具体的缓冲类有filebuf,stringbuf,由于filebuf的大部分工作都转交给了C流,不好分析,所以重点分析的还是stringbuf。
对于stringstream,我们最常用的语句就是:
string s="1.2 5.6 7 7 ";
istringstream is(s);
float f;
is >> f;上述语句,给出了stringbuf的基本形式:以string初始化;
首先,假设我们已经都了解了stringstream的基本用法:ostringstream:向string中写数据;istringstream:从string中读取数据;
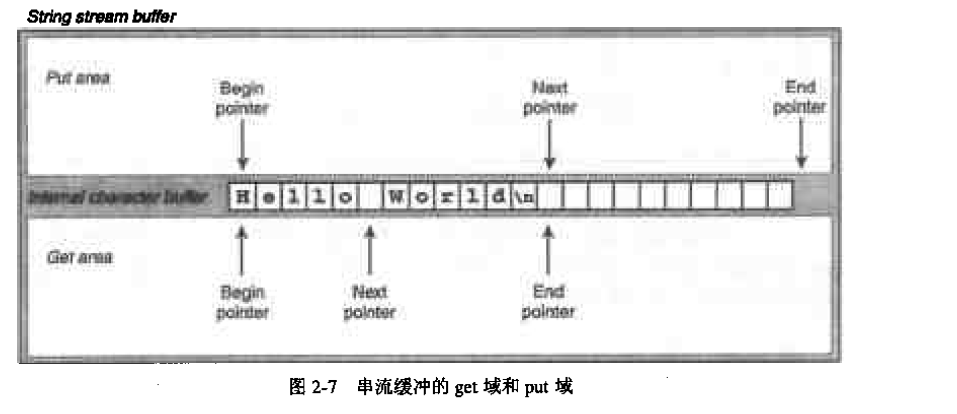
首先我们来说明一下stringbuf中的六个指针:其实在basic_stingbuf<>中,input和output共用缓冲区,且read操作的字符永远包含在write操作的字符之内,即先write后read:
这六个指针明确了,大部分问题就解决了。
首先看一下数据成员:
typedef basic_stringbuf<_Elem,_Traits,_Alloc> _Myt;
typedef _Alloc allocator_type;
typedef basic_streambuf<_Elem,_Traits> _Mysb;
typedef basic_string<_Elem,_Traits,_Alloc> _Mystr;
typedef typename _Traits::int_type int_type;
typedef typename _Traits::pos_type pos_type;
typedef typename _Traits::off_type off_type;
_Elem* _seekhigh;
_Strstate _mystate;//stream state
allocator_type _alloc;对于流缓冲类需要知道一些状态信息,来决定basic_stringbuf<>的行为,具体的状态信息如下:
enum
{//constants for bits in stream state
_Allocated=1,//set if character array storage has been allocated
_Constant=2,//set if character array nonmutable
_Noread=4,//set if character array cannot be read
_Append=8,//set if all writes are qppends
_Atend=16};//set if initial writes are appends
typedef int _Strstate;
_Strstate _Getstate(ios_base::openmode _mode)
{//convert open mode to stream state bits
_Strstate _state=(_Strstate)0;
if(!(_mode &ios_base::in))
_state|=_Noread;
if(!(_mode&ios_base::out))
_state|=_Constant;
if(_mdoe&ios_base::app)
_state|=_Append;
if(_mode&ios_base::ate)
_state|=_Atend;
return (_state);
}
其中_Getstate()用来将openmode的信息,转化成自己所需要的状态信息。
初始化过程:
explicit basic_stringbuf(ios_base::openmode _mode=ios_base::in|ios_base::out)
{
_Init(0,0,_Getstate(_mode));
}
explicit basic_stringbuf(const _Mystr& _str,ios_base::openmode _mode=ios_base::in|ios_base::out)
{
_Init(_str.c_str(),_str.size(),_Getstate(_mode));
}
void _Init(const _Elem* _ptr,size_t _count,_Strstate _state)
{//initialize buffer to[_ptr,_ptr+_count),set state
_seekhigh=0;
_mystate=_state;
if(_count!=0 &&(_mystate&(_Noread|_Constant))!=(_Noread|_Constant)){
//buffer that be read or writer
_Elem* _pnew=_alloc.allocate(_count);
_Traits::copy(_pnew,_ptr,_count);
_seekhigh=_pnew+_count;
if(!(_mystate &_Noread))
_Mysb::setg(_pnew,_pnew,_pnew+_count);//set up read buffer
if(!(_mystate &_Constant)){
//set up writer buffer,是追加模式还是重置模式
_Mysb::setp(_pnew,(_mystate&_Atend)?_pnew+_count:_pnew,_pnew+_count);
if(_Mysb::gptr()==0)
_Mysb::setg(_pnew,0,_pnew);
}
_mystate|=_Allocate;
}
}
其中的主要工作转交给了_init函数,首先复制ptr指向的数组的内容,然后此函数根据状态信息初始化六个指针;
然后是stringstream中特有的两个函数str()和str(newstr),str()用来返回流中的内容,如果流既可以读也可以写,返回所有而不只是input缓冲区中的,如果这可以读,则返回input区中的内容,具体实现参见下述代码,而str(newstr)用来将流中的数据重置为newstr;
_Mystr str() const
{//return string copy of character array
if(!(_mystate&_Constant)&&_Mysb::pptr()!=0)
{//writable,make string from write buffer
_Mystr _str(_Mysb::pbase(),(_seekhigh<_Mysb::pptr()
?_Mysb::pptr() :_seekhigh)-_Mysb::pbase());
return (_str);
}else if(!(_mystate& _Noread) &&_Myssb::gptr()!=0){
//readable.make string from read buffer
_Mystr _str(_Mysb::eback(),_Mysb::egptr()-_Mysb::eback());
return (_str);
}else{
_Mystr _nul;
return (_nul);
}
}
void str(const _Mystr& _newstr)
{
_Tidy();
_Init(_newstr.c_str(),_newstr.size(),_mystate);
}下面进入正题,正如我们上一篇文章中讨论的那样,一个流的具体实现的关键环节在于那几个关键的虚函数,overflow,underflow,uflow,pbackfail,seekpos,seekoff:
virtual int_type overflow(int_type _meta=_Traits::eof())
{
if(_mystate &_Append &&_Mysb::pptr()!=0 &&_Mysb::pptr()<_seekhigh)
_Mysb::setp(_Mysb::pbase(),_seekhigh,_mystate);
if(_Traits::eq_int_type(_Traits::eof(),_meta))
return (_Traits::not_eof(_meta));//EOF return success code
else if(_Mysb::pptr()!=0 &&_Mysb::pptr()<_Mysb::epptr()){
*_Mysb::_Pninc=_Traits::to_char_type(_meta);
return (_meta);
}
else if(_mystate &_Constant)
return (_Traits::eof());//array cannot write,fail
else{//grow buffer and store
size_t _oldsize=_mysb::pptr()==0?0:_Mysb::epptr()-_Mysb::eback();
size_t _newsize=_oldsize;
size_t _inc=_newsize/2<_MINSIZE?_MINSIZE:_newsize/2;//grow by 0.5 _MINSIZE=32
while(0<_inc &&INT_MAX-_inc<_newsize)
_inc/=2;
if(_inc==0)
return(_Traits::eof());//buffer cannot grow,增长的极限
_newsize+=_inc;
//上述代码确定增长的大小
//分配空间
_Elem* _newptr=_alloc.allocate(_newsize);
_Elem* _oldptr=_Mysb::eback();
//先将原来的数据复制进新的缓冲区
if(0<_oldsize)
_Traits::copy(_newptr,_oldptr,_oldsize);
//如果原来的缓冲区大小为0,根据状态信息设置指针位置
if(_oldsize==0){//first growth,set up pointer
_seekhigh=_newptr;
_Mysb::setp(_newptr,_newptr+_newsize);
if(_mystate &_Noread)
_Mysb::setg(_newptr,0,_newptr);
else
_Mysb::setg(_newptr,_newptr,_newptr+1);
}
else{//一般情况下的指针位置设置
_seekhigh=_newptr+(_seekhigh-_oldptr);
_Mysb::setp(_newptr+(_Mysb::pbase()-_oldptr),_newptr + (_Mysb::pptr() - _oldptr),_newptr + _newsize);
if(_mystate &_Noread)
_Mysb::setg(_newptr,0,_newptr);
else
_Mysb::setg(_newptr,_newptr+(_Mysb::gptr()-_oldptr),_Mysb::pptr()+1);
}
//如果我们以前的内存是通过分配器分的,那么就再通过它删除,同时,这次的内存一定是分配器分的,所以
//设置状态
if(_mystate &_Allocated)
_alloc.deallocate(_oldptr,_oldsize);
_mystate|=_Allocated;
//写入字符
*_Mysb::_Pninc()=_Traits::to_char_type(_meta);
return(_meta);
}
}上述代码给出了overflow的实现,也就是当write缓冲区已满,我们应该怎么做?这里的实现是使缓冲区增长为原来的1.5倍。具体的代码
对于underflow和uflow:
virtual int_type underflow()
{
//不能读取得情况下,读取失败
if(_Mysb::gptr()==0)
return (_Traits::eof());
//正常情况下,正常读取
else if (_Mysb::gptr()<_Mysb::egptr())
return(_Traits::to_int_type(*_Mysb::gptr()));
//不能读取情况有下述几种情况:
else if(_mystate & _Noread || _Mysb::pptr() == 0|| _Mysb::pptr() <= _Mysb::gptr()
&& _seekhigh <= _Mysb::gptr())
return (_Traits::eof()); // can't read, fail
else{//extend read buffer into written area
//这才是underflow的菜,如果发现read区的结尾指针小于write区,那么把结尾指针移动write区的pptr()
if(_seekhigh<_Mysb::pptr())
_seekhigh=_Mysb::pptr();
_Mysb::setg(_Mysb::eback(),_Mysb::gptr(),_seekhigh);
return (_Traits::to_int_type(*_Mysb::gptr()));
}
}下面是pbackfail:
virtual int_type pbackfail(int_type _meta=_Traits::eof())
{//put an element back to stream
if (_Mysb::gptr() == 0|| _Mysb::gptr() <= _Mysb::eback()|| !_Traits::eq_int_type(_Traits::eof(), _meta)
&& !_Traits::eq(_Traits::to_char_type(_meta), _Mysb::gptr()[-1])&& _mystate & _Constant)
return (_Traits::eof());//fail
else{
_Mysb::gbump(-1);
if(!_Traits::eq_int_type(_Traits::eof(),_meta))
*_Mysb::gptr()=_Traits::to_char_type(_mate);
return (_Traits::not_eof(_meta));
}
}最后是seekoff和seekpos,由于在stringbuf中两者的相似性,下面仅附seekoff的代码:
virtual pos_type seekoff(off_type _off,ios_base::seekdir _way,ios_base::openmode _mode=ios_base::in | ios_base::out)
{
//首先更新_seekhigh
if(_Mysb::pptr()!=0 &&_seekhigh<_Mysb::pptr())
_seekhigh=_Mysb::pptr();//update seekhigh
//调整read区
if(_mode&ios_base::in && _Mysb::gptr()!=0){//position within read buffer
if(_way==ios_base::end)
_off+=(off_type)(_Mysb::gptr()-_Mysb::eback());
else if (_way == ios_base::cur
&& (_mode & ios_base::out) == 0)
_off += (off_type)(_Mysb::gptr() - _Mysb::eback());
else if (_way != ios_base::beg)
_off = _BADOFF;
if (0 <= _off && _off <= _seekhigh - _Mysb::eback())
{ // change read position
_Mysb::gbump((int)(_Mysb::eback() - _Mysb::gptr() + _off));
if (_mode & ios_base::out && _Mysb::pptr() != 0)
_Mysb::setp(_Mysb::pbase(), _Mysb::gptr(),
_Mysb::epptr()); // change write position to match
}
else
_off = _BADOFF;
}
//调整write区
else if (_mode & ios_base::out && _Mysb::pptr() != 0)
{ // position within write buffer
if (_way == ios_base::end)
_off += (off_type)(_seekhigh - _Mysb::eback());
else if (_way == ios_base::cur)
_off += (off_type)(_Mysb::pptr() - _Mysb::eback());
else if (_way != ios_base::beg)
_off = _BADOFF;
if (0 <= _off && _off <= _seekhigh - _Mysb::eback())
_Mysb::pbump((int)(_Mysb::eback()
- _Mysb::pptr() + _off)); // change write position
else
_off = _BADOFF;
}
else if (_off != 0)
_off = _BADOFF; // neither read nor write buffer selected, fail
return (pos_type(_off));
}
//seekpos 就不写了至此,basic_stringbuf<>的关键部分就完成了。
对于针对是istringstream还是ostreamstring所用的缓冲区,对basic_stringbuf的openmode传递不同的参数即可。
























 1401
1401

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








