本节主要内容
- 隐式转换简介
- 隐式转换函数
- 隐式转换规则
- 隐式参数
1. 隐式转换简介
在scala语言当中,隐式转换是一项强大的程序语言功能,它不仅能够简化程序设计,也能够使程序具有很强的灵活性。要想更进一步地掌握scala语言,了解其隐式转换的作用与原理是很有必要的,否则很难得以应手地处理日常开发中的问题。
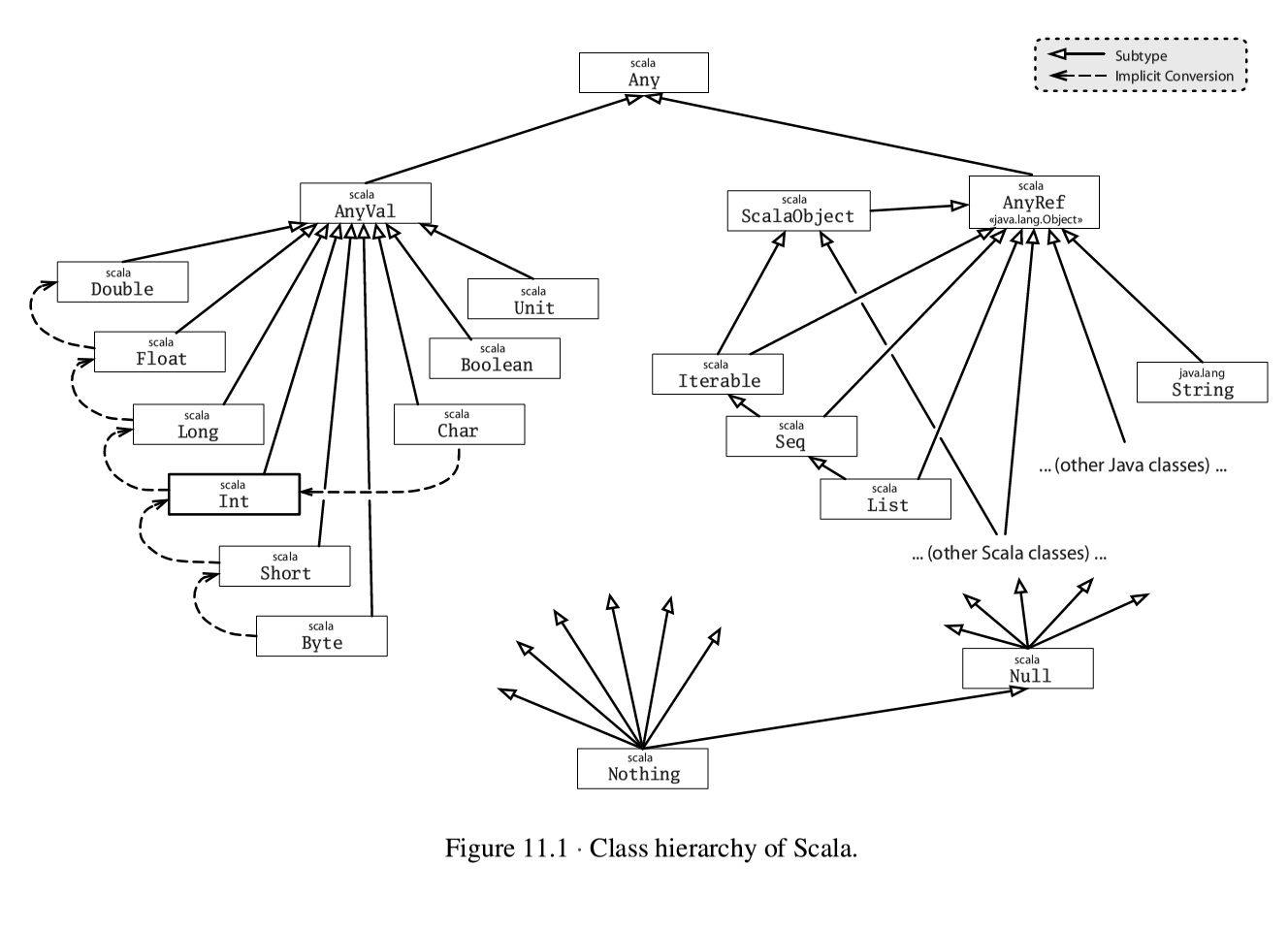
在scala语言中,隐式转换是无处不在的,只不过scala语言为我们隐藏了相应的细节,例如scala中的类继承层次结构中:
它们存在固有的隐式转换,不需要人工进行干预,例如Float在必要情况下自动转换为Double类型
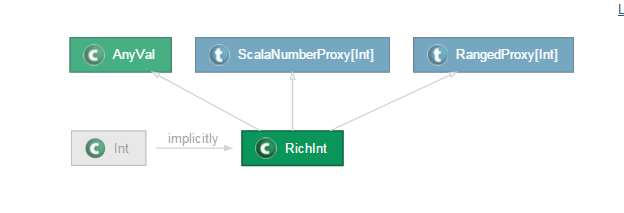
在前一讲的视图界定中我们也提到,视图界定可以跨越类层次结构进行,它背后的实现原理就是隐式转换,例如Int类型会视图界定中会自动转换成RichInt,而RichInt实现了Comparable接口,当然这里面的隐式转换也是scala语言为我们设计好的
本节将对隐式转换中的隐式转换函数、隐式转换规则、隐式参数进行介绍,使大家明白如何自己实现隐式转换操作。
2. 隐式转换函数
下列赋值如果没有隐式转换的话会报错:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
添加隐式转换函数后可以实现Double类型到Int类型的赋值
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
隐式函数的名称对结构没有影响,即implicit def double2Int(x:Double)=x.toInt函数可以是任何名字,只不能采用source2Target这种方式函数的意思比较明确,阅读代码的人可以见名知义,增加代码的可读性。
隐式转换功能十分强大,可以快速地扩展现有类库的功能,例如下面的代码:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
3. 隐式转换规则
隐式转换可以定义在目标文件当中,例如
- 1
- 2
隐式转换函数与目标代码在同一个文件当中,也可以将隐式转换集中放置在某个包中,在使用进直接将该包引入即可,例如:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
这种方式在scala语言中比较常见,在前面我们也提到,scala会默认帮我们引用Predef对象中所有的方法,Predef中定义了很多隐式转换函数,下面是Predef的部分隐式转换源码:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
那什么时候会发生隐式转换呢?主要有以下几种情况:
1 当方法中参数的类型与实际类型不一致时,例如
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
2 当调用类中不存在的方法或成员时,会自动将对象进行隐式转换,例如:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
前面我们讲了什么情况下会发生隐式转换,下面我们讲一下什么时候不会发生隐式转换:
1 编译器可以不在隐式转换的编译通过,则不进行隐式转换,例如
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
2 如果转换存在二义性,则不会发生隐式转换,例如
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
编译提示隐式转换存在二义性(ambiguous)
3 隐式转换不会嵌套进行,例如
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
- 20
- 21
- 22
- 23
- 24
- 25
- 26
- 27
- 28
- 29
- 30
- 31
- 32
- 33
- 34
- 35
理解了这些规则之后,在使用隐式转换时才能够得心应手
4. 隐式参数
在一般的函数据定义过程中,需要明确传入函数的参数,代码如下:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- 6
- 7
- 8
- 9
- 10
- 11
- 12
- 13
- 14
- 15
- 16
- 17
- 18
- 19
如果给函数定义隐式参数的话,则在使用时可以不带参数,代码如下:






















 181
181

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








