提要
经过前面的关于GLSL基础学习,可以参考OpenGL进阶专栏中的一些文章。
接下来的内容将会非常的有意思,比如全局光照,环境贴图,法线贴图,景深....是不是听着就很棒!想要学习的话,当然需要付出更多的努力!不过一切都是值得的。
今天的内容主要是关于光照的一些基础着色。
在光照模型中,光照主要由三部分组成:环境光(ambient),漫反射(diffuse),镜面反射(specular)。环境光是那些在环境中进行充分的散射,无法分辨方向的光,它似乎时来自所有方向的。漫反射来自某个方向,因此,如果它从正面照射表面,它看起来显得更亮一些,反之,如果它是斜着掠过表面,它看起来就显得暗一些,当它撞击到物体的表面的时候,它会均匀地向所有的方向发散。镜面光来自一个特定的方向,并且倾向于从表面某个特定的方向反射,当有一束激光从一面镜子上反弹回来时,它所产生的几乎是百分百的镜面反射光。
关于光照的原理及编程实现,可以参考另一篇文章:光线追踪(RayTracing)算法理论与实践(三)光照
单点光照下的漫反射着色
这里需要用到一个模型,来自stanford的兔子 - bunny,在文章的最后有下载,最好自己加载到blender里面再导出一遍,不然似乎没有法线信息。
程序实现的思路:
1)加载obj模型。
2)将顶点法线坐标存到VBO中,并作为参数传到shader中去。
3)在shader中定义关于光照以及MVP的Uniform变量。
4)在程序中设置uniform变量。
5)在定点shader中计算顶点位置和光照强度,在片段shader中对片段进行着色。
具体的代码实现如下。
首先在代码中添加一个ObjObject类,用来表示Obj模型类。
objobject.h
- #ifndef OBJOBJECT_H
- #define OBJOBJECT_H
- #include "util.h"
- class ObjObject
- {
- public:
- ObjObject();
- ObjObject(const char * path);
- virtual ~ObjObject();
- int getVerticesCount();
- vector<glm::vec3> vertices;
- vector<glm::vec2> uvs;
- vector<glm::vec3> normals;
- protected:
- private:
- };
- #endif // TEAPOT_H
#ifndef OBJOBJECT_H
#define OBJOBJECT_H
#include "util.h"
class ObjObject
{
public:
ObjObject();
ObjObject(const char * path);
virtual ~ObjObject();
int getVerticesCount();
vector<glm::vec3> vertices;
vector<glm::vec2> uvs;
vector<glm::vec3> normals;
protected:
private:
};
#endif // TEAPOT_H
objobject.cpp
- #include "objobject.h"
- ObjObject::ObjObject()
- {
- //ctor
- }
- ObjObject::~ObjObject()
- {
- //dtor
- }
- ObjObject::ObjObject(const char * path)
- {
- Util u;
- u.loadOBJ(path, this->vertices, this->uvs, this->normals);
- }
- int ObjObject::getVerticesCount()
- {
- return this->vertices.size();
- }
#include "objobject.h"
ObjObject::ObjObject()
{
//ctor
}
ObjObject::~ObjObject()
{
//dtor
}
ObjObject::ObjObject(const char * path)
{
Util u;
u.loadOBJ(path, this->vertices, this->uvs, this->normals);
}
int ObjObject::getVerticesCount()
{
return this->vertices.size();
}
接着就是在渲染中一步步实现上面提到的步骤了。
在initGL中对bunny进行初始化:
- bunny = ObjObject("bunny.obj");
bunny = ObjObject("bunny.obj");然后生成定点和法线相对应的 VAO,VBO,同时加载shader
- void CGL::compileShader()
- {
- glGenVertexArrays(1, &VertexArrayID);
- glBindVertexArray(VertexArrayID);
- glGenBuffers(1, &vertexbuffer);
- glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbuffer);
- glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, bunny.vertices.size() * sizeof(glm::vec3), &bunny.vertices[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW);
- //glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 12 * sizeof(GLfloat), positionData, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
- // 1rst attribute buffer : vertices
- glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
- glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbuffer);
- glVertexAttribPointer(
- 0, // attribute
- 3, // size
- GL_FLOAT, // type
- GL_FALSE, // normalized?
- 0, // stride
- (void*)0 // array buffer offset
- );
- GLuint normalbuffer;
- glGenBuffers(1, &normalbuffer);
- glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, normalbuffer);
- glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, bunny.normals.size() * sizeof(glm::vec3), &bunny.normals[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW);
- // 3rd attribute buffer : normals
- glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
- glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, normalbuffer);
- glVertexAttribPointer(
- 1, // attribute
- 3, // size
- GL_FLOAT, // type
- GL_FALSE, // normalized?
- 0, // stride
- (void*)0 // array buffer offset
- );
- if( ! prog.compileShaderFromFile("shader/basic1.vert",GLSLShader::VERTEX) )
- {
- printf("Vertex shader failed to compile!\n%s",
- prog.log().c_str());
- exit(1);
- }
- if( ! prog.compileShaderFromFile("shader/basic1.frag",GLSLShader::FRAGMENT))
- {
- printf("Fragment shader failed to compile!\n%s",
- prog.log().c_str());
- exit(1);
- }
- prog.bindAttribLocation(0, "VertexPosition");
- prog.bindAttribLocation(1, "VertexNormal");
- if( ! prog.link() )
- {
- printf("Shader program failed to link!\n%s",
- prog.log().c_str());
- exit(1);
- }
- if( ! prog.validate() )
- {
- printf("Program failed to validate!\n%s",
- prog.log().c_str());
- exit(1);
- }
- prog.use();
- }
void CGL::compileShader()
{
glGenVertexArrays(1, &VertexArrayID);
glBindVertexArray(VertexArrayID);
glGenBuffers(1, &vertexbuffer);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbuffer);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, bunny.vertices.size() * sizeof(glm::vec3), &bunny.vertices[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW);
//glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, 12 * sizeof(GLfloat), positionData, GL_STATIC_DRAW);
// 1rst attribute buffer : vertices
glEnableVertexAttribArray(0);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, vertexbuffer);
glVertexAttribPointer(
0, // attribute
3, // size
GL_FLOAT, // type
GL_FALSE, // normalized?
0, // stride
(void*)0 // array buffer offset
);
GLuint normalbuffer;
glGenBuffers(1, &normalbuffer);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, normalbuffer);
glBufferData(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, bunny.normals.size() * sizeof(glm::vec3), &bunny.normals[0], GL_STATIC_DRAW);
// 3rd attribute buffer : normals
glEnableVertexAttribArray(1);
glBindBuffer(GL_ARRAY_BUFFER, normalbuffer);
glVertexAttribPointer(
1, // attribute
3, // size
GL_FLOAT, // type
GL_FALSE, // normalized?
0, // stride
(void*)0 // array buffer offset
);
if( ! prog.compileShaderFromFile("shader/basic1.vert",GLSLShader::VERTEX) )
{
printf("Vertex shader failed to compile!\n%s",
prog.log().c_str());
exit(1);
}
if( ! prog.compileShaderFromFile("shader/basic1.frag",GLSLShader::FRAGMENT))
{
printf("Fragment shader failed to compile!\n%s",
prog.log().c_str());
exit(1);
}
prog.bindAttribLocation(0, "VertexPosition");
prog.bindAttribLocation(1, "VertexNormal");
if( ! prog.link() )
{
printf("Shader program failed to link!\n%s",
prog.log().c_str());
exit(1);
}
if( ! prog.validate() )
{
printf("Program failed to validate!\n%s",
prog.log().c_str());
exit(1);
}
prog.use();
}
设置uniform变量:
- void CGL::setUniform()
- {
- mat4 model = mat4(1.0f);
- //model *= glm::rotate(model, -35.0f, vec3(1.0f,0.0f,0.0f));
- // model *= glm::rotate(model, 35.0f, vec3(0.0f,1.0f,0.0f));
- mat4 view = glm::lookAt(vec3(0.0f,5.0f,10.0f), vec3(-1.0f,2.0f,0.0f), vec3(0.0f,1.0f,0.0f));
- mat4 projection = glm::perspective(45.0f, 4.0f / 3.0f, 0.1f, 100.0f);
- mat4 mv = view * model;
- prog.setUniform("Kd", 0.6f, 0.9f, 0.9f);
- prog.setUniform("Ld", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
- prog.setUniform("LightPosition", view * vec4(-5.0f,20.0f,15.0f,1.0f) );
- prog.setUniform("ModelViewMatrix", mv);
- prog.setUniform("NormalMatrix",mat3( vec3(mv[0]), vec3(mv[1]), vec3(mv[2]) ));
- prog.setUniform("MVP", projection * mv);
- }
void CGL::setUniform()
{
mat4 model = mat4(1.0f);
//model *= glm::rotate(model, -35.0f, vec3(1.0f,0.0f,0.0f));
// model *= glm::rotate(model, 35.0f, vec3(0.0f,1.0f,0.0f));
mat4 view = glm::lookAt(vec3(0.0f,5.0f,10.0f), vec3(-1.0f,2.0f,0.0f), vec3(0.0f,1.0f,0.0f));
mat4 projection = glm::perspective(45.0f, 4.0f / 3.0f, 0.1f, 100.0f);
mat4 mv = view * model;
prog.setUniform("Kd", 0.6f, 0.9f, 0.9f);
prog.setUniform("Ld", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
prog.setUniform("LightPosition", view * vec4(-5.0f,20.0f,15.0f,1.0f) );
prog.setUniform("ModelViewMatrix", mv);
prog.setUniform("NormalMatrix",mat3( vec3(mv[0]), vec3(mv[1]), vec3(mv[2]) ));
prog.setUniform("MVP", projection * mv);
}
顶点shader:
- #version 400
- layout (location = 0) in vec3 VertexPosition;
- layout (location = 1) in vec3 VertexNormal;
- out vec3 LightIntensity;
- uniform vec4 LightPosition; // Light position in eye coords.
- uniform vec3 Kd; // Diffuse reflectivity
- uniform vec3 Ld; // Diffuse light intensity
- uniform mat4 ModelViewMatrix;
- uniform mat3 NormalMatrix;
- uniform mat4 MVP;
- void main()
- {
- vec3 tnorm = normalize(NormalMatrix * VertexNormal);
- vec4 eyeCoords = ModelViewMatrix * vec4(VertexPosition, 1.0);
- vec3 s = normalize(vec3(LightPosition - eyeCoords));
- LightIntensity = Ld * Kd * max(dot(s,tnorm),0.0);
- gl_Position = MVP * vec4( VertexPosition, 1.0);
- }
#version 400
layout (location = 0) in vec3 VertexPosition;
layout (location = 1) in vec3 VertexNormal;
out vec3 LightIntensity;
uniform vec4 LightPosition; // Light position in eye coords.
uniform vec3 Kd; // Diffuse reflectivity
uniform vec3 Ld; // Diffuse light intensity
uniform mat4 ModelViewMatrix;
uniform mat3 NormalMatrix;
uniform mat4 MVP;
void main()
{
vec3 tnorm = normalize(NormalMatrix * VertexNormal);
vec4 eyeCoords = ModelViewMatrix * vec4(VertexPosition, 1.0);
vec3 s = normalize(vec3(LightPosition - eyeCoords));
LightIntensity = Ld * Kd * max(dot(s,tnorm),0.0);
gl_Position = MVP * vec4( VertexPosition, 1.0);
}片段shader:
- #version 400
- in vec3 LightIntensity;
- out vec4 gl_FragColor;
- void main(void)
- {
- gl_FragColor = vec4(LightIntensity, 1.0);
- }
#version 400
in vec3 LightIntensity;
out vec4 gl_FragColor;
void main(void)
{
gl_FragColor = vec4(LightIntensity, 1.0);
}最后就是渲染了:
- glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, bunny.vertices.size() );
glDrawArrays(GL_TRIANGLES, 0, bunny.vertices.size() );跳出渲染循环的时候,别忘了删除缓存内容:
- void CGL::clean()
- {
- glDeleteBuffers(1, &vertexbuffer);
- prog.deleteProgram();
- glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &VertexArrayID);
- }
void CGL::clean()
{
glDeleteBuffers(1, &vertexbuffer);
prog.deleteProgram();
glDeleteVertexArrays(1, &VertexArrayID);
}
运行结果如下:
ADS 着色(AmbientDiffuseSpecular Shading)
ADS就是上面提到的光照模型,也称做Phong reflection model 或者 Phong Shading model。这时候光照的计算模型就是:
主要需要修改的是顶点shader,在着色器中实现对光照效果的计算:
basic.vert
- #version 400
- layout (location = 0) in vec3 VertexPosition;
- layout (location = 1) in vec3 VertexNormal;
- out vec3 LightIntensity;
- struct LightInfo{
- vec4 Position;
- vec3 La;
- vec3 Ld;
- vec3 Ls;
- };
- struct MaterialInfo{
- vec3 Ka;
- vec3 Kd;
- vec3 Ks;
- float Shininess;
- };
- uniform LightInfo Light;
- uniform MaterialInfo Material;
- uniform mat4 ModelViewMatrix;
- uniform mat3 NormalMatrix;
- uniform mat4 ProjectionMatrix;
- uniform mat4 MVP;
- void getEyeSpace(out vec3 norm, out vec4 position)
- {
- norm = normalize(NormalMatrix * VertexNormal);
- position = ModelViewMatrix * vec4(VertexPosition, 1.0);
- }
- vec3 phongModel(vec4 position, vec3 norm)
- {
- vec3 s = normalize(vec3(Light.Position - position));
- vec3 v = normalize(-position.xyz);
- vec3 r = reflect(-s, norm);
- vec3 ambient = Light.La * Material.Ka;
- float sDotN = max(dot(s, norm), 0.0);
- vec3 diffuse = Light.Ld * Material.Kd * sDotN;
- vec3 spec = vec3(0.0);
- if(sDotN >0.0)
- spec = Light.Ls * Material.Ks * pow(max(dot(r,v), 0.0), Material.Shininess);
- return ambient + diffuse + spec;
- }
- void main()
- {
- vec3 eyeNorm;
- vec4 eyePosition;
- getEyeSpace(eyeNorm, eyePosition);
- LightIntensity = phongModel(eyePosition, eyeNorm);
- gl_Position = MVP * vec4( VertexPosition, 1.0);
- //gl_Position = vec4( VertexPosition, 1.0);
- }
#version 400
layout (location = 0) in vec3 VertexPosition;
layout (location = 1) in vec3 VertexNormal;
out vec3 LightIntensity;
struct LightInfo{
vec4 Position;
vec3 La;
vec3 Ld;
vec3 Ls;
};
struct MaterialInfo{
vec3 Ka;
vec3 Kd;
vec3 Ks;
float Shininess;
};
uniform LightInfo Light;
uniform MaterialInfo Material;
uniform mat4 ModelViewMatrix;
uniform mat3 NormalMatrix;
uniform mat4 ProjectionMatrix;
uniform mat4 MVP;
void getEyeSpace(out vec3 norm, out vec4 position)
{
norm = normalize(NormalMatrix * VertexNormal);
position = ModelViewMatrix * vec4(VertexPosition, 1.0);
}
vec3 phongModel(vec4 position, vec3 norm)
{
vec3 s = normalize(vec3(Light.Position - position));
vec3 v = normalize(-position.xyz);
vec3 r = reflect(-s, norm);
vec3 ambient = Light.La * Material.Ka;
float sDotN = max(dot(s, norm), 0.0);
vec3 diffuse = Light.Ld * Material.Kd * sDotN;
vec3 spec = vec3(0.0);
if(sDotN >0.0)
spec = Light.Ls * Material.Ks * pow(max(dot(r,v), 0.0), Material.Shininess);
return ambient + diffuse + spec;
}
void main()
{
vec3 eyeNorm;
vec4 eyePosition;
getEyeSpace(eyeNorm, eyePosition);
LightIntensity = phongModel(eyePosition, eyeNorm);
gl_Position = MVP * vec4( VertexPosition, 1.0);
//gl_Position = vec4( VertexPosition, 1.0);
}注意这里在shader中使用了function,使用的方式和c语言中非常相似,但是返回值的定义有些不同,而且不能有重复定义,即使在不同的作用域。
程序中只要设置好相关的uniform就可以了:
- void CGL::setUniform()
- {
- mat4 model = mat4(1.0f);
- mat4 view = glm::lookAt(vec3(0.0f,5.0f,10.0f), vec3(-1.0f,2.0f,0.0f), vec3(0.0f,1.0f,0.0f));
- mat4 projection = glm::perspective(45.0f, 4.0f / 3.0f, 0.1f, 100.0f);
- mat4 mv = view * model;
- prog.setUniform("Material.Kd", 0.9f, 0.5f, 0.3f);
- prog.setUniform("Light.Ld", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
- prog.setUniform("Material.Ka", 0.9f, 0.5f, 0.3f);
- prog.setUniform("Light.La", 0.4f, 0.4f, 0.4f);
- prog.setUniform("Material.Ks", 0.8f, 0.8f, 0.8f);
- prog.setUniform("Light.Ls", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
- prog.setUniform("Material.Shininess", 100.0f);
- prog.setUniform("ModelViewMatrix", mv);
- prog.setUniform("NormalMatrix",mat3( vec3(mv[0]), vec3(mv[1]), vec3(mv[2]) ));
- prog.setUniform("MVP", projection * mv);
- }
void CGL::setUniform()
{
mat4 model = mat4(1.0f);
mat4 view = glm::lookAt(vec3(0.0f,5.0f,10.0f), vec3(-1.0f,2.0f,0.0f), vec3(0.0f,1.0f,0.0f));
mat4 projection = glm::perspective(45.0f, 4.0f / 3.0f, 0.1f, 100.0f);
mat4 mv = view * model;
prog.setUniform("Material.Kd", 0.9f, 0.5f, 0.3f);
prog.setUniform("Light.Ld", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
prog.setUniform("Material.Ka", 0.9f, 0.5f, 0.3f);
prog.setUniform("Light.La", 0.4f, 0.4f, 0.4f);
prog.setUniform("Material.Ks", 0.8f, 0.8f, 0.8f);
prog.setUniform("Light.Ls", 1.0f, 1.0f, 1.0f);
prog.setUniform("Material.Shininess", 100.0f);
prog.setUniform("ModelViewMatrix", mv);
prog.setUniform("NormalMatrix",mat3( vec3(mv[0]), vec3(mv[1]), vec3(mv[2]) ));
prog.setUniform("MVP", projection * mv);
}渲染一下。
由于关于着色的计算是在顶点shader中完成的,所以也可以称为逐顶点着色(per-vertex lighting)。
双面着色 two-sided shading
当渲染的模型是完全封闭的时候,模型中所有面的背面都是不可见的,但是,如果模型有开口的话就比较麻烦了,渲染的结果很可能并不正确,因为面的法线并不正确。这时候就需要将法线反向,然后根据反向后的法线来计算光强。
直接渲染带洞的model,结果如下:
修改一下shader:
basic.vert
- #version 400
- layout (location = 0) in vec3 VertexPosition;
- layout (location = 1) in vec3 VertexNormal;
- //out vec3 LightIntensity;
- out vec3 frontColor;
- out vec3 backColor;
- struct LightInfo{
- vec4 Position;
- vec3 La;
- vec3 Ld;
- vec3 Ls;
- };
- struct MaterialInfo{
- vec3 Ka;
- vec3 Kd;
- vec3 Ks;
- float Shininess;
- };
- uniform LightInfo Light;
- uniform MaterialInfo Material;
- uniform mat4 ModelViewMatrix;
- uniform mat3 NormalMatrix;
- uniform mat4 ProjectionMatrix;
- uniform mat4 MVP;
- void getEyeSpace(out vec3 norm, out vec4 position)
- {
- norm = normalize(NormalMatrix * VertexNormal);
- position = ModelViewMatrix * vec4(VertexPosition, 1.0);
- }
- vec3 phongModel(vec4 position, vec3 norm)
- {
- vec3 s = normalize(vec3(Light.Position - position));
- vec3 v = normalize(-position.xyz);
- vec3 r = reflect(-s, norm);
- vec3 ambient = Light.La * Material.Ka;
- float sDotN = max(dot(s, norm), 0.0);
- vec3 diffuse = Light.Ld * Material.Kd * sDotN;
- vec3 spec = vec3(0.0);
- if(sDotN >0.0)
- spec = Light.Ls * Material.Ks * pow(max(dot(r,v), 0.0), Material.Shininess);
- return ambient + diffuse + spec;
- }
- void main()
- {
- vec3 eyeNorm;
- vec4 eyePosition;
- getEyeSpace(eyeNorm, eyePosition);
- frontColor = phongModel(eyePosition, eyeNorm);
- backColor = phongModel(eyePosition, -eyeNorm);
- gl_Position = MVP * vec4( VertexPosition, 1.0);
- //gl_Position = vec4( VertexPosition, 1.0);
- }
#version 400
layout (location = 0) in vec3 VertexPosition;
layout (location = 1) in vec3 VertexNormal;
//out vec3 LightIntensity;
out vec3 frontColor;
out vec3 backColor;
struct LightInfo{
vec4 Position;
vec3 La;
vec3 Ld;
vec3 Ls;
};
struct MaterialInfo{
vec3 Ka;
vec3 Kd;
vec3 Ks;
float Shininess;
};
uniform LightInfo Light;
uniform MaterialInfo Material;
uniform mat4 ModelViewMatrix;
uniform mat3 NormalMatrix;
uniform mat4 ProjectionMatrix;
uniform mat4 MVP;
void getEyeSpace(out vec3 norm, out vec4 position)
{
norm = normalize(NormalMatrix * VertexNormal);
position = ModelViewMatrix * vec4(VertexPosition, 1.0);
}
vec3 phongModel(vec4 position, vec3 norm)
{
vec3 s = normalize(vec3(Light.Position - position));
vec3 v = normalize(-position.xyz);
vec3 r = reflect(-s, norm);
vec3 ambient = Light.La * Material.Ka;
float sDotN = max(dot(s, norm), 0.0);
vec3 diffuse = Light.Ld * Material.Kd * sDotN;
vec3 spec = vec3(0.0);
if(sDotN >0.0)
spec = Light.Ls * Material.Ks * pow(max(dot(r,v), 0.0), Material.Shininess);
return ambient + diffuse + spec;
}
void main()
{
vec3 eyeNorm;
vec4 eyePosition;
getEyeSpace(eyeNorm, eyePosition);
frontColor = phongModel(eyePosition, eyeNorm);
backColor = phongModel(eyePosition, -eyeNorm);
gl_Position = MVP * vec4( VertexPosition, 1.0);
//gl_Position = vec4( VertexPosition, 1.0);
}basic.frag
- #version 400
- //in vec3 LightIntensity;
- in vec3 frontColor;
- in vec3 backColor;
- out vec4 gl_FragColor;
- void main(void)
- {
- if(gl_FrontFacing) gl_FragColor = vec4(frontColor, 1.0);
- else gl_FragColor = vec4(backColor, 1.0);
- }
#version 400
//in vec3 LightIntensity;
in vec3 frontColor;
in vec3 backColor;
out vec4 gl_FragColor;
void main(void)
{
if(gl_FrontFacing) gl_FragColor = vec4(frontColor, 1.0);
else gl_FragColor = vec4(backColor, 1.0);
}在basic.vert中计算出内部和外部的片段颜色,然后在片段着色器中根据 gl_FrontFacing 来判断面是否为背面,然后分开着色,再渲染一下
平坦着色 flat shading
这个着色方式是想对于Gouraud Shading (高洛德着色/高氏着色)来说的。
Gouraud Shading 在游戏中使用最广泛的一种着色方式。它可对3D模型各顶点的颜色进行平滑、融合处理,将每个多边形上的每个点赋以一组色调值,同时将多边形着上较为顺滑的渐变色,使其外观具有更强烈的实时感和立体动感,不过其着色速度比平面着色慢得多。
在shader中要实现flat shading非常简单,只要在 in out 参数的前面加上flat关键字就可以了。
baisic .vert
- ......
- flat out vec3 LightIntensity;
- ....
......
flat out vec3 LightIntensity;
....basic.frag
- ...
- flat in vec3 LightIntensity;
- ...
...
flat in vec3 LightIntensity;
...渲染一下,对比两种效果:









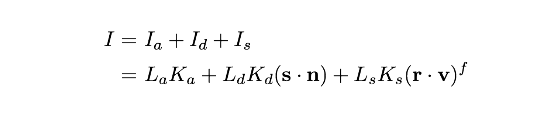


















 2896
2896

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








