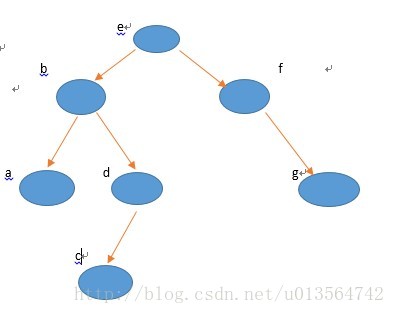
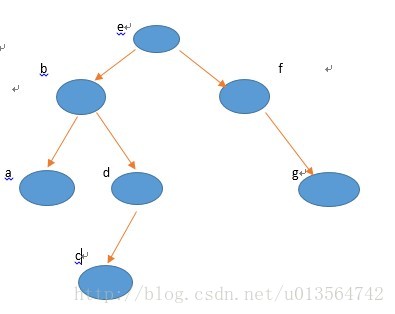
二叉树是一种很重要的树形结构,利用它可以显著提高查找数据的速度,我们可以用层次输入的方法构建二叉树。例如构建下面的二叉树
为了构建这样的一棵二叉树,需要在键盘上输入顺序如下:
e b f a d . g . . c #
#表示输入结束。
.代表该结点为空,也应该输入,这是为了保持结点的顺序不会发生变化。
现在来详细说说构建的方法:可以使用队列来帮助构建二叉树,该方法中要用到两个队列,主要是起到一个桥梁的作用
queue<DataType*> A;
queue<DataType*> B;
具体步骤为:
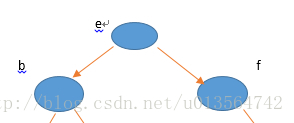
1、先将输入的节点放进队列A中,然后从A中取出第一个节点作为根结点,放进B队列中
(1):
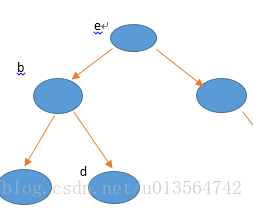
2、之后每一步都是从A中取出两个节点,放进B中(节点若为空的则不放,本例中以“.”代表空节点),从B中取出一个节点,以B中的节点作为父结点,A中先取出的作为左孩子,后取出的作为右孩子,将父结点和左右孩子连起来。
(2):
(3):
3、重复2直到A为空或者B为空,构建完成。
(4):
附上代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
typedef struct BinTreeNode* pBinTreeNode;
struct BinTreeNode //节点
{
char s;
pBinTreeNode lchild;
pBinTreeNode rchild;
};
pBinTreeNode get_lchildren(pBinTreeNode pnode) //取左孩子
{
if(pnode == NULL)
return NULL;
return pnode->lchild;
}
pBinTreeNode get_rchildren(pBinTreeNode pnode) //取右孩子
{
if(pnode == NULL)
return NULL;
return pnode->rchild;
}
void pre_tree(pBinTreeNode pnode) //遍历
{
if(pnode == NULL || pnode->s == '.')
return;
cout<<pnode->s<<" ";
pre_tree(get_lchildren(pnode));
pre_tree(get_rchildren(pnode));
}
int main()
{
queue<pBinTreeNode> A;
queue<pBinTreeNode> B;
char x;
cin>>x;
while(x!='#') //按层次顺序输入数据,以“#”结束输入
{
pBinTreeNode node = new BinTreeNode();
node->s = x;
node->lchild = NULL;
node->rchild = NULL;
A.push(node);
cin>>x;
}
pBinTreeNode tree = A.front();
A.pop();
//pBinTreeNode father = tree;
B.push(tree);
while(true)
{
if(A.empty() || B.empty()) //如果A或者B为空,结束
break;
pBinTreeNode father = B.front();
B.pop();
while(father->s == '.') //如果B中取出的是 . 继续取
{
father = B.front();
B.pop();
}
pBinTreeNode lchildren = A.front();
A.pop();
if(A.empty()) //从A取出一个数后,若A为空,则结束
{
father->lchild = lchildren;
break;
}
pBinTreeNode rchildren = A.front();
A.pop();
father->lchild = lchildren;
father->rchild = rchildren;
if(lchildren->s!='.') //如果取出的结点不为空,将结点放进B队列中
B.push(lchildren);
if(rchildren->s!='.')
B.push(rchildren);
//father = A.front();
}
cout<<"先根访问次序为:"<<endl;
pre_tree(tree);
system("pause");
return 0;
}

























 610
610

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








