即可
# By default, tgt-admin looks for its config file in /etc/tgt/targets.conf
# This one includes other config files:
include /etc/tgt/temp/*.conf
# Set the driver. If not specified, defaults to "iscsi".
default-driver iscsi
# Set iSNS parameters, if needed
#iSNSServerIP 192.168.111.222
#iSNSServerPort 3205
#iSNSAccessControl On
#iSNS On
# Continue if tgtadm exits with non-zero code (equivalent of
# --ignore-errors command line option)
#ignore-errors yes
# Sample target with one LUN only. Defaults to allow access for all initiators:
<target iqn.2008-09.com.example:server.target1>
backing-store /dev/LVM/somedevice
</target>
# Similar, but we use "direct-store" instead of "backing-store".
# "direct-store" reads drive parameters with sg_inq command and sets them to
# the target.
# Parameters fatched with sg_inq are:
# - Vendor identification
# - Product identification
# - Product revision level
# - Unit serial number (if present)
# We also specify "incominguser".
<target iqn.2008-09.com.example:server.target2>
direct-store /dev/sdd
incominguser someuser secretpass12
</target>
# An example with multiple LUNs, disabled write-cache (tgtd enables write-cache
# by default) and vendor identification set to "MyVendor"
<target iqn.2008-09.com.example:server.target3>
backing-store /dev/LVM/somedevice1 # Becomes LUN 1
backing-store /dev/LVM/somedevice2 # Becomes LUN 2
backing-store /dev/LVM/somedevice3 # Becomes LUN 3
write-cache off
vendor_id MyCompany Inc.
</target>
# Similar to the one above, but we fetch vendor_id, product_id, product_rev and
# scsi_sn from the disks.
# Vendor identification (vendor_id) is replaced in all disks by "MyVendor"
<target iqn.2008-09.com.example:server.target4>
direct-store /dev/sdb # Becomes LUN 1
direct-store /dev/sdc # Becomes LUN 2
direct-store /dev/sdd # Becomes LUN 3
write-cache off
vendor_id MyCompany Inc.
</target>
# Note that "first-device-first-lun numbering" will work only for simple
# scenarios above, where _only_ direct-store _or_ backing-store is used.
# If you mix backing-store and direct-store, then all backing-store entries
# are processed before direct-store-entries.
<target iqn.2008-09.com.example:server.target4>
direct-store /dev/sdb # Becomes LUN 3
backing-store /dev/sdc # Becomes LUN 1
direct-store /dev/sdd # Becomes LUN 4
backing-store /dev/sde # Becomes LUN 2
</target>
# Even more complicated example - each device has different parameters.
# You can use indentation to make the config file more readable.
# Note that LUNs will be assigned more or less randomly here (and still
# backing-store get LUNs assigned before drect-store).
# You can specify multiple mode_page parameters (they are commented out
# in this example).
# Note that some parameters (write-cache, scsi_sn) were specified "globally".
# "Global" parameters will be applied to all LUNs; they can be overwritten
# "locally", per LUN.
# If lun is not specified, it will be allocated automatically (first available).
<target iqn.2008-09.com.example:server.target5>
<direct-store /dev/sdd>
vendor_id VENDOR1
removable 1
device-type cd
lun 1
</direct-store>
<direct-store /dev/sda>
vendor_id VENDOR2
lun 2
</direct-store>
<backing-store /dev/sdb1>
vendor_id back1
scsi_sn SERIAL
write-cache on
# lun 3 # lun is commented out - will be allocated automatically
</backing-store>
<backing-store /dev/sdd1>
vendor_id back2
#mode_page 8:0:18:0x10:0:0xff....
#mode_page 8:0:18:0x10:0:0xff....
#bs-type aio
#params element_type=4,start_address=500,quantity=3,media_home=/root/tapes
#params element_type=4,address=500,tid=1,lun=1
lun 15
</backing-store>
# Some more parameters which can be specified locally or globally:
#scsi_id ...
#scsi_sn ...
#vendor_id ...
#product_id ...
#product_rev ...
#sense_format ...
#removable ...
#online ...
#readonly ...
#path ...
#mode_page 8:0:18:0x10:0:0xff....
#mode_page 8:0:18:0x10:0:0xff....
#device-type ...
#bs-type ... # backing store type - default rdwr, can be aio, etc...
#params element_type=4,start_address=500,quantity=3,media_home=/root/tapes
#params element_type=4,address=500,tid=1,lun=1
#allow-in-use yes # if specified globally, can't be overwritten locally
write-cache off
scsi_sn multipath-10
# Parameters below are only global. They can't be configured per LUN.
# Only allow connections from 192.168.100.1 and 192.168.200.5
initiator-address 192.168.100.1
initiator-address 192.168.200.5
# Tuning parameters (global, per target)
#MaxRecvDataSegmentLength 8192
#MaxXmitDataSegmentLength 8192
#HeaderDigest None
#DataDigest None
#InitialR2T Yes
#MaxOutstandingR2T 1
#ImmediateData Yes
#FirstBurstLength 65536
#MaxBurstLength 262144
#DataPDUInOrder Yes
#DataSequenceInOrder Yes
#ErrorRecoveryLevel 0
#IFMarker No
#OFMarker No
#DefaultTime2Wait 2
#DefaultTime2Retain 20
#OFMarkInt Reject
#IFMarkInt Reject
#MaxConnections 1
# Allowed incoming users
incominguser user1 secretpass12
incominguser user2 secretpass23
# Outgoing user
outgoinguser userA secretpassA
# TID of controller
controller_tid 10
</target>
# The device will have lun 1 unless you specify something else
<target iqn.2008-09.com.example:server.target6>
backing-store /dev/LVM/somedevice
lun 10
</target>
# Devices which are in use (by system: mounted, for swap, part of RAID, or by
# userspace: dd, by tgtd for another target etc.) can't be used, unless you use
# --force flag or add 'allow-in-use yes' option
<target iqn.2008-09.com.example:server.target7>
backing-store /dev/LVM/somedevice
allow-in-use yes
</target>
<target iqn.2008-09.com.example:server.target8>
<backing-store /dev/LVM/somedevice>
scsi_sn serial1
</backing-store>
<backing-store /dev/LVM/somedevice2>
scsi_sn serial2
</backing-store>
allow-in-use yes
</target>
# Specify controller TID of target
# Must be unique for all targets
# To reduce risk of duplicating controller TIDs, specify TID for all targets
# or none
<target iqn.2008-09.com.example:server.target9>
backing-store /dev/LVM/somedevice
allow-in-use yes
controller_tid 10
</target>
# Not supported configurations, and therefore, commented out:
#<target iqn.2008-09.com.example:server.badtarget1>
# backing-store /dev/LVM/somedevice1
# backing-store /dev/LVM/somedevice2
# lun 10
# lun 11
#</target>
#<target iqn.2008-09.com.example:server.badtarget2>
# <direct-store /dev/sdd>
# vendor_id VENDOR1
# </direct-store>
#
# direct-store /dev/sdc
#</target>
# This one will break the parser:
#<target iqn.2008-09.com.example:server.badtarget3>
# <direct-store /dev/sdd>
# vendor_id VENDOR1
# </direct-store>
#
# direct-store /dev/sdc
#
# <direct-store /dev/sdd>
# vendor_id VENDOR1
# </direct-store>
#</target>
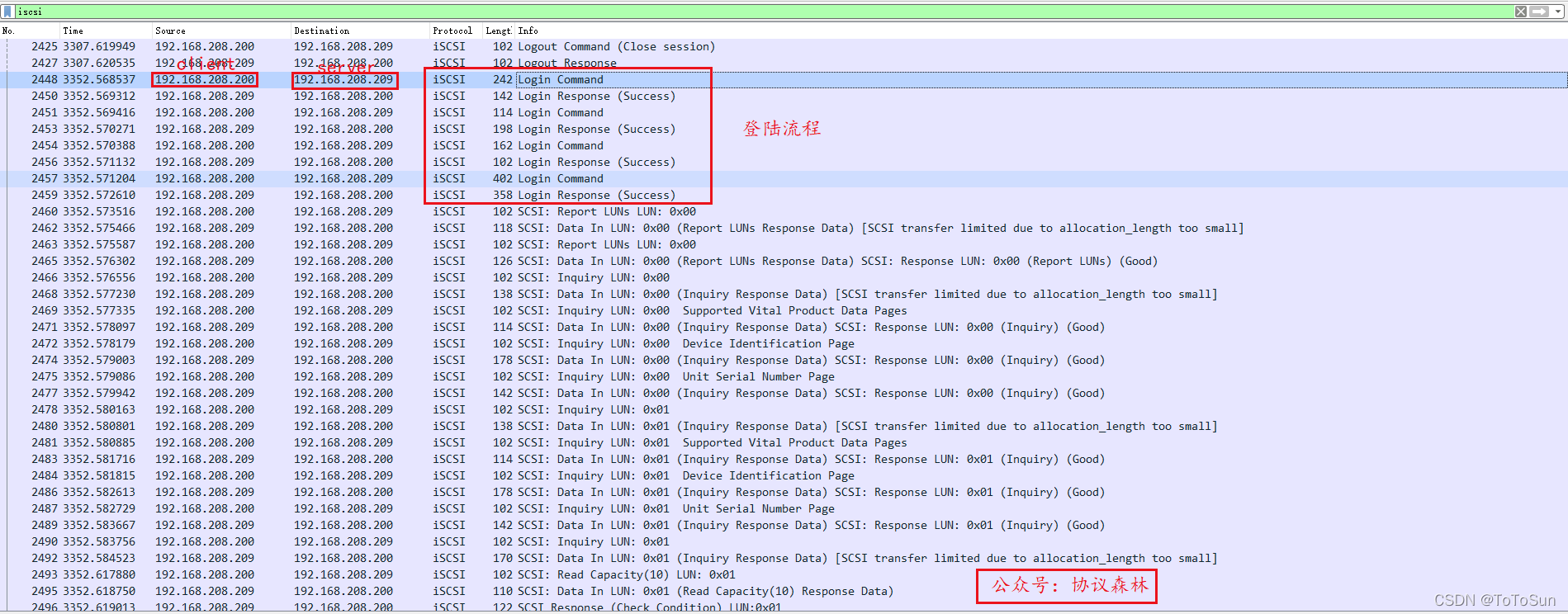
6.抓包
7.加入讨论









 本文详细介绍了如何使用tgtadm工具在Linux系统中配置iSCSI目标服务器,包括安装服务、创建和管理target、添加磁盘、设置访问权限、CHAP认证以及配置文件详解。此外,还提到了抓包和相关讨论。
本文详细介绍了如何使用tgtadm工具在Linux系统中配置iSCSI目标服务器,包括安装服务、创建和管理target、添加磁盘、设置访问权限、CHAP认证以及配置文件详解。此外,还提到了抓包和相关讨论。
















 1479
1479

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








