注:机翻,未校对。
识别以太网帧有效负载
Identifying Ethernet Frame Payloads
Ethernet frames contain payload data encapsulated within header and trailer fields used to deliver packets over Layer 2 networks. This article provides an overview of how the structure and organization of Ethernet frame formats enables destination network devices to identify the payload type of received Ethernet frames.
以太网帧包含封装在报头和尾部字段中的有效负载数据,用于通过第 2 层网络传输数据包。本文概述了以太网帧格式的结构和组织如何使目标网络设备能够识别接收的以太网帧的有效负载类型。
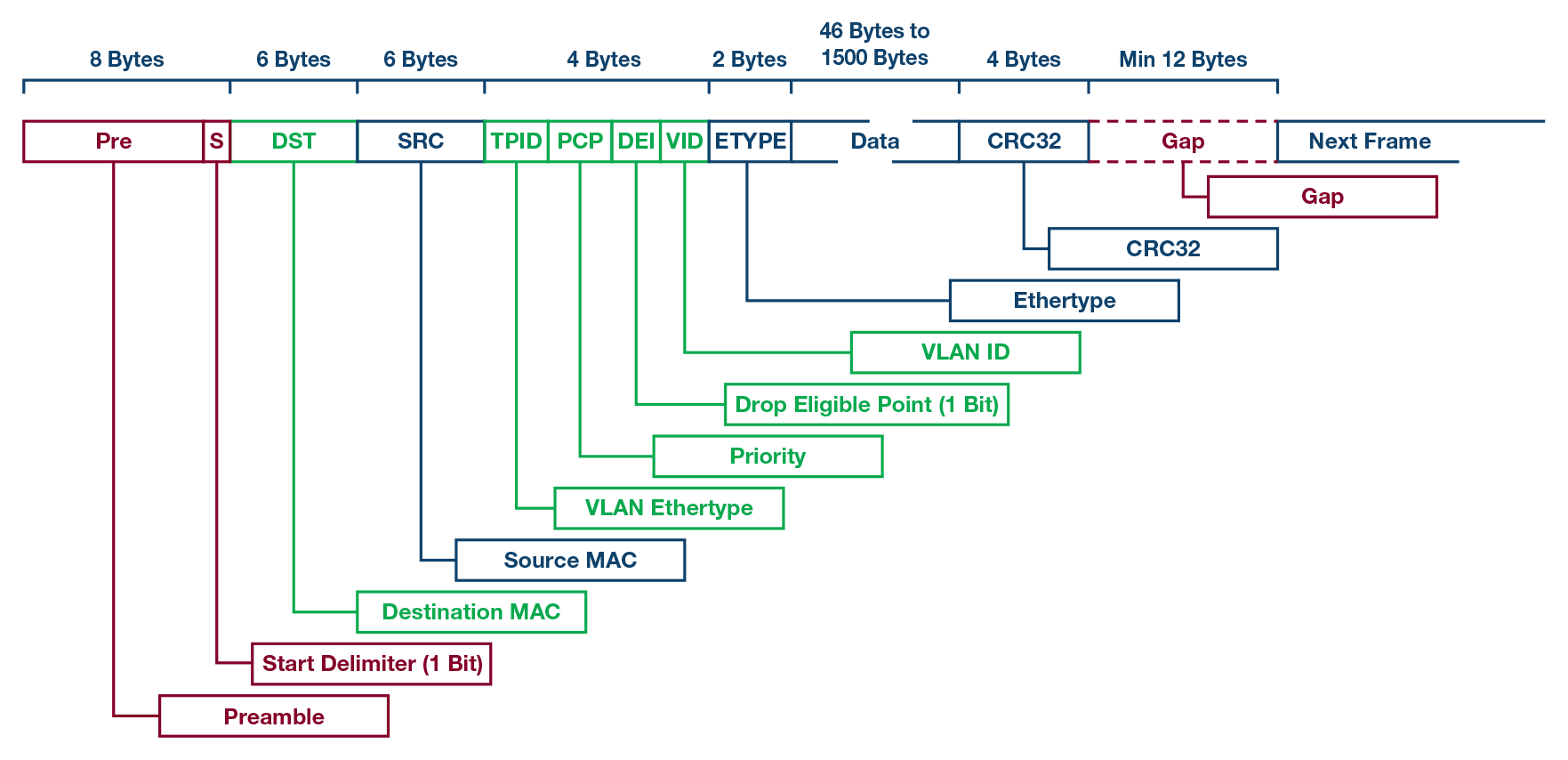
以太网帧格式概述
Ethernet Frame Format Overview
An Ethernet frame is the basic data transmission format for communication over IEEE 802.3 Ethernet networks. The standard Ethernet frame structure consists of several fields that identify and delimit the payload data carried inside the frame:
以太网帧是通过 IEEE 802.3 以太网进行通信的基本数据传输格式。标准以太网帧结构由几个字段组成,用于标识和分隔帧内携带的有效负载数据:
-
Preamble and Start Frame Delimiter – The preamble contains seven bytes of alternating 1s and 0s ending with the Start Frame Delimiter byte marking the start of the frame.
前导码和起始帧分隔符 – 前导码包含七个字节,这些字节交替出现 1 和 0,以标记帧开始的起始帧分隔符字节结尾。 -
Destination and Source MAC Addresses – These 6-byte hardware addresses identify the intended destination device and source device for the frame.
目标和源 MAC 地址 — 这些 6 字节硬件地址标识帧的预期目标设备和源设备。 -
EtherType/Length – A 2-byte field identifying the payload protocol or specifying the length of the payload data.
EtherType/Length – 一个 2 字节字段,用于标识有效负载协议或指定有效负载数据的长度。 -
Payload Data – Between 46 and 1500 bytes containing the encapsulated data for upper layer protocols.
有效负载数据 – 46 到 1500 字节之间,包含上层协议的封装数据。 -
Frame Check Sequence (FCS) – A 4-byte cyclic redundancy check value used to detect transmission errors.
帧校验序列 (FCS) – 用于检测传输错误的 4 字节循环冗余校验值。
Within this basic structure, the EtherType and Length fields directly enable devices to identify the specific type and contents of payload data inside an Ethernet frame on local networks.
在此基本结构中,EtherType 和 Length 字段直接使设备能够识别本地网络以太网帧内有效负载数据的特定类型和内容。
“以太网类型”和“长度”字段
Ethernet Type and Length Fields
The EtherType and Length fields provide critical information to network interfaces handling Ethernet frames. This 2-byte field has a dual significance depending on its numeric value:
EtherType 和 Length 字段为处理以太网帧的网络接口提供关键信息。此 2 字节字段具有双重意义,具体取决于其数值:
字段长度
For values 0-1500, it specifies the number of bytes in the payload data field. This allows support for legacy IEEE 802.3 Ethernet frames.
对于 0-1500 的值,它指定有效负载数据字段中的字节数。这允许支持传统的 IEEE 802.3 以太网帧。
协议类型
For values of 1536 (0x0600) and above, it indicates the protocol identifier for the encapsulated payload using EtherType values assigned by the IEEE.
对于 1536 (0x0600) 及以上的值,它使用 IEEE 分配的 EtherType 值指示封装有效负载的协议标识符。
If the value is below 1536, receiving network interfaces treat it as a Length field and expect a raw payload of the specified size. Values of 1536 or above indicate an EtherType identifying the payload protocol. This provides extensibility to support many layered protocols carried over native Ethernet networks.
如果该值低于 1536,则接收网络接口会将其视为“长度”字段,并期望获得指定大小的原始有效负载。值为 1536 或更高表示标识有效负载协议的 EtherType。这提供了可扩展性,以支持通过本地以太网网络传输的许多分层协议。
常见有效负载类型标识符值
Common Payload Type Identifier Values
Standard EtherType values are used to identify some widely adopted protocols commonly encapsulated and transmitted using Ethernet framing:
标准 EtherType 值用于识别一些广泛采用的协议,这些协议通常使用以太网成帧进行封装和传输:
-
IPv4 – Defined as EtherType 0x0800, indicates the frame payload contains an IPv4 packet.
IPv4 – 定义为 EtherType 0x0800,表示帧有效负载包含 IPv4 数据包。 -
IPv6 – EtherType 0x86DD signifies the presence of an IPv6 packet inside the frame.
IPv6 – EtherType 0x86DD 表示帧内存在 IPv6 数据包。 -
ARP – The Address Resolution Protocol used to map IP addresses to MAC addresses is identified by EtherType 0x0806.
ARP – 用于将 IP 地址映射到 MAC 地址的地址解析协议由 EtherType 0x0806 标识。 -
VLAN – Virtual LAN tagging protocols use EtherType 0x8100 to multiplex multiple virtual networks over a shared physical medium.
VLAN – 虚拟 LAN 标记协议使用 EtherType 0x8100 在共享物理介质上多路复用多个虚拟网络。 -
MPLS – Multiprotocol Label Switching, EtherType 0x8847 and 0x8848, tags packets for optimized forwarding and routing.
MPLS – 多协议标签交换,EtherType 0x8847 和 0x8848,标记数据包以优化转发和路由。
In this way, the 2-byte EtherType field provides a simple, extensible indicator allowing Ethernet interfaces to dynamically identify and handle many types of Layer 3 payload data encapsulated within a Layer 2 Ethernet frame structure.
通过这种方式,2 字节 EtherType 字段提供了一个简单、可扩展的指示器,允许以太网接口动态识别和处理封装在第 2 层以太网帧结构中的多种类型的第 3 层有效负载数据。
IPv4 和 IPv6 有效负载标识
IPv4 and IPv6 Payload Identification
The most ubiquitous protocols transported over Ethernet are the Internet Protocol (IP), version 4 and 6. When an Ethernet frame contains an IP packet as its payload data, the EtherType field is set to the corresponding IP identifier:
通过以太网传输的最普遍的协议是 Internet 协议 (IP) 版本 4 和 6。当以太网帧包含 IP 数据包作为其有效负载数据时,EtherType 字段将设置为相应的 IP 标识符:
- IPv4 – 0x0800 tells the receiving interface to expect an IPv4 header and packet following the Ethernet frame header.
IPv4 – 0x0800告诉接收接口在以太网帧报头之后需要 IPv4 报头和数据包。 - IPv6 – 0x86DD indicates the presence of an IPv6 packet, formatted with a distinct IPv6 header.
IPv6 – 0x86DD表示存在 IPv6 数据包,该数据包使用不同的 IPv6 标头进行格式化。
With these EtherType values, the Ethernet interface can parse the IP payload correctly. It can check packet validity, verify checksums, and either process the contents or hand off to higher level services. Up to 1500 bytes of IP packet data can be encapsulated within a standard Ethernet frame structure this way.
使用这些 EtherType 值,以太网接口可以正确解析 IP 有效负载。它可以检查数据包的有效性,验证校验和,并处理内容或移交给更高级别的服务。通过这种方式,最多 1500 字节的 IP 数据包数据可以封装在标准以太网帧结构中。
Notably, IPv4 and IPv6 themselves have identifier fields. An IPv4 header contains a Protocol field specifying how to interpret the IP payload. Common payload protocols here include TCP, UDP, and ICMP. Similarly, IPv6 uses a Next Header field to identify payload contents like TCP/UDP data or extension headers. So handling payload identification involves nested processing of identifiers at multiple layers.
值得注意的是,IPv4 和 IPv6 本身具有标识符字段。IPv4 标头包含一个协议字段,用于指定如何解释 IP 有效负载。此处常见的有效负载协议包括 TCP、UDP 和 ICMP。同样,IPv6 使用 Next Header 字段来标识有效负载内容,如 TCP/UDP 数据或扩展标头。因此,处理有效负载标识涉及在多个层对标识符进行嵌套处理。
有效负载识别
ARP Payload Identification ARP
The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), EtherType 0x0806, provides a special payload case. ARP is a Layer 3 protocol used to resolve hardware MAC addresses from known IP addresses. However, it runs directly over Ethernet, not over IP. So ARP packets represent an exception case:
地址解析协议 (ARP) EtherType 0x0806 提供了一个特殊的有效负载案例。ARP 是一种第 3 层协议,用于从已知 IP 地址解析硬件 MAC 地址。但是,它直接通过以太网运行,而不是通过 IP 运行。因此,ARP 数据包表示例外情况:
- Layer 2 Encapsulation – ARP runs directly above Ethernet and relies on EtherType 0x0806 identification.
第 2 层封装 – ARP 直接在以太网上方运行,并依赖于 EtherType 0x0806 识别。 - Layer 3 Purpose – ARP handles IP address to MAC resolution, a core Layer 3 routing function.
第 3 层用途 – ARP 处理 IP 地址到 MAC 的解析,这是第 3 层核心路由功能。
Thus ARP highlights the dual functions of Layer 2 framing. The Ethernet headers encapsulate Layer 3 packets containing ARP data used to facilitate routing and interconnection of logical IP networks. This demonstrates the flexibility of the Ethernet model to blend multiple levels of processing – using EtherType values for parsing, while carrying packets handling inter-network routing functions.
因此,ARP 突出了 Layer 2 成帧的双重功能。以太网报头封装了包含 ARP 数据的第 3 层数据包,用于促进逻辑 IP 网络的路由和互连。这展示了以太网模型混合多级处理的灵活性——使用 EtherType 值进行解析,同时携带处理网络间路由功能的数据包。
VLAN 和 MPLS 有效负载识别
VLAN and MPLS Payload Identification
Virtual LAN (VLAN) and Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) protocols utilize alternative framing and EtherTypes to tag and forward packets flows based on labels rather than destination IP addresses. They represent two complex payload identification cases:
虚拟局域网 (VLAN) 和多协议标签交换 (MPLS) 协议利用替代帧格式和 EtherType 根据标签而不是目标 IP 地址标记和转发数据包流。它们代表了两种复杂的有效载荷识别案例:
- VLAN – Inserts VLAN tags using EtherType 0x8100 inside Ethernet frames to demarcate Virtual LAN routing domains.
- VLAN — 使用 EtherType 0x8100在以太网帧内插入 VLAN 标记以划分虚拟 LAN 路由域。
- MPLS – Defines EtherTypes 0x8847 and 0x8848 for Multi-Protocol Label Switching, using stacked labels for path specifications.
MPLS – 定义用于多协议标签交换的 EtherTypes 0x8847 和 0x8848,使用堆叠标签作为路径规范。 - VLAN allows a single physical network to be partitioned into multiple isolated logical networks through the insertion of VLAN tagging headers after the source MAC address field in an Ethernet frame. Routers and switches use this additional 12-bit VLAN Identifier field to forward such tagged packets only between ports within the same tagged VLAN domain.
VLAN 允许通过在以太网帧中的源 MAC 地址字段后插入 VLAN 标记标头,将单个物理网络划分为多个隔离的逻辑网络。路由器和交换机使用此附加的 12 位 VLAN 标识符字段仅在同一标记 VLAN 域中的端口之间转发此类标记数据包。
In MPLS meanwhile, labels stacked after the source MAC specify next hop forwarding rules. This allows construction of label switched paths to optimize routing across core networks. MPLS uses these multilayer labels rather than traditional destination-based IP forwarding to streamline traffic flows based on service policies and traffic engineering rules.
同时,在 MPLS 中,堆叠在源 MAC 之后的标签指定下一跳转发规则。这允许构建标签交换路径,以优化跨核心网络的路由。MPLS 使用这些多层标签而不是传统的基于目标的 IP 转发来简化基于服务策略和流量工程规则的流量。
In both cases, inspection of EtherType identifiers (0x8100 for VLAN, 0x8847/0x8848 for MPLS) signals that the Ethernet payloads have encapsulated headers defining alternate optimized forwarding and routing semantics. This highlights the power of Ethernet framing to flexibly carry varied higher level data and control plane protocols.
在这两种情况下,对 EtherType 标识符(0x8100 用于 VLAN,0x8847/0x8848 用于 MPLS)的检查表明,以太网有效负载具有封装的标头,定义了替代优化的转发和路由语义。这凸显了以太网成帧的强大功能,可以灵活地承载各种更高级别的数据和控制平面协议。
具有有效负载类型标识的以太网帧示例
Example Ethernet Frames with Payload Type Identification
Let’s examine some hexadecimal Ethernet frame dumps to see EtherType identifiers flag the presence of different payload protocols in real network traces:
让我们检查一些十六进制以太网帧转储,看看 EtherType 标识符标记了实际网络跟踪中存在不同的有效负载协议:
Frame 1 (IPv4 Packet):
Destination MAC: 01:23:45:67:89:ab
Source MAC:02:45:67:89:ab:cd
EtherType: 0800 (IPv4)
Payload: 450000280691c0a864984da8b036
Frame 2 (IPv6 Packet):
Destination MAC:23:45:98:ab:cd:ef
Source MAC: 12:34:56:78:90:12
EtherType: 86dd (IPv6)
Payload: 6ff06f206da173222ef600d60ddae36789b25de367b35f
Frame 3 (ARP Packet):
Destination MAC: ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
Source MAC:ab:cd:ef:01:23:45
EtherType: 0806 (ARP)
Payload: 0001080006040001abcf0123edef45600c29bf5e802
注:本段着色区域无特殊意义,仅是防止字符被网页错误渲染为emoji。
Here we see the same source and destination MAC addresses on each frame, but the varying EtherType field values flag the presence of different payload protocols – IPv4, IPv6, and ARP carried over the Layer 2 Ethernet fabric between the same two devices. This allows the receiver to correctly parse and handle the different formatted IP and ARP data present in the payloads.
在这里,我们在每个帧上看到相同的源和目标 MAC 地址,但不同的 EtherType 字段值标记了存在不同的有效负载协议 —— IPv4、IPv6 和 ARP 通过两个设备之间的同一第 2 层以太网结构传输。这允许接收方正确解析和处理有效负载中存在的不同格式的 IP 和 ARP 数据。
Identification of payload types thus begins at the very start of an Ethernet frame with the EtherTypeclassify. Combined with destination MAC addressing, this mechanism elegantly enables extensible heterogeneous communications over unified physical and datalink layer networks.
有效负载类型的识别从以太网帧的开头即 EtherType 分类开始,结合目标 MAC 地址寻址,这种机制巧妙地实现了在统一的物理和数据链路层网络上进行可扩展的异构通信。
by NE 101 ,March 1, 2024






















 966
966











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








