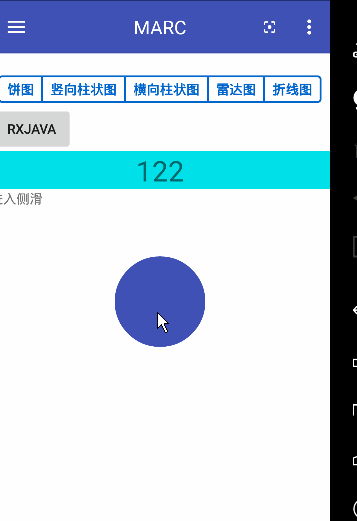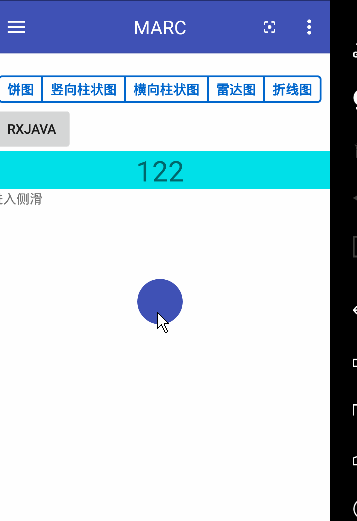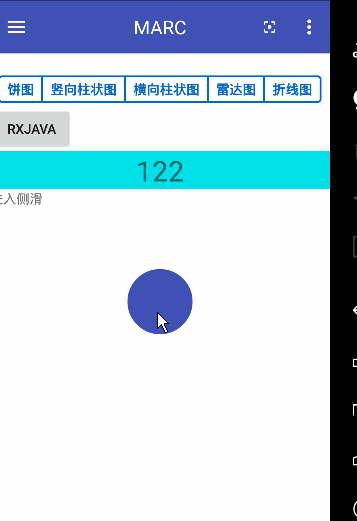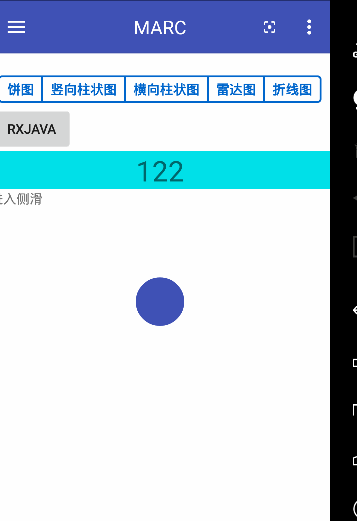
先看效果图
自定义view其实完全可以集成自view,viewgroup,或者现有的view。
public JumpCircleView(Context context) {
this(context, null);//可以直接new
}
public JumpCircleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);//可以在xml文件中使用
}
注释的很清楚了
这里还有个构造方法,是3个参数的,可以使用自定义的属性
public JumpCircleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.JumpCircleView, defStyleAttr, R.style.AppTheme);
custom_size = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.JumpCircleView_size, SIZE);
custom_background = a.getColor(R.styleable.JumpCircleView_background_color, DEFAULT_COLOR);
a.recycle();
init();
}第三个构造函数比第二个构造函数多了一个int型的值,名字叫defStyleAttr,从名称上判断,这是一个关于自定义属性的参数,实际上我们的猜测也是正确的,第三个构造函数不会被系统默认调用,而是需要我们自己去显式调用,比如在第二个构造函数里调用调用第三个函数,并将第三个参数设为0。
onMeasure–>onLayout–>onDraw
具体实行过程
在Android里,一个view的绘制流程包括:Measure,Layout和Draw,通过onMeasure知道一个view要占界面的大小,然后通过onLayout知道这个控件应该放在哪个位置,最后通过onDraw方法将这个控件绘制出来,然后才能展现在用户面前,下面我将挨个分析一下这三个方法的作用.
- onMeasure 测量,通过测量知道一个一个view要占的大小,方法参数是两个int型的值,我们都知道,在java中,int型由4个字节(32bit)组成,在MeasureSpce中,用前两位表示mode,用后30位表示size
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int measuredHeight, measuredWidth;
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
measuredWidth = widthSize;
} else {
measuredWidth = SIZE;
}
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
measuredHeight = heightSize;
} else {
measuredHeight = SIZE;
}
setMeasuredDimension(measuredWidth, measuredHeight);MeasureSpce的mode有三种:EXACTLY, AT_MOST,UNSPECIFIED,除却UNSPECIFIED不谈,其他两种mode:当父布局是EXACTLY时,子控件确定大小或者match_parent,mode都是EXACTLY,子控件是wrap_content时,mode为AT_MOST;当父布局是AT_MOST时,子控件确定大小,mode为EXACTLY,子控件wrap_content或者match_parent时,mode为AT_MOST。所以在确定控件大小时,需要判断MeasureSpec的mode,不能直接用MeasureSpec的size。在进行一些逻辑处理以后,调用setMeasureDimension()方法,将测量得到的宽高传进去供layout使用。
需要明白的一点是 ,测量所得的宽高不一定是最后展示的宽高,最后宽高确定是在onLayout方法里,layou(left,top,right,bottom),不过一般都是一样的。
onLayout 实际上,我在自定义SketchView的时候是没有重写onLayout方法的,因为SketchView只是一个单纯的view,它不是一个view容器,没有子view,而onLayout方法里主要是具体摆放子view的位置,水平摆放或者垂直摆放,所以在单纯的自定义view是不需要重写onLayout方法,不过需要注意的一点是,子view的margin属性是否生效就要看parent是否在自身的onLayout方法进行处理,而view得padding属性是在onDraw方法中生效的。
onDraw 终于说到了重头戏,一般自定义控件耗费心思最多的就是这个方法了,需要在这个方法里,用Paint在Canvas上画出你想要的图案,这样一个自定义view才算结束。下面会详细讲如何在画布上画出自己想要的图案。
关于onDraw方法,在补充一句,如果是直接继承的View,那么在重写onDraw的方法是时候完全可以把super.ondraw(canvas)删掉,因为它的默认实现是空。其实任何时候都应该去点进入看一下super()方法是否是空实现。例如如果继承自button,那么ondraw方法的super()方法就不能删除。
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
//super()前面是绘制想要的效果
if(mProgressEnable){
Drawable drawable = new ColorDrawable(Color.BLUE);
int left = 0;
int top = 0;
int right = (int) (mProgress * 1.0f / mMax * getMeasuredWidth() + .5f);
int bottom = getBottom();
drawable.setBounds(left, top, right, bottom);// 必须的.告知绘制的范围
drawable.draw(canvas);
}
super.onDraw(canvas);// 绘制文本,还会绘制背景
}得到一个正方形
在日常开发中,我们偶尔会需要一个正方形的imageView,一般都是通过指定宽高,但是当宽高不确定时,我们就只能寄希望于Android原声支持定义view的比例,但是现实是残酷的,系统好像是没有提供类似属性的,所以我们就只能自己去实现,其实自己写起来也特别的简单,只需要改一个参数就OK了,
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, widthMeasureSpec);
}不仔细观察是看不出来其中的奥妙的,虽然这里复写了view的onMeasure,但是貌似没有做任何处理,直接调用了super方法,但是仔细观察的话就会发现,在调用super方法的时候,第二个参数变了,本来应该是heightMeasureSpec却换成了widthMeasureSpec,这样view的高度就是view的宽度,一个SquareView就实现了,甚至如果通过自定义属性实现一个自定义比例view。
自定义属性
<!--自定义view蹦跳-->
<declare-styleable name="JumpCircleView">
<attr name="background_color" format="color" />
<attr name="size" format="dimension" />
</declare-styleable>使用
<com.marc.chatpicture.widget.JumpCircleView
android:id="@+id/sketch_view"
app:size="24dp"
app:background_color="@color/colorPrimary"
android:layout_width="200dp"
android:layout_height="200dp"
android:layout_gravity="center" />如果想真正的使用,别忘了:
public JumpCircleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.JumpCircleView, defStyleAttr, R.style.AppTheme);
custom_size = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.JumpCircleView_size, SIZE);
custom_background = a.getColor(R.styleable.JumpCircleView_background_color, DEFAULT_COLOR);
a.recycle();
init();
}下面贴出来一个具体的例子:
public class JumpCircleView extends View {
private int custom_size;
private int custom_background;
private Paint mPaint;
private int mHeight;
private int mWidth;
private float scale = 1f;
private final int SIZE = 15;//默认大小
private final int DEFAULT_COLOR = Color.BLUE;//默认球的颜色
public JumpCircleView(Context context) {
this(context, null);//可以直接new
}
public JumpCircleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
this(context, attrs, 0);//可以在xml文件中使用
}
public JumpCircleView(Context context, AttributeSet attrs, int defStyleAttr) {
super(context, attrs, defStyleAttr);
TypedArray a = context.obtainStyledAttributes(attrs, R.styleable.JumpCircleView, defStyleAttr, R.style.AppTheme);
custom_size = a.getDimensionPixelSize(R.styleable.JumpCircleView_size, SIZE);
custom_background = a.getColor(R.styleable.JumpCircleView_background_color, DEFAULT_COLOR);
a.recycle();
init();
}
private void init() {
mPaint = new Paint();
mPaint.setColor(custom_background);
mPaint.setAntiAlias(true);
mPaint.setStyle(Paint.Style.FILL);
}
@Override
protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) {
int widthMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec);
int widthSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec);
int heightMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec);
int heightSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec);
int measuredHeight, measuredWidth;
if (widthMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
measuredWidth = widthSize;
} else {
measuredWidth = SIZE;
}
if (heightMode == MeasureSpec.EXACTLY) {
measuredHeight = heightSize;
} else {
measuredHeight = SIZE;
}
setMeasuredDimension(measuredWidth, measuredHeight);
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
mHeight = getHeight();
mWidth = getWidth();
}
private ValueAnimator mAnimator;
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
/*参数
* 圆心x 圆心y 半径(这里要一直改变的) 画笔
* */
canvas.drawCircle(mWidth / 2, mHeight / 2, custom_size * scale, mPaint);
}
public void startAnimation() {
mAnimator = ValueAnimator.ofFloat(1, 2);//从1-2不断变化
mAnimator.addUpdateListener(new ValueAnimator.AnimatorUpdateListener() {
@Override
public void onAnimationUpdate(ValueAnimator animation) {
//拿到每时每刻变化的值
scale = (float) animation.getAnimatedValue();
postInvalidate();
}
});
// 重复次数 -1表示无限循环
mAnimator.setRepeatCount(-1);
// 重复模式, RESTART: 重新开始 REVERSE:恢复初始状态再开始
mAnimator.setRepeatMode(ValueAnimator.REVERSE);
mAnimator.start();
}
public void stopAnimation() {
if (mAnimator != null) {
// mAnimator.end();
mAnimator.cancel();
}
}
// @Override
// public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
// switch (event.getAction()) {
// case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
// mAnimator.end();
int scale = (int) mAnimator.getAnimatedValue();
// case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
// break;
// case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
startAnimation();
// mAnimator.start();
// break;
// }
// return true;
// }
@Override
protected void onDetachedFromWindow() {
super.onDetachedFromWindow();
//从视图移除
// 关闭动画
mAnimator.end();
}
@Override
protected Parcelable onSaveInstanceState() {
return super.onSaveInstanceState();
}
@Override
protected void onRestoreInstanceState(Parcelable state) {
super.onRestoreInstanceState(state);
}
}
使用
jumpView.startAnimation();
jumpView.setOnTouchListener(new View.OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
switch (event.getAction()){
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
jumpView.stopAnimation();
case MotionEvent.ACTION_MOVE:
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
jumpView.startAnimation();
break;
}
return true;
}
});注释已经非常清楚了 ,这里要注意的是,可以在view中 重写onTouchEvetn,也可以在调用的地方写。但是:如果要监听手势,一般会想到onTouch,但是我们发现View的onTouch事件只是相应action-down。原因:onTouch中return false。解决办法:1, return true2、在xml布局里加上 Android:longClickable=”true”这两者并不完全是等价的。return true就意味着该view会继续处理抬起事件,而不会将此时间传递给父View———这也意味着只有一个view可以继续监听touch事件因此必须注意ontouch事件的传递过程。由子view传给父view,如果return false,可以传给父view,true则不能。手势最好在activity中的dispatchTouchEvent中做,这个是无法被子view屏蔽的。另外onTouch如果返回true,则不能监听onClick






















 8万+
8万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








