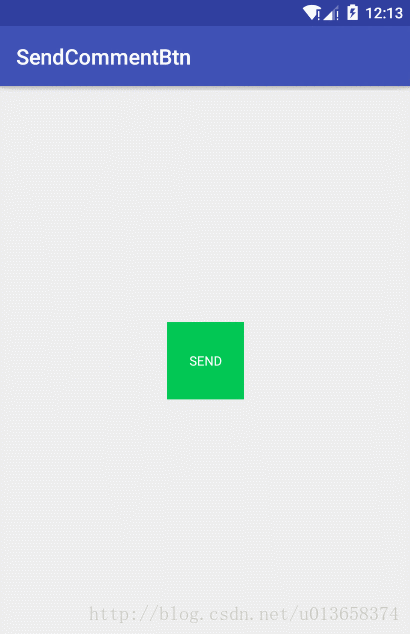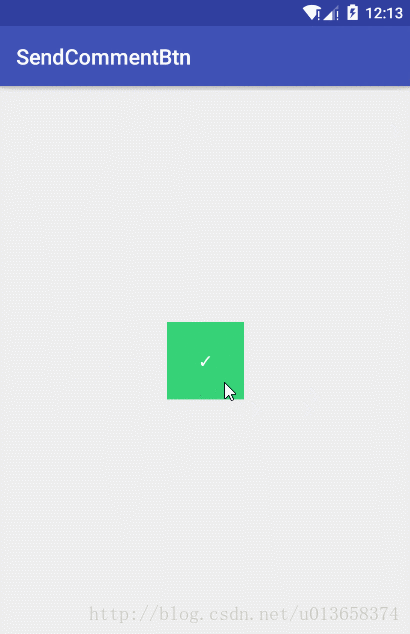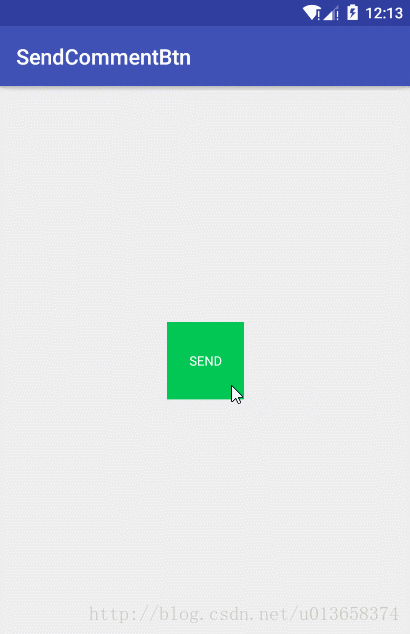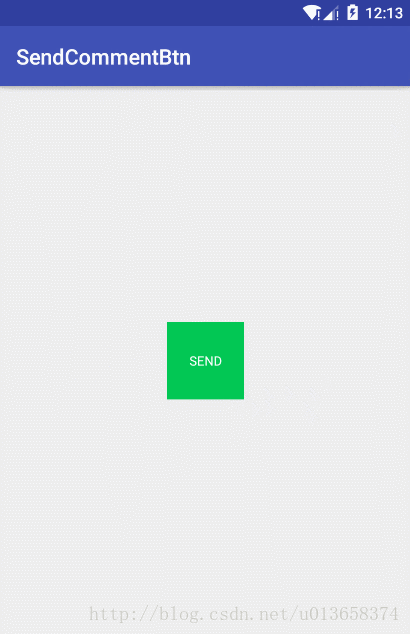
效果图
准备知识
merge标签的使用,可以参考Android 布局优化之include与merge- ViewAnimator
Android自定义组件
SendCommentButton
新建SendCommentButton继承自ViewAnimator,而ViewAnimator是继承自FrameLayout的。
public class SendCommentButton extends ViewAnimator{
//通过代码new执行该方法
public SendCommentButton(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
//通过xml引入会执行该方法
public SendCommentButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
}init()方法
private void init() {
LayoutInflater.from(getContext()).inflate(R.layout.view_send_comment_button, this, true);
}把布局依附到该控件上
R.layout.view_send_comment_button布局
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<merge xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tvSend"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="SEND"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="12sp" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/tvDone"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:gravity="center"
android:text="✓"
android:textColor="#ffffff"
android:textSize="12sp" />
</merge>执行init()方法之后会回调ViewAnimator的addView方法,我们来看看ViewAnimator是怎么处理的
......
@Override
public void addView(View child, int index, ViewGroup.LayoutParams params) {
super.addView(child, index, params);
if (getChildCount() == 1) {
child.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
} else {
child.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
if (index >= 0 && mWhichChild >= index) {
// Added item above current one, increment the index of the displayed child
setDisplayedChild(mWhichChild + 1);
}
}
......从上面可以看到把第一个子View设置为可见,其他设置GONE,也就是说merge的✓设置为GONE了。
接下来我们补充SendCommentButton其他逻辑代码
public class SendCommentButton extends ViewAnimator implements View.OnClickListener {
public static final int STATE_SEND = 0;
public static final int STATE_DONE = 1;
private static final long RESET_STATE_DELAY_MILLIS = 2000;
private int currentState;
private OnSendClickListener onSendClickListener;
//通过代码new执行该方法
public SendCommentButton(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
//通过xml引入会执行该方法
public SendCommentButton(Context context, AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
private void init() {
LayoutInflater.from(getContext()).inflate(R.layout.view_send_comment_button, this, true);
}
@Override
protected void onAttachedToWindow() {
super.onAttachedToWindow();
currentState = STATE_SEND;
setOnClickListener(this);
}
@Override
public void onClick(View view) {
if (onSendClickListener != null) {
onSendClickListener.onSendClickListener(this);
}
}
@Override
protected void onDetachedFromWindow() {
removeCallbacks(revertStateRunnable);
super.onDetachedFromWindow();
}
public void setCurrentState(int state) {
if (state == currentState) {
return;
}
currentState = state;
if (state == STATE_DONE) {
setEnabled(false);
postDelayed(revertStateRunnable, RESET_STATE_DELAY_MILLIS);
setInAnimation(getContext(), R.anim.slide_in_done);
setOutAnimation(getContext(), R.anim.slide_out_send);
} else if (state == STATE_SEND) {
setEnabled(true);
setInAnimation(getContext(), R.anim.slide_in_send);
setOutAnimation(getContext(), R.anim.slide_out_done);
}
showNext();
}
private Runnable revertStateRunnable = new Runnable() {
@Override
public void run() {
setCurrentState(STATE_SEND);
}
};
public interface OnSendClickListener {
void onSendClickListener(View v);
}
public void setOnSendClickListener(OnSendClickListener onSendClickListener) {
this.onSendClickListener = onSendClickListener;
}
}上面定义了两种状态,暴露了一个接口和设置了进入和进出动画。这里解析一下ViewAnimator的showNext()方法,在ViewAnimator的源码中
......
public void showNext() {
setDisplayedChild(mWhichChild + 1);
}
......showNext会调用setDisplayedChild方法
/**
* Sets which child view will be displayed.
*设置哪个子View将被显示
* @param whichChild the index of the child view to display 要显示子view的下标
*/
public void setDisplayedChild(int whichChild) {
mWhichChild = whichChild;
if (whichChild >= getChildCount()) {
mWhichChild = 0;
} else if (whichChild < 0) {
mWhichChild = getChildCount() - 1;
}
boolean hasFocus = getFocusedChild() != null;
// This will clear old focus if we had it
showOnly(mWhichChild);
if (hasFocus) {
// Try to retake focus if we had it
requestFocus(FOCUS_FORWARD);
}
}setDisplayedChild中的主要展示逻辑交给了showOnly方法
/**
* Shows only the specified child. The other displays Views exit the screen,
* optionally with the with the {@link #getOutAnimation() out animation} and
* the specified child enters the screen, optionally with the
* {@link #getInAnimation() in animation}.
*
* @param childIndex The index of the child to be shown.
* @param animate Whether or not to use the in and out animations, defaults
* to true.
*/
void showOnly(int childIndex, boolean animate) {
final int count = getChildCount();
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (i == childIndex) {
if (animate && mInAnimation != null) {
child.startAnimation(mInAnimation);
}
child.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
mFirstTime = false;
} else {
if (animate && mOutAnimation != null && child.getVisibility() == View.VISIBLE) {
child.startAnimation(mOutAnimation);
} else if (child.getAnimation() == mInAnimation)
child.clearAnimation();
child.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
}
}
/**
* Shows only the specified child. The other displays Views exit the screen
* with the {@link #getOutAnimation() out animation} and the specified child
* enters the screen with the {@link #getInAnimation() in animation}.
*正在展示的view退出屏幕,展示指定的view,指定的view以getInAnimation的动画进入,退出的view以getOutAnimation的动画退出
* @param childIndex The index of the child to be shown.
*/
void showOnly(int childIndex) {
final boolean animate = (!mFirstTime || mAnimateFirstTime);
showOnly(childIndex, animate);
}重点看下这段代码
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
final View child = getChildAt(i);
if (i == childIndex) {
if (animate && mInAnimation != null) {
child.startAnimation(mInAnimation);
}
child.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
mFirstTime = false;
} else {
if (animate && mOutAnimation != null && child.getVisibility() == View.VISIBLE) {
child.startAnimation(mOutAnimation);
} else if (child.getAnimation() == mInAnimation)
child.clearAnimation();
child.setVisibility(View.GONE);
}
}从上面可以看到ViewAnimator把我们之前设置的setInAnimation(getContext(), R.anim.slide_in_done); 应用到进入和退出
setOutAnimation(getContext(), R.anim.slide_out_send);View上。






















 3160
3160

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








