因为几个算法使用了递归,这里测试用的数组大小又比较大,如果使用vs编译的话,需要调整一下堆栈的大小,否则容易发生stackOverflow的错误。
代码如下
#include"stdafx.h"
#include<iostream>
#include<ctime>
#include<cstdlib>
using namespace std;
#define NUM 50000;
void bubbleSort(int temp1[], int length);
void insertSort(int temp2[], int length);
void shellSort(int temp3[], int length);
void selectSort(int temp4[], int length);
void mergeSort(int temp5[], int left, int right);
void quickSort(int temp6[], int left, int right);
void heapSort(int temp7[], int length);
void heapRebuild(int arr[], int root, int size);
int main()
{
int length = 50000;
int arr[50000];
srand(time(0));
for (int i = 0; i<length; i++)
{
arr[i] = rand() % NUM;
}
int temp1[50000];
int temp2[50000];
int temp3[50000];
int temp4[50000];
int temp5[50000];
int temp6[50000];
int temp7[50000];
int copySize = length * 4;
memcpy(temp1, arr, copySize);
memcpy(temp2, arr, copySize);
memcpy(temp3, arr, copySize);
memcpy(temp4, arr, copySize);
memcpy(temp5, arr, copySize);
memcpy(temp6, arr, copySize);
memcpy(temp7, arr, copySize);
bubbleSort(temp1, length);
insertSort(temp2, length);
shellSort(temp3, length);
selectSort(temp4, length);
clock_t start = clock();
mergeSort(temp5, 0, length-1);
clock_t end = clock();
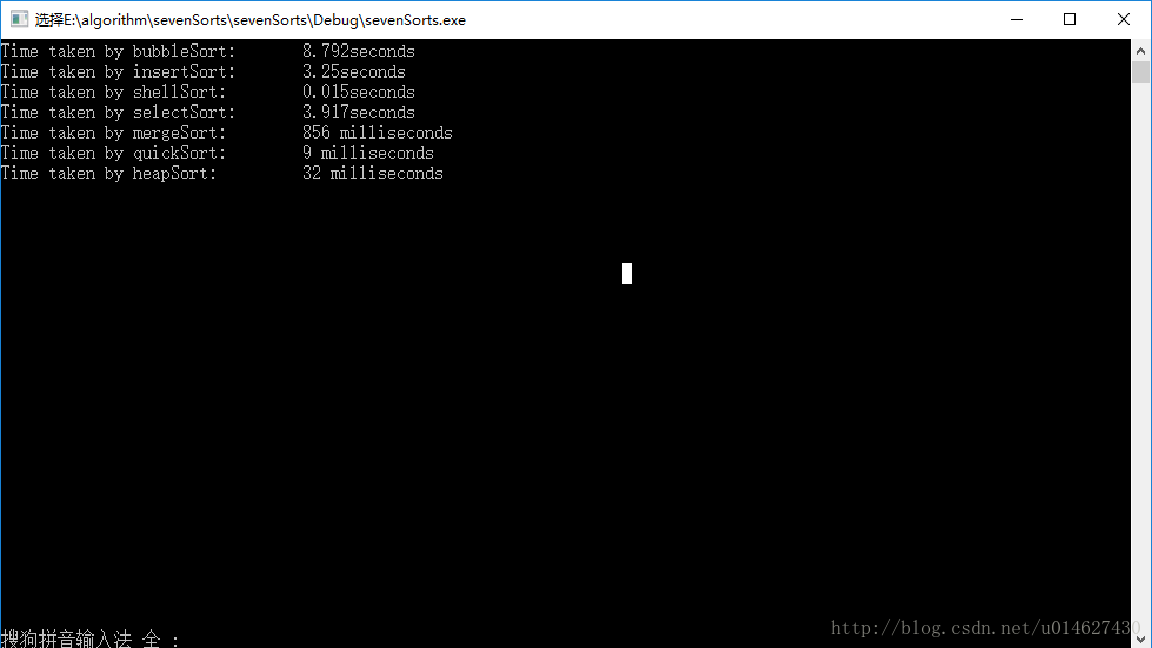
cout << "Time taken by mergeSort:\t" << (double)(end - start) << " milliseconds" << endl;
clock_t start1 = clock();
quickSort(temp6, 0, length - 1);
clock_t end1 = clock();
cout << "Time taken by quickSort:\t" << (double)(end1 - start1) << " milliseconds" << endl;
clock_t start2 = clock();
heapSort(temp7, length);
clock_t end2 = clock();
cout << "Time taken by heapSort:\t" << (double)(end2 - start2) << " milliseconds" << endl;
getchar();
return 0;
}
//冒泡排序
void bubbleSort(int temp1[], int length)
{
int i, j, temp;
clock_t start = clock();
for (i = 0; i<length; i++)
{
for (j = 1; j<length - i; j++)
{
if ((*(temp1 + j - 1))>(*(temp1 + j)))
{
temp = (*(temp1 + j));
(*(temp1 + j)) = (*(temp1 + j - 1));
(*(temp1 + j - 1)) = temp;
}
}
}
clock_t end = clock();
cout << "Time taken by bubbleSort:\t" << (double)(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "seconds" << endl;
}
//插入排序
void insertSort(int temp2[], int length)//有数组的地方需要考虑边界
{
int i, j, temp, k, l;
clock_t start = clock();
for (i = 0; i<length; i++)
{
for (j = i - 1; j >= 0; j--)//结束之后,j=-1,如果没有break。
{
if ((*(temp2 + j))<(*(temp2 + i)))
{
break;
}
}
if (j != i - 1)
{
temp = (*(temp2 + i));
for (k = i - 1; k>j; k--)
{
(*(temp2 + k + 1)) = (*(temp2 + k));
}
(*(temp2 + k + 1)) = temp;
}
}
clock_t end = clock();
cout << "Time taken by insertSort:\t" << (double)(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "seconds" << endl;
}
//希尔排序;
void shellSort(int temp3[], int length)
{
int i, j;
int temp = 0;
clock_t start = clock();
for (int gap = length / 2; gap>0; gap /= 2)
{
for (int i = gap; i<length; i++)
{
for (j = i - gap; j >= 0 && ((*(temp3 + j))>(*(temp3 + j + gap))); j -= gap)
{
temp = (*(temp3 + j));
(*(temp3 + j)) = (*(temp3 + j + gap));
(*(temp3 + j + gap)) = temp;
}
}
}
clock_t end = clock();
cout << "Time taken by shellSort:\t" << (double)(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "seconds" << endl;
}
//选择排序;
void selectSort(int temp4[], int length)
{
int i, j, temp, min;
clock_t start = clock();
for (i = 0; i<length; i++)
{
min = i;
for (j = i + 1; j<length; j++)
{
if ((*(temp4 + j))<(*(temp4 + min)))
{
min = j;
}
}
temp = (*(temp4 + i));
(*(temp4 + i)) = (*(temp4 + min));
(*(temp4 + min)) = temp;
}
clock_t end = clock();
cout << "Time taken by selectSort:\t" << (double)(end - start) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "seconds" << endl;
}
//归并排序;
void mergeSort(int temp5[], int left, int right)
{
int temp[50000];
int i, j, k, mid;
if (left<right)
{
mid = (left + right) / 2;
//递归
mergeSort(temp5, left, mid);
mergeSort(temp5, mid + 1, right);
//合并
i = left;
j = mid + 1;
k = 0;
while ((i <= mid) &&(j<= right))
{
if ((*(temp5 + i))<(*(temp5 + j)))
{
temp[k] = (*(temp5 + i));
k++;
i++;
}
else
{
temp[k] = (*(temp5 + j));
k++;
j++;
}
}
while (i <= mid)
{
temp[k] = (*(temp5 + i));
k++;
i++;
}
while (j <= right)
{
temp[k] = (*(temp5 + j));
k++;
j++;
}
for (int l = 0; l<k; l++)
temp5[left + l] = temp[l];
}
}
//快速排序;
void quickSort(int temp6[], int left, int right)
{
if (left<right)//递归的结束
{
//temp作为第一个基数
int i = left, j = right, temp = *(temp6 + left);
while (i<j)//循环,直到对于基数的一轮交换全部完成
{
while ((i<j) && ((*(temp6 + j)) >= temp))
{
j--;
}
if (i<j)
{
(*(temp6 + i)) = (*(temp6 + j));
i++;
}
while ((i<j) && ((*(temp6 + i))<temp))
{
i++;
}
if (i<j)
{
(*(temp6 + j)) = (*(temp6 + i));
j--;
}
}
(*(temp6 + i)) = temp;//到此,一轮基于基数的交换完成
quickSort(temp6, left, i - 1);//缩小范围,在left到i-1范围内的数都比刚才的基数小,在这个范围内再选出基数做重复交换,不断递归,直到left<right不成立。
quickSort(temp6, i + 1, right);
}
}
//堆排序;
/*
堆排序是一种基于二叉堆这个数据结构的排序算法,属于原地排序
二叉堆满足二个特性:
1.父结点的键值总是大于或等于(小于或等于)任何一个子节点的键值。
2.每个结点的左子树和右子树都是一个二叉堆(都是最大堆或最小堆)。
*/
void heapSort(int temp7[], int length)
{
for (int i = length / 2; i >= 0; i--)
{
heapRebuild(temp7, i, length);//堆化数组,根节点是数组中最大的数
}
int last = length - 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= length; i++, last--)
{
int temp = *temp7;
*temp7 = *(temp7 + last);
*(temp7 + last) = temp;
heapRebuild(temp7, 0, last);//每次都从根节点取走数值,然后缩小范围再重建二叉堆
}
}
void heapRebuild(int temp7[], int root, int size)
{
int child = 2 * root + 1;//i结点的父结点下标就为(i – 1) / 2,所以2*root+1是子节点
if (child <= size - 1)
{
int rightChild = child + 1;
int largest = child;
if (rightChild <= size - 1)
if ((*(temp7 + child))<(*(temp7 + rightChild)))
largest = rightChild;
if ((*(temp7 + root))<(*(temp7 + largest)))//根节点的数值如果比最大的子节点小,那么就交换他们
{
int temp = (*(temp7 + largest));
(*(temp7 + largest)) = (*(temp7 + root));
(*(temp7 + root)) = temp;
heapRebuild(temp7, largest, size);//递归,原来最大的那个子节点作为下一层递归的根节点
}
}
}





















 1376
1376











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








