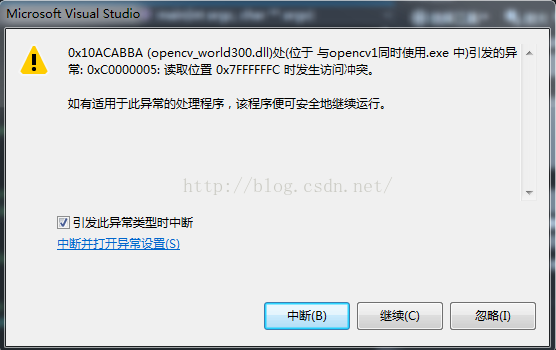
错误:opencv文档中的core,“与opencv1同时使用“的例程,运行时报内存访问冲突的错误。 如图:
原因是由于vector<Mat>planes;容器planes为空,与I_YUV不符合,可以改为Mat planes[3]。
改后marge需要输入三个参数,输入矩阵,输入矩阵个数,输出矩阵
即:把merge(planes, I_YUV);改为merge(planes,3, I_YUV);
修改之后的代码:
#include<opencv2/opencv.hpp>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
static void help(char* progName)
{
cout << endl << progName
<< " shows how to use cv::Mat and IplImages together (converting back and forth)." << endl
<< "Also contains example for image read, spliting the planes, merging back and " << endl
<< " color conversion, plus iterating through pixels. " << endl
<< "Usage:" << endl
<< progName << " [image-name Default: ../data/lena.jpg]" << endl << endl;
}
//! [start]
// comment out the define to use only the latest C++ API
#define DEMO_MIXED_API_USE
#ifdef DEMO_MIXED_API_USE
# include <opencv2/highgui/highgui_c.h>
# include <opencv2/imgcodecs/imgcodecs_c.h>
#endif
int main(int argc, char** argv)
{
help(argv[0]);
const char* imagename = "DSC_2257.JPG";
#ifdef DEMO_MIXED_API_USE
Ptr<IplImage> IplI(cvLoadImage(imagename)); // Ptr<T> is a safe ref-counting pointer class
if (!IplI)
{
cerr << "Can not load image " << imagename << endl;
return -1;
}
Mat I = cv::cvarrToMat(IplI); // Convert to the new style container. Only header created. Image not copied.
#else
Mat I = imread(imagename); // the newer cvLoadImage alternative, MATLAB-style function
if (I.empty()) // same as if( !I.data )
{
cerr << "Can not load image " << imagename << endl;
return -1;
}
#endif
//! [start]
//! [new]
// convert image to YUV color space. The output image will be created automatically.
Mat I_YUV;
cvtColor(I, I_YUV, COLOR_BGR2YCrCb);
Mat planes[3]; // Use the STL's vector structure to store multiple Mat objects
split(I_YUV, planes); // split the image into separate color planes (Y U V)
//! [new]
#if 1 // change it to 0 if you want to see a blurred and noisy version of this processing
//! [scanning]
// Mat scanning
// Method 1. process Y plane using an iterator
MatIterator_<uchar> it = planes[0].begin<uchar>(), it_end = planes[0].end<uchar>();
for (; it != it_end; ++it)
{
double v = *it * 1.7 + rand() % 21 - 10;
*it = saturate_cast<uchar>(v*v / 255);
}
for (int y = 0; y < I_YUV.rows; y++)
{
// Method 2. process the first chroma plane using pre-stored row pointer.
uchar* Uptr = planes[1].ptr<uchar>(y);
for (int x = 0; x < I_YUV.cols; x++)
{
Uptr[x] = saturate_cast<uchar>((Uptr[x] - 128) / 2 + 128);
// Method 3. process the second chroma plane using individual element access
uchar& Vxy = planes[2].at<uchar>(y, x);
Vxy = saturate_cast<uchar>((Vxy - 128) / 2 + 128);
}
}
//! [scanning]
#else
//! [noisy]
Mat noisyI(I.size(), CV_8U); // Create a matrix of the specified size and type
// Fills the matrix with normally distributed random values (around number with deviation off).
// There is also randu() for uniformly distributed random number generation
randn(noisyI, Scalar::all(128), Scalar::all(20));
// blur the noisyI a bit, kernel size is 3x3 and both sigma's are set to 0.5
GaussianBlur(noisyI, noisyI, Size(3, 3), 0.5, 0.5);
const double brightness_gain = 0;
const double contrast_gain = 1.7;
#ifdef DEMO_MIXED_API_USE
// To pass the new matrices to the functions that only work with IplImage or CvMat do:
// step 1) Convert the headers (tip: data will not be copied).
// step 2) call the function (tip: to pass a pointer do not forget unary "&" to form pointers)
IplImage cv_planes_0 = planes[0], cv_noise = noisyI;
cvAddWeighted(&cv_planes_0, contrast_gain, &cv_noise, 1, -128 + brightness_gain, &cv_planes_0);
#else
addWeighted(planes[0], contrast_gain, noisyI, 1, -128 + brightness_gain, planes[0]);
#endif
const double color_scale = 0.5;
// Mat::convertTo() replaces cvConvertScale.
// One must explicitly specify the output matrix type (we keep it intact - planes[1].type())
planes[1].convertTo(planes[1], planes[1].type(), color_scale, 128 * (1 - color_scale));
// alternative form of cv::convertScale if we know the datatype at compile time ("uchar" here).
// This expression will not create any temporary arrays ( so should be almost as fast as above)
planes[2] = Mat_<uchar>(planes[2] * color_scale + 128 * (1 - color_scale));
// Mat::mul replaces cvMul(). Again, no temporary arrays are created in case of simple expressions.
planes[0] = planes[0].mul(planes[0], 1. / 255);
//! [noisy]
#endif
//! [end]
merge(planes,3, I_YUV); // now merge the results back
cvtColor(I_YUV, I, COLOR_YCrCb2BGR); // and produce the output RGB image
namedWindow("image with grain", WINDOW_AUTOSIZE); // use this to create images
#ifdef DEMO_MIXED_API_USE
// this is to demonstrate that I and IplI really share the data - the result of the above
// processing is stored in I and thus in IplI too.
cvShowImage("image with grain", IplI);
#else
imshow("image with grain", I); // the new MATLAB style function show
#endif
//! [end]
waitKey();
// Tip: No memory freeing is required!
// All the memory will be automatically released by the Vector<>, Mat and Ptr<> destructor.
return 0;
}





















 2358
2358

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








