背景:本人最近开始刷leetcode,已经按顺序刷完leetcode前200道题目,现在进行二刷,分类进行刷前200道题目,本次分享动态规划(Dynamic Programming),动态规划题目的难度大部分medium难度和hard,题目类型分为一维动态规划和二维动态规划,下面分类进行介绍。
1.一维动态规划
5. Longest Palindromic Substring
Given a string s, find the longest palindromic substring in s. You may assume that the maximum length of s is 1000.
Example 1:
Input: "babad"
Output: "bab"
Note: "aba" is also a valid answer.
Example 2:
Input: "cbbd"
Output: "bb"
class Solution {
public String longestPalindrome(String s) {
/*
* 使用dp思想,从中间向两边扩展。
复杂度:
时间:O(n**2) 空间:O(1)
* */
if (s==null || s.length()==0){
return "";
}
int len = 0;
int start = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
int cur = Math.max(getLength(s,i,i),getLength(s,i,i+1));
if (cur > len){
len = cur;
// 奇数和偶数情况考虑到 case:aba和abba
start = i - (cur-1)/2;
}
}
return s.substring(start,start+len);
}
private int getLength(String s,int l,int r){
while (l>=0 && r<s.length() &&s.charAt(l)==s.charAt(r)){
r++;
l--;
}
return (r-l-1);
}
}
53. Maximum Subarray
Given an integer array nums, find the contiguous subarray (containing at least one number) which has the largest sum and return its sum.
Example:
Input: [-2,1,-3,4,-1,2,1,-5,4],
Output: 6
Explanation: [4,-1,2,1] has the largest sum = 6.
Follow up:
If you have figured out the O(n) solution, try coding another solution using the divide and conquer approach, which is more subtle.
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
// dp[i]表示i位置之前连续子数组的和
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
dp[0] = nums[0];
int max =dp[0];
for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++){
dp[i] = Math.max(nums[i],dp[i-1]+nums[i]);
max = Math.max(max,dp[i]);
}
return max;
}
}
70. Climbing Stairs
You are climbing a stair case. It takes n steps to reach to the top.
Each time you can either climb 1 or 2 steps. In how many distinct ways can you climb to the top?
Note: Given n will be a positive integer.
Example 1:
Input: 2
Output: 2
Explanation: There are two ways to climb to the top.
1. 1 step + 1 step
2. 2 steps
Example 2:
Input: 3
Output: 3
Explanation: There are three ways to climb to the top.
3. 1 step + 1 step + 1 step
4. 1 step + 2 steps
5. 2 steps + 1 step
class Solution {
// public int climbStairs(int n) {
// if(n==1){
// return 1;
// }
// if(n==2){
// return 2;
// }
// return climbStairs(n-1)+climbStairs(n-2);
// }
public int climbStairs(int n) {
int[] dp = new int[n+1];
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for(int i=2;i<=n;i++){
dp[i] = dp[i-1] + dp[i-2];
}
return dp[n];
}
}
91. Decode Ways
A message containing letters from A-Z is being encoded to numbers using the following mapping:
'A' -> 1
'B' -> 2
...
'Z' -> 26
Given a non-empty string containing only digits, determine the total number of ways to decode it.
Example 1:
Input: "12"
Output: 2
Explanation: It could be decoded as "AB" (1 2) or "L" (12).
Example 2:
Input: "226"
Output: 3
Explanation: It could be decoded as "BZ" (2 26), "VF" (22 6), or "BBF" (2 2 6).
// class Solution {
// private Map<String,Integer> map;
// public int numDecodings(String s) {
// // 给你一个加密的数字字符串,问你一共有多少种不同的解密方式。
// // 记忆话递归
// map =new HashMap<String,Integer>();
// map.put("",1);
// if(s==null || s.length()==0){
// return 0;
// }
// return memorized(s);
// }
// private int memorized(String s){
// if(map.containsKey(s)){
// return map.get(s);
// }
// if(s.charAt(0)=='0'){
// return 0;
// }
// if(s.length()==1){
// return 1;
// }
// int w = memorized(s.substring(1));
// String sub = s.substring(0,2);
// if(Integer.parseInt(sub)>0&&Integer.parseInt(sub)<=26){
// w+= memorized(s.substring(2));
// }
// map.put(s,w);
// return w;
// }
// }
class Solution {
public int numDecodings(String s) {
// Dp解法
if(s==null || s.charAt(0)=='0'){
return 0;
}
if(s.length()==1){
return 1;
}
int[] dp = new int[s.length()+1];
dp[0] = 1;
dp[1] = 1;
for(int i=1;i<s.length();i++){
char c1 = s.charAt(i-1);
char c2 = s.charAt(i);
if(!isValid(c2)&&(!isValid(c1,c2))){
return 0;
}
if(isValid(c2)){
dp[i+1] = dp[i];
}
if(isValid(c1,c2)){
dp[i+1] += dp[i-1];
}
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(dp));
}
return dp[s.length()];
}
private boolean isValid(char c){
return c!='0';
}
private boolean isValid(char c1,char c2){
int num = 10*(c1-'0')+(c2-'0');
return num>=10&&num<=26;
}
}
96. Unique Binary Search Trees
Share
Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1 ... n?
Example:
Input: 3
Output: 5
Explanation:
Given n = 3, there are a total of 5 unique BST's:
1 3 3 2 1
\ / / / \ \
3 2 1 1 3 2
/ / \ \
2 1 2 3
class Solution {
public int numTrees(int n) {
// dp[2] = dp[0] * dp[1] (1为根的情况,则左子树一定不存在,右子树可以有一个数字)
// + dp[1] * dp[0] (2为根的情况,则左子树可以有一个数字,右子树一定不存在)
// 同理可写出 n = 3 的计算方法:
// dp[3] = dp[0] * dp[2] (1为根的情况,则左子树一定不存在,右子树可以有两个数字)
// + dp[1] * dp[1] (2为根的情况,则左右子树都可以各有一个数字)
// + dp[2] * dp[0] (3为根的情况,则左子树可以有两个数字,右子树一定不存在)
int[] dp = new int[n+1];
dp[0] = 1;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
dp[i] += dp[j]*dp[i-j-1];
}
}
return dp[n];
}
}
121. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock
Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i.
If you were only permitted to complete at most one transaction (i.e., buy one and sell one share of the stock), design an algorithm to find the maximum profit.
Note that you cannot sell a stock before you buy one.
Example 1:
Input: [7,1,5,3,6,4]
Output: 5
Explanation: Buy on day 2 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 6), profit = 6-1 = 5.
Not 7-1 = 6, as selling price needs to be larger than buying price.
Example 2:
Input: [7,6,4,3,1]
Output: 0
Explanation: In this case, no transaction is done, i.e. max profit = 0.
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
int res = 0;
if(prices.length<=1){
return 0;
}
int n = prices.length;
int[] dp = new int[n];
dp[0] = 0;
int min = prices[0];
for(int i=1;i<n;i++){
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i-1],prices[i]-min);
min = Math.min(min,prices[i]);
}
return dp[n-1];
}
}
123. Best Time to Buy and Sell Stock III
Say you have an array for which the ith element is the price of a given stock on day i.
Design an algorithm to find the maximum profit. You may complete at most two transactions.
Note: You may not engage in multiple transactions at the same time (i.e., you must sell the stock before you buy again).
Example 1:
Input: [3,3,5,0,0,3,1,4]
Output: 6
Explanation: Buy on day 4 (price = 0) and sell on day 6 (price = 3), profit = 3-0 = 3.
Then buy on day 7 (price = 1) and sell on day 8 (price = 4), profit = 4-1 = 3.
Example 2:
Input: [1,2,3,4,5]
Output: 4
Explanation: Buy on day 1 (price = 1) and sell on day 5 (price = 5), profit = 5-1 = 4.
Note that you cannot buy on day 1, buy on day 2 and sell them later, as you are
engaging multiple transactions at the same time. You must sell before buying again.
Example 3:
Input: [7,6,4,3,1]
Output: 0
Explanation: In this case, no transaction is done, i.e. max profit = 0.
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
if(prices.length <= 1) return 0;
int[] left = new int[prices.length];
int min = prices[0];
for(int i = 1; i < prices.length; ++i) {
left[i] = Math.max(left[i-1], prices[i]-min);
min = Math.min(min, prices[i]);
}
int[] right = new int[prices.length];
int max = prices[prices.length-1];
for(int i = prices.length-2; i >= 0; --i) {
right[i] = Math.max(right[i+1], max - prices[i]);
max = Math.max(max, prices[i]);
}
int ret = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < prices.length; ++i) {
int transaction2 = (i == prices.length-1) ? 0 : right[i+1];
ret = Math.max(ret, left[i] + transaction2);
}
return ret;
}
}
152. Maximum Product Subarray
Given an integer array nums, find the contiguous subarray within an array (containing at least one number) which has the largest product.
Example 1:
Input: [2,3,-2,4]
Output: 6
Explanation: [2,3] has the largest product 6.
Example 2:
Input: [-2,0,-1]
Output: 0
Explanation: The result cannot be 2, because [-2,-1] is not a subarray.
class Solution {
public int maxProduct(int[] nums) {
int[] max = new int[nums.length];
int[] min = new int[nums.length];
max[0] = nums[0];
min[0] = nums[0];
int res = max[0];
for(int i=1;i<nums.length;i++){
if(nums[i]>0){
max[i] = Math.max(nums[i],nums[i]*max[i-1]);
min[i] = Math.min(nums[i],nums[i]*min[i-1]);
}else{
max[i] = Math.max(nums[i],nums[i]*min[i-1]);
min[i] = Math.min(nums[i],nums[i]*max[i-1]);
}
res = Math.max(res,max[i]);
}
return res;
}
}
198. House Robber
You are a professional robber planning to rob houses along a street. Each house has a certain amount of money stashed, the only constraint stopping you from robbing each of them is that adjacent houses have security system connected and it will automatically contact the police if two adjacent houses were broken into on the same night.
Given a list of non-negative integers representing the amount of money of each house, determine the maximum amount of money you can rob tonight without alerting the police.
Example 1:
Input: [1,2,3,1]
Output: 4
Explanation: Rob house 1 (money = 1) and then rob house 3 (money = 3).
Total amount you can rob = 1 + 3 = 4.
Example 2:
Input: [2,7,9,3,1]
Output: 12
Explanation: Rob house 1 (money = 2), rob house 3 (money = 9) and rob house 5 (money = 1).
Total amount you can rob = 2 + 9 + 1 = 12.
class Solution {
// private int[] memory;
public int rob(int[] nums) {
// /*
// * 记忆化递归
// * */
// memory = new int[nums.length];
// Arrays.fill(memory, -1);
// return rob(nums,nums.length-1);
// }
// private int rob(int[] nums,int i){
// if (i<0){
// return 0;
// }
// if (memory[i] >= 0){
// return memory[i];
// }
// return memory[i] = Math.max(rob(nums,i-1),rob(nums,i-2)+nums[i]);
// }
//维护一个dp数组,dp[i]代表[0,i]之间最大值,对于i位置来说,有两种选择,抢或者不抢。
if (nums==null || nums.length==0){
return 0;
}
if (nums.length==1){
return nums[0];
}
if (nums.length==2){
return Math.max(nums[0],nums[1]);
}
int[] dp = new int[nums.length];
dp[0] = nums[0];
dp[1] = Math.max(nums[0],nums[1]);
for (int i = 2; i < nums.length; i++) {
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i-1],dp[i-2]+nums[i]);
}
return dp[nums.length-1];
}
}
2.二维动态规划
62. Unique Paths
A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked 'Start' in the diagram below).
The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked 'Finish' in the diagram below).
How many possible unique paths are there?
Example 1:
Input: m = 3, n = 2
Output: 3
Explanation:
From the top-left corner, there are a total of 3 ways to reach the bottom-right corner:
1. Right -> Right -> Down
2. Right -> Down -> Right
3. Down -> Right -> Right
Example 2:
Input: m = 7, n = 3
Output: 28
class Solution {
public int uniquePaths(int m, int n) {
if(m<=0||n<=0){
return 0;
}
int[][] dp = new int[m][n];
dp[0][0] = 1;
for(int i=1;i<m;i++){
dp[i][0] = 1;
}
for(int j=1;j<n;j++){
dp[0][j] = 1;
}
for(int i=1;i<m;i++){
for(int j=1;j<n;j++){
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j]+dp[i][j-1];
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1];
}
}
63. Unique Paths II
A robot is located at the top-left corner of a m x n grid (marked 'Start' in the diagram below).
The robot can only move either down or right at any point in time. The robot is trying to reach the bottom-right corner of the grid (marked 'Finish' in the diagram below).
Now consider if some obstacles are added to the grids. How many unique paths would there be?
An obstacle and empty space is marked as 1 and 0 respectively in the grid.
Note: m and n will be at most 100.
Example 1:
Input:
[
[0,0,0],
[0,1,0],
[0,0,0]
]
Output: 2
Explanation:
There is one obstacle in the middle of the 3x3 grid above.
There are two ways to reach the bottom-right corner:
1. Right -> Right -> Down -> Down
2. Down -> Down -> Right -> Right
class Solution {
public int uniquePathsWithObstacles(int[][] obstacleGrid) {
int m = obstacleGrid.length;
int n = obstacleGrid[0].length;
int[][] dp = new int[m][n];
for(int i=0;i<m;i++){
if(obstacleGrid[i][0]==0){
dp[i][0] = 1;
}else{
break;
}
}
for(int j=0;j<n;j++){
if(obstacleGrid[0][j]==0){
dp[0][j] = 1;
}else{
break;
}
}
for(int i=1;i<m;i++){
for(int j=1;j<n;j++){
if(obstacleGrid[i][j]==0){
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + dp[i][j-1];
}else{
dp[i][j] = 0;
}
}
}
return dp[m-1][n-1];
}
}
64. Minimum Path Sum
Given a m x n grid filled with non-negative numbers, find a path from top left to bottom right which minimizes the sum of all numbers along its path.
Note: You can only move either down or right at any point in time.
Example:
Input:
[
[1,3,1],
[1,5,1],
[4,2,1]
]
Output: 7
Explanation: Because the path 1→3→1→1→1 minimizes the sum.
class Solution {
// public int minPathSum(int[][] grid) {
// return calculate(grid,0,0);
// }
// private int calculate(int[][] grid,int row,int col){
// if(row>=grid.length||col>=grid[0].length){
// return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
// }
// if(row==grid.length-1&&col==grid[0].length-1){
// return grid[row][col];
// }
// return grid[row][col] + Math.min(calculate(grid,row+1,col),calculate(grid,row,col+1));
// }
public int minPathSum(int[][] grid) {
//动态规划解法
int m = grid.length;
int n = grid[0].length;
int[][] dp = new int[m][n];
dp[0][0] = grid[0][0];
for(int i=1;i<m;i++){
dp[i][0] = dp[i-1][0]+grid[i][0];
System.out.println(dp[i][0]);
}
for(int j=1;j<n;j++){
dp[0][j] = dp[0][j-1] + grid[0][j];
System.out.println(dp[0][j]);
}
int i = 1;
int j = 1;
while(i<m){
while(j<n){
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i-1][j],dp[i][j-1])+grid[i][j];
System.out.println(dp[i][j]);
j++;
}
j=1;
i++;
}
return dp[m-1][n-1];
}
}
72. Edit Distance
Given two words word1 and word2, find the minimum number of operations required to convert word1 to word2.
You have the following 3 operations permitted on a word:
Insert a character
Delete a character
Replace a character
Example 1:
Input: word1 = "horse", word2 = "ros"
Output: 3
Explanation:
horse -> rorse (replace 'h' with 'r')
rorse -> rose (remove 'r')
rose -> ros (remove 'e')
Example 2:
Input: word1 = "intention", word2 = "execution"
Output: 5
Explanation:
intention -> inention (remove 't')
inention -> enention (replace 'i' with 'e')
enention -> exention (replace 'n' with 'x')
exention -> exection (replace 'n' with 'c')
exection -> execution (insert 'u')
class Solution {
public int minDistance(String word1, String word2) {
int m = word1.length();
int n = word2.length();
int[][] dp = new int[m+1][n+1];
for(int i=0;i<=m;i++){
dp[i][0] = i;
}
for(int j=0;j<=n;j++){
dp[0][j] = j;
}
for(int i=1;i<=m;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=n;j++){
char chi = word1.charAt(i-1);
char chj = word2.charAt(j-1);
if(chi==chj){
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1];
}else{
dp[i][j] = 1+Math.min(dp[i-1][j],Math.min(dp[i][j-1],dp[i-1][j-1]));
}
}
}
return dp[m][n];
}
}
85. Maximal Rectangle
Given a 2D binary matrix filled with 0's and 1's, find the largest rectangle containing only 1's and return its area.
Example:
Input:
[
["1","0","1","0","0"],
["1","0","1","1","1"],
["1","1","1","1","1"],
["1","0","0","1","0"]
]
Output: 6
class Solution {
public int maximalRectangle(char[][] matrix) {
int max = 0;
if(matrix==null || matrix.length==0||matrix[0].length==0){
return max;
}
int row = matrix.length;
int col = matrix[0].length;
int[] heights = new int[col];
for(int i=0;i<row;i++){
for(int j=0;j<col;j++){
if(matrix[i][j]=='0'){
heights[j]=0;
}else{
heights[j]+=1;
}
}
int area = largestMaximalRectangle(heights);
max = Math.max(max,area);
}
return max;
}
private int largestMaximalRectangle(int[] heights){
int max = 0;
if(heights==null || heights.length==0){
return max;
}
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
for(int i=0;i<heights.length;i++){
if(stack.isEmpty()||heights[i]>heights[stack.peek()]){
stack.push(i);
}else{
// 右边界
int right = i;
int index = stack.pop();
//高度相同向左进行移动
while(!stack.isEmpty()&&heights[index]==heights[stack.peek()]){
index = stack.pop();
}
int leftmost = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek();
max = Math.max(max,(right-leftmost-1)*heights[index]);
i--;
}
}
// 数组处理完毕
// 有边界不变
int rightmost = stack.peek()+1;
while(!stack.isEmpty()){
int index = stack.pop();
int left = stack.isEmpty() ? -1 : stack.peek();
max = Math.max(max,heights[index]*(rightmost-left-1));
}
return max;
}
}
115. Distinct Subsequences
Given a string S and a string T, count the number of distinct subsequences of S which equals T.
A subsequence of a string is a new string which is formed from the original string by deleting some (can be none) of the characters without disturbing the relative positions of the remaining characters. (ie, "ACE" is a subsequence of "ABCDE" while "AEC" is not).
Example 1:
Input: S = "rabbbit", T = "rabbit"
Output: 3
Explanation:
As shown below, there are 3 ways you can generate "rabbit" from S.
(The caret symbol ^ means the chosen letters)
rabbbit
^^^^ ^^
rabbbit
^^ ^^^^
rabbbit
^^^ ^^^
Example 2:
Input: S = "babgbag", T = "bag"
Output: 5
Explanation:
As shown below, there are 5 ways you can generate "bag" from S.
(The caret symbol ^ means the chosen letters)
babgbag
^^ ^
babgbag
^^ ^
babgbag
^ ^^
babgbag
^ ^^
babgbag
^^^
class Solution {
public int numDistinct(String s, String t) {
// 二维动态规划
int ls = s.length();
int lt = t.length();
int[][] dp = new int[lt+1][ls+1];
for(int j=0;j<=ls;j++){
dp[0][j] = 1;
}
for(int i=1;i<=lt;i++){
for(int j=1;j<=ls;j++){
if(t.charAt(i-1)==s.charAt(j-1)){
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j-1]+dp[i-1][j-1];
}else{
dp[i][j] = dp[i][j-1];
}
}
}
return dp[lt][ls];
}
}
120. Triangle
Given a triangle, find the minimum path sum from top to bottom. Each step you may move to adjacent numbers on the row below.
For example, given the following triangle
[
[2],
[3,4],
[6,5,7],
[4,1,8,3]
]
The minimum path sum from top to bottom is 11 (i.e., 2 + 3 + 5 + 1 = 11).
Note:
Bonus point if you are able to do this using only O(n) extra space, where n is the total number of rows in the triangle.
class Solution {
public int minimumTotal(List<List<Integer>> triangle) {
//动态规划
int m = triangle.size();
int[][] dp = new int[m][m];
dp[0][0] = triangle.get(0).get(0);
int res = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
List<Integer> list0=triangle.get(0);
if(list0.size()==0){
return 0;
}
if(m==1){
return list0.get(0);
}
for(int i=1;i<m;i++){
List<Integer> list = triangle.get(i);
for(int j=0;j<=i;j++){
if(j==0){
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j] + list.get(j);
}else if(j==i){
System.out.println(j);
dp[i][j] = dp[i-1][j-1] + list.get(j);
}else{
dp[i][j] = Math.min(dp[i-1][j-1],dp[i-1][j]) + list.get(j);
}
if(i==(m-1)){
res = Math.min(res,dp[i][j]);
}
}
}
return res;
}
}
132. Palindrome Partitioning II
Given a string s, partition s such that every substring of the partition is a palindrome.
Return the minimum cuts needed for a palindrome partitioning of s.
Example:
Input: "aab"
Output: 1
Explanation: The palindrome partitioning ["aa","b"] could be produced using 1 cut.
class Solution {
public int minCut(String s) {
int n = s.length();
int[] dp = new int[n];
Arrays.fill(dp,n);
boolean[][] valid = new boolean[n][n];
//初始化回文矩阵
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
valid[i][i] = true;
}
for(int l=2;l<=n;l++){
if(l==2){
for(int i=0,j=i+l-1;j<n;i++,j++){
valid[i][j] = s.charAt(i)==s.charAt(j);
}
continue;
}
for(int i=0,j=i+l-1;j<n;i++,j++){
valid[i][j] = (s.charAt(i)==s.charAt(j) && valid[i+1][j-1]);
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
if(valid[0][i]){
dp[i] = 0;
continue;
}
for(int j=0;j<i;j++){
if(valid[j+1][i]){
dp[i] = Math.min(dp[i],dp[j]+1);
}
}
}
return dp[n-1];
}
}
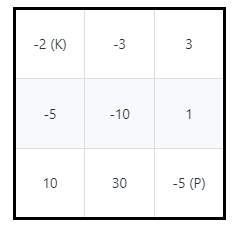
174. Dungeon Game
The demons had captured the princess (P) and imprisoned her in the bottom-right corner of a dungeon. The dungeon consists of M x N rooms laid out in a 2D grid. Our valiant knight (K) was initially positioned in the top-left room and must fight his way through the dungeon to rescue the princess.
The knight has an initial health point represented by a positive integer. If at any point his health point drops to 0 or below, he dies immediately.
Some of the rooms are guarded by demons, so the knight loses health (negative integers) upon entering these rooms; other rooms are either empty (0's) or contain magic orbs that increase the knight's health (positive integers).
In order to reach the princess as quickly as possible, the knight decides to move only rightward or downward in each step.
Write a function to determine the knight's minimum initial health so that he is able to rescue the princess.
For example, given the dungeon below, the initial health of the knight must be at least 7 if he follows the optimal path RIGHT-> RIGHT -> DOWN -> DOWN.
class Solution {
public int calculateMinimumHP(int[][] dungeon) {
// 考虑极端情况,只有一个格子。如果格子值val是负数,则英雄血量至少为1-val;如果是整数,则英雄只需要1点血量保证存活即可。
int m = dungeon.length;
int n = dungeon[0].length;
int[][] dp = new int[m+1][n+1];
for(int i=0;i<=m;i++){
Arrays.fill(dp[i],Integer.MAX_VALUE);
}
dp[m][n-1]=dp[m-1][n] = 1;
for(int i=m-1;i>=0;i--){
for(int j=n-1;j>=0;j--){
dp[i][j] = Math.max(1,Math.min(dp[i][j+1],dp[i+1][j])-dungeon[i][j]);
}
}
return dp[0][0];
}
}






















 266
266











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








