1、使用static关键字:
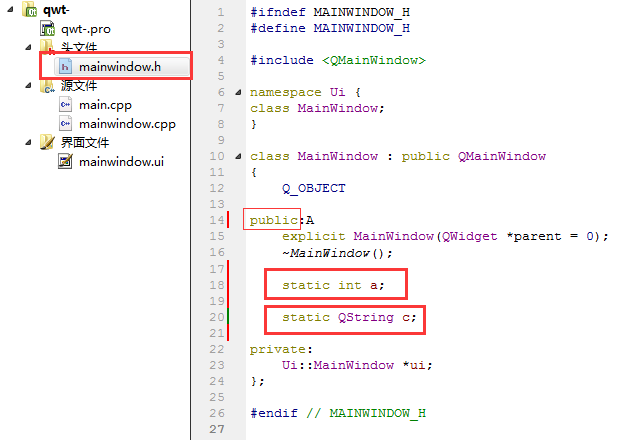
头文件声明:声明为public类型变量
mainwindow.h
#ifndef MAINWINDOW_H
#define MAINWINDOW_H
#include <QMainWindow>
namespace Ui {
class MainWindow;
}
class MainWindow : public QMainWindow
{
Q_OBJECT
public:
explicit MainWindow(QWidget *parent = 0);
~MainWindow();
static int a;
static QString c;
private:
Ui::MainWindow *ui;
};
#endif // MAINWINDOW_H
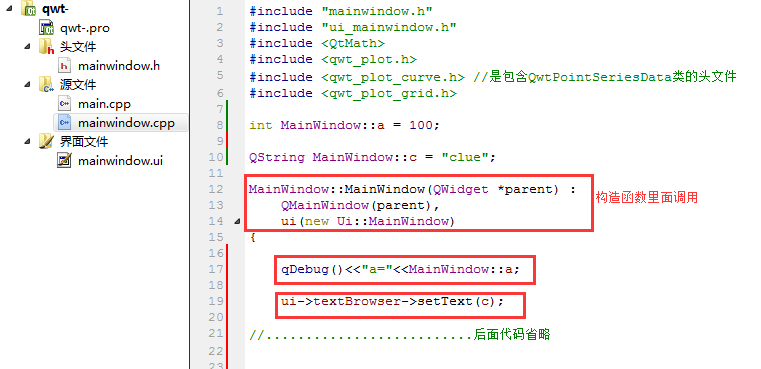
源文件定义:注意这里的变量定义,一定要写在函数的外面。
mainwindow.cpp
#include "mainwindow.h"
#include "ui_mainwindow.h"
#include <QtMath>
#include <qwt_plot.h>
#include <qwt_plot_curve.h> //是包含QwtPointSeriesData类的头文件
#include <qwt_plot_grid.h>
int MainWindow::a = 100;
QString MainWindow::c = "clue";
MainWindow::MainWindow(QWidget *parent) :
QMainWindow(parent),
ui(new Ui::MainWindow)
{
qDebug()<<"a="<< a;
ui->textBrowser->setText(c);
//..........................后面代码省略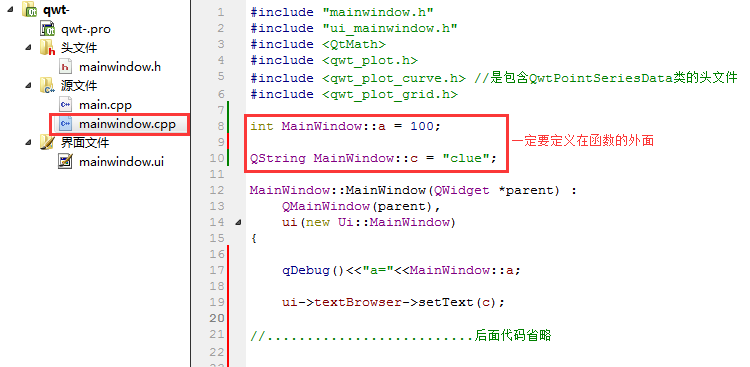
调用方式:在函数里面调用全局变量
2、使用extern关键字:
cglobal.h (声明写在类和命名控件的外面)
cglobal.cpp (在函数外面定义变量)
调用方式
墙裂推荐第一种使用static关键字的全局变量,第二种会破坏封装性。






















 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








