自定义RPC框架实现
代码参考Hadoop common包 org.apache.rpc
代码地址:https://github.com/dll02/commons-rpc
源代码地址:https://github.com/LantaoJin/commons-rpc
架构图
RPC远程过程调用
分布式是在不可靠的通信之上通过TCP/IP协议实现,在远程机器上执行代码的过程像调用本地函数一样
客户端的执行:
创建消息缓冲区-> 将所需信息打包到消息缓冲区中 ->将消息发送到目标RPC服务器 ->等待回复 ->解包返回代码和其他参数->返回调用者
服务端的执行:
解包消息 -> 调用实际函数 -> 打包结果 -> 发送回复
缺点:
会占用一定的线程资源,没有解决连接空闲{无数据交互}时的资源占用问题,连接一定要占用线程资源,直至消亡
使用demo
server端代码
public interface DemoService extends ProtocolInterface {
public static final long versionID = 1L;
public int sum(int a, int b);
public int sub(int a, int b);
}
public class DemoServiceImpl implements DemoService {
public long getProtocolVersion(String protocol, long clientVersion) throws IOException {
return 1;
}
public int sum(int a, int b) {
return a + b;
}
public int sub(int a, int b) {
return a - b;
}
}
public class RpcServer {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
conf.set("server.ip.name","localhost");
conf.set("name.port","8888");
// 设置rpc代理的实现server类
Server server = RPC.getServer(new DemoServiceImpl(), conf.get("server.ip.name"),
conf.getInt("name.port", 8888),
new Configuration());
server.start();
}
}RPC框架代码
rpc client端代码阅读分析
client端发起请求:
client端发起请求:
DemoService proxy = (DemoService) RPC.getProxy(DemoService.class, DemoService.versionID,
new InetSocketAddress(conf.get("client.ip.name"), conf.getInt("name.port", 8888)), conf, 1000);
proxy()->Invoker.invoke()->client.call()->call.wait()
=> {CLIENTS.getClient(conf, factory)}=> new Client(socketFactory)
=> value=client.call(new Invocation(method, args), remoteId) # 向远程发起请求返回
=> Invocation[methodName,parameterClasses,parameters,conf]
=> new Call(param)[id,param,conn]{setValue->callComplete()->done=true;notify();}
=> getConnection(remoteId, call)-> connection.addCall(call)->setupIOstreams()
=> setupConnection()->socket.bind()
=> setIOStream -> in=SocketInputStream;out=SocketOutputStream;
=> start() => while(waitForWork()等待calls队列插入call 可以工作){receiveResponse()}
=> in.readXxx() -> reader.doIO(dst, SelectionKey.OP_READ) io等待可读事件发生
=> Writable value = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(valueClass, conf) 生成结果对象
=> value.readFields(in) 从in流中逐个读入字段
=> call.setValue(value)-> callComplete()-> notify() client端发起请求:
public class RpcClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Configuration conf = new Configuration();
conf.set("client.ip.name","localhost");
conf.set("name.port","8888");
DemoService proxy = (DemoService) RPC.getProxy(DemoService.class, DemoService.versionID,
new InetSocketAddress(conf.get("client.ip.name"), conf.getInt("name.port", 8888)), conf, 1000);
System.out.println("client receive:" + proxy.sum(100, 68));
System.out.println("client receive:" + proxy.sub(100, 68));
System.out.println("client receive:" + proxy.sum(888, 666));
System.out.println("client receive:" + proxy.sub(888, 666));
RPC.stopProxy(proxy);
}
}client端发起请求时会代理server的接口DemoService.class,实际的发起请求会在代理类的invoke()方法执行中
和远程remoteId 的server端建立真正的scoket请求连接
封装请求内容到Call中
通过socket connection 内发送请求 connection.sendParam(call);
等待该call的结果响应并取出结果
rpc server端代码阅读分析
server端的服务请求:
server端的服务请求:
Server server = RPC.getServer(new DemoServiceImpl(), conf.get("server.ip.name"),
conf.getInt("name.port", 8888),
new Configuration());
=> getServer()=> new Server(instance, conf, bindAddress, port, numHandlers, verbose)
=> Server extends org.apache.ipc.Server => 设置相关参数[bindAddress,port,conf,callQueue]
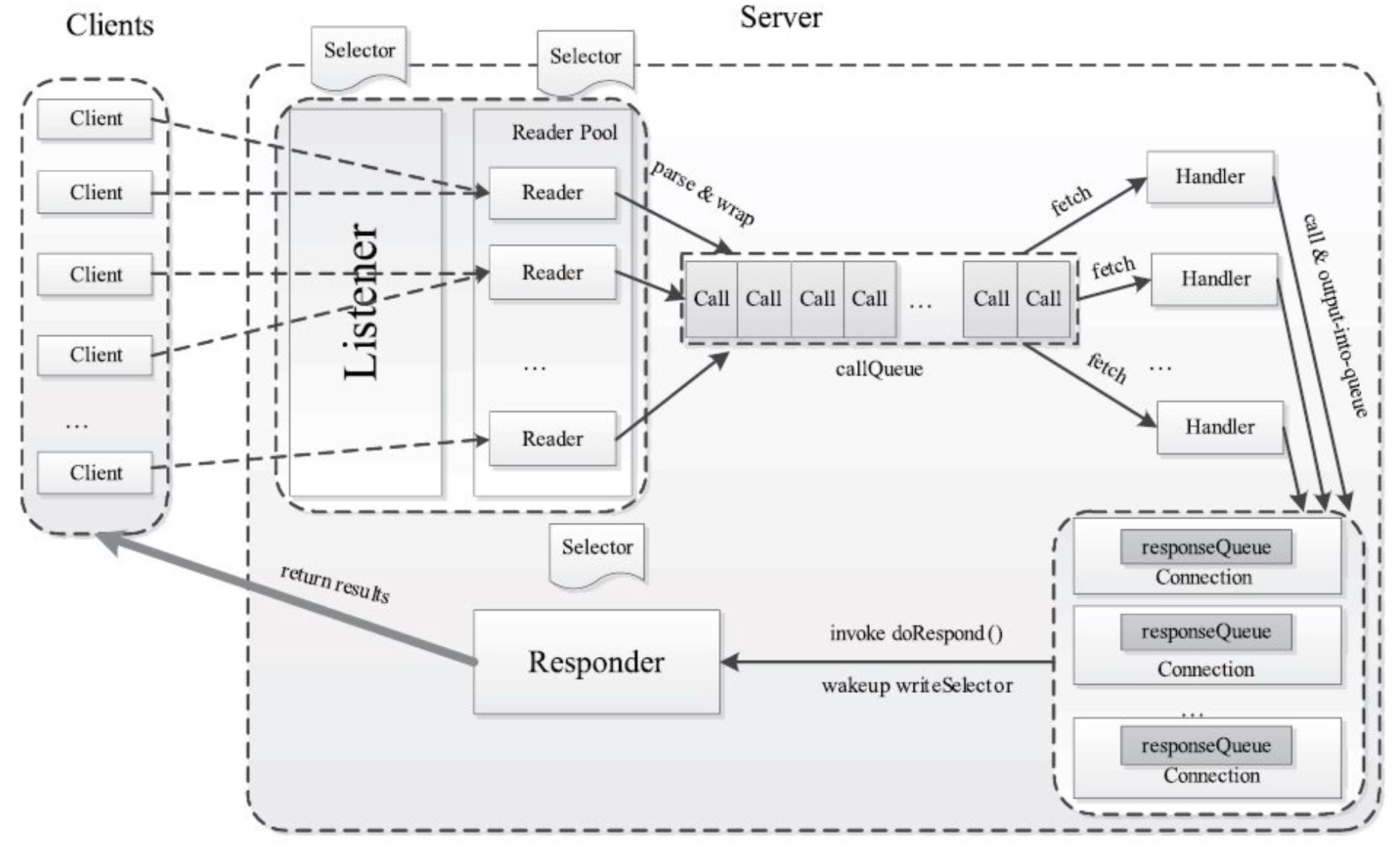
=> new Listener()监听请求->Selector.open()->Reader[i]->
=> readPool.execute(Reader) 监听当前Reader对象的连接中是否有RPC请求到达
=> Reader.run()->readSelector.selectedKeys().iterator()->doRead(key)
=> doRead(key) 找到Connection对象并读取RPC请求
=> c=(Connection)key.attachment()->c.readAndProcess()
=>!rpcHeaderRead -> channelRead(channel, dataLengthBuffer)读header
=> c.processHeader(buf)
=>c.processOneRpc(data.array()) 读请求连接内的数据并实际处理
=> c.processData(buf)->callQueue.put(new Call(id, param, this))
=> acceptChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT)注册事件
=>run()监听accept事件->acceptSelector.selectedKeys().iterator()->doAccept(key)
=>doAccept()->while(channel = server.accept())->getReader()->
->c=new Connection(readKey, channel, time)->readKey.attach(c)
-> 收到来自客户端的Socket连接请求后初始化连接Connection,
-> 从readers线程池中选一个Reader线程处理,并在readSelector注册一个OP_READ事件
=> new Responder()返回响应
=>run() -> while{writeSelector.selectedKeys.iter->doAsyncWrite(key)}
=>(Call)key.attachment()[id,param,connection,response]
->(processResponse(conn.responseQueue, false)
=> processResponse(call.responseQueue) 读conn的响应队列往channel输出结果
=> responseQueue.removeFirst(call).connection.channel
=> channelWrite(channel, call.response)
-> writer.doIO(src, SelectionKey.OP_WRITE)
=> Server.start()-> responder.start()->listener.start()->Handler[i].start()
=>Handler -> run() -> while(running) -> call = callBlockingQueue.take()
-> value = call(call.connection.protocol, call.param, call.timestamp)
=>server.call()->Invocation paramCall = (Invocation)param
->Object value = method.invoke(instance, call.getParameters())
->return new ObjectWritable(method.getReturnType(), value)
-> setupResponse(call,value) call设置执行结果 -> responder.doRespond(call)
-> call.connection.responseQueue.addLast(call) 往conn的响应队列加call
-> responder.doRespond(call)->Responder.processResponse()server端启动代码:
/** Starts the service. Must be called before any calls will be handled. */
public synchronized void start() {
// 启动responder 和listener
responder.start();
listener.start();
handlers = new Handler[handlerCount];
for (int i = 0; i < handlerCount; i++) {
handlers[i] = new Handler(i);
handlers[i].start();
}
}
/** Listens on the socket. Creates jobs for the handler threads
* 监听接入方的链接
* */
private class Listener extends Thread {
private ServerSocketChannel acceptChannel = null; //the accept channel
// 链接监听
private Selector selector = null; //the selector that we use for the server
private Reader[] readers = null;
private int currentReader = 0;
private InetSocketAddress address; //the address we bind at
private Random rand = new Random();
private long lastCleanupRunTime = 0; //the last time when a cleanup connec-
//-tion (for idle connections) ran
private long cleanupInterval = 10000; //the minimum interval between
//two cleanup runs
private int backlogLength = conf.getInt("ipc.server.listen.queue.size", 128);
private ExecutorService readPool;
// Listener 的构造函数初始化
public Listener() throws IOException {
address = new InetSocketAddress(bindAddress, port);
// Create a new server socket and set to non blocking mode
acceptChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
// 设置为非阻塞IO
acceptChannel.configureBlocking(false);
// Bind the server socket to the local host and port
bind(acceptChannel.socket(), address, backlogLength);
port = acceptChannel.socket().getLocalPort(); //Could be an ephemeral port
// create a selector;
selector= Selector.open();
readers = new Reader[readThreads];
readPool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(readThreads);
for (int i = 0; i < readThreads; i++) {
// 为每个线程都创建一个新的readSelector 绑定
Selector readSelector = Selector.open();
Reader reader = new Reader(readSelector);
readers[i] = reader;
readPool.execute(reader);
}
// Register accepts on the server socket with the selector.
acceptChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
this.setName("IPC Server listener on " + port);
this.setDaemon(true);
}
@Override
public void run() {
...
while (running) {
SelectionKey key = null;
try {
selector.select();
Iterator<SelectionKey> iter = selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while (iter.hasNext()) {
key = iter.next();
iter.remove();
try {
if (key.isValid()) {
if (key.isAcceptable())
doAccept(key);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
}
key = null;
}
...
}
} server端的服务启动,通过启动不同功能的线程实现功能
Listener线程:负责监听来自客户端的Socket连接请求
通过Selector监听OP_ACCEPT事件
启动一个
Reader线程:为每个建立连接的scoket connection分配一个专属Reader线程
负责当前Reader对象的连接中是否有RPC请求—I/O事件到达
启动指定个数,形成线程池readPool,在server.start()启动Listener线程初始化时批量启动备用
读取I/O的OP_READ事件内的具体RPC请求数据data,封装到内部Call添加到该connection上的callQueue中等待处理
Handler线程:异步真正的执行RPC请求的运行,计算请求的结果
启动配置数量的线程数
代理真正服务service对象,根据param执行请求,并把结果封装回Call
把结果放回connection上的responseQueue队列等待把结果发回client
Responder线程:把有结果的Call发送回client端
启动一个
监听OP_WRITE事件, 向client写回结果
实现responder.doRespond()和processResponse()方法,往conn的channel写结果
使用netty实现rpc
在一些简单的rpc里会区分调远程服务,或者直接访问本地JVM中的对象,通过区分传入的是实现接口的对象,或者只是接口来简单实现
已实现的具体类直接执行方法
接口对象则向远程调用
public class RpcProxy {
public static <T> T create(Class<?> clazz){
//clazz传进来本身就是interface
// 生成代理方法
MethodProxy proxy = new MethodProxy(clazz);
// 拿到接口类class
Class<?> [] interfaces = clazz.isInterface() ?
new Class[]{clazz} :
clazz.getInterfaces();
T result = (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(clazz.getClassLoader(),interfaces,proxy);
return result;
}
private static class MethodProxy implements InvocationHandler {
private Class<?> clazz;
public MethodProxy(Class<?> clazz){
this.clazz = clazz;
}
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
//如果传进来是一个已实现的具体类(本次演示略过此逻辑)
if (Object.class.equals(method.getDeclaringClass())) {
try {
return method.invoke(this, args);
} catch (Throwable t) {
t.printStackTrace();
}
//如果传进来的是一个接口(核心)
} else {
// 远程访问
return rpcInvoke(proxy,method, args);
}
return null;
}
/**
* 实现接口的核心方法
* @param method
* @param args
* @return
*/
public Object rpcInvoke(Object proxy,Method method,Object[] args){
//传输协议封装
InvokerProtocol msg = new InvokerProtocol();
msg.setClassName(this.clazz.getName());
msg.setMethodName(method.getName());
msg.setValues(args);
msg.setParames(method.getParameterTypes());
final RpcProxyHandler consumerHandler = new RpcProxyHandler();
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
Bootstrap b = new Bootstrap();
b.group(group)
.channel(NioSocketChannel.class)
.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true)
.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
//自定义协议解码器
/** 入参有5个,分别解释如下
maxFrameLength:框架的最大长度。如果帧的长度大于此值,则将抛出TooLongFrameException。
lengthFieldOffset:长度字段的偏移量:即对应的长度字段在整个消息数据中得位置
lengthFieldLength:长度字段的长度:如:长度字段是int型表示,那么这个值就是4(long型就是8)
lengthAdjustment:要添加到长度字段值的补偿值
initialBytesToStrip:从解码帧中去除的第一个字节数
*/
pipeline.addLast("frameDecoder", new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, 4, 0, 4));
//自定义协议编码器
pipeline.addLast("frameEncoder", new LengthFieldPrepender(4));
//对象参数类型编码器
pipeline.addLast("encoder", new ObjectEncoder());
//对象参数类型解码器
pipeline.addLast("decoder", new ObjectDecoder(Integer.MAX_VALUE, ClassResolvers.cacheDisabled(null)));
pipeline.addLast("handler",consumerHandler);
}
});
ChannelFuture future = b.connect("localhost", 8080).sync();
future.channel().writeAndFlush(msg).sync();
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch(Exception e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
return consumerHandler.getResponse();
}
}
}使用netty实现简单的服务端
在RegistryHandler内扫描注册真正的server执行方法的对象
public class RpcRegistry {
private int port;
public RpcRegistry(int port){
this.port = port;
}
public void start(){
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
ServerBootstrap b = new ServerBootstrap();
b.group(bossGroup, workerGroup)
.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class)
.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
protected void initChannel(SocketChannel ch) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = ch.pipeline();
//自定义协议解码器
/** 入参有5个,分别解释如下
maxFrameLength:框架的最大长度。如果帧的长度大于此值,则将抛出TooLongFrameException。
lengthFieldOffset:长度字段的偏移量:即对应的长度字段在整个消息数据中得位置
lengthFieldLength:长度字段的长度。如:长度字段是int型表示,那么这个值就是4(long型就是8)
lengthAdjustment:要添加到长度字段值的补偿值
initialBytesToStrip:从解码帧中去除的第一个字节数
*/
pipeline.addLast(new LengthFieldBasedFrameDecoder(Integer.MAX_VALUE, 0, 4, 0, 4));
//自定义协议编码器
pipeline.addLast(new LengthFieldPrepender(4));
//对象参数类型编码器
pipeline.addLast("encoder",new ObjectEncoder());
//对象参数类型解码器
pipeline.addLast("decoder",new ObjectDecoder(Integer.MAX_VALUE,ClassResolvers.cacheDisabled(null)));
pipeline.addLast(new RegistryHandler());
}
})
.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 128)
.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
ChannelFuture future = b.bind(port).sync();
System.out.println("GP RPC Registry start listen at " + port );
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} catch (Exception e) {
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
// 启动服务
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
new RpcRegistry(8080).start();
}
}
RegistryHandler的实现
在构造方法中指定需要扫描的包,把服务类加入classNames 列表中
doRegister()实现对classNames 列表中的类生成<class名,对象>的映射, 存在registryMap中
接受到远程rpc请求时,执行channelRead()方法响应结果
请求转为执行的协议对象InvokerProtocol[className,methodName,parames,values]
代理执行method返回结果 method.invoke(clazz, request.getValues())
public class RegistryHandler extends ChannelInboundHandlerAdapter {
//用保存所有可用的服务
public static ConcurrentHashMap<String, Object> registryMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<String,Object>();
//保存所有相关的服务类
private List<String> classNames = new ArrayList<String>();
public RegistryHandler(){
//完成递归扫描
scannerClass("com.netty.rpc.provider");
doRegister();
}
@Override
public void channelRead(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object msg) throws Exception {
Object result = new Object();
InvokerProtocol request = (InvokerProtocol)msg;
//当客户端建立连接时,需要从自定义协议中获取信息,拿到具体的服务和实参
//使用反射调用
if(registryMap.containsKey(request.getClassName())){
// 拿到执行方法的对象
Object clazz = registryMap.get(request.getClassName());
Method method = clazz.getClass().getMethod(request.getMethodName(), request.getParames());
result = method.invoke(clazz, request.getValues());
}
ctx.write(result);
ctx.flush();
ctx.close();
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
cause.printStackTrace();
ctx.close();
}
/*
* 递归扫描
*/
private void scannerClass(String packageName){
URL url = this.getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(packageName.replaceAll("\\.", "/"));
File dir = new File(url.getFile());
for (File file : dir.listFiles()) {
//如果是一个文件夹,继续递归
if(file.isDirectory()){
scannerClass(packageName + "." + file.getName());
}else{
classNames.add(packageName + "." + file.getName().replace(".class", "").trim());
}
}
}
/**
* 完成注册
*/
private void doRegister(){
if(classNames.size() == 0){ return; }
for (String className : classNames) {
try {
Class<?> clazz = Class.forName(className);
// 反射生成对象
Class<?> i = clazz.getInterfaces()[0];
registryMap.put(i.getName(), clazz.newInstance());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}自定义传输协议InvokerProtocol
@Data
public class InvokerProtocol implements Serializable {
private String className;//类名
private String methodName;//函数名称
private Class<?>[] parames;//形参列表
private Object[] values;//实参列表
}



















 357
357











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








