1. 介绍
并发修改ConcurrentModificationException错误是开发中一个常见错误,多发生在对一个Collection边遍历边做影响size变化的操作中,下面以ArrayList为例分析ConcurrentModificationException错误。
2. 分析
ArrayList初始数据如下。
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);场景1:不会有并发修改错误
int length = list.size();
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++) {
if (list.get(i).equals(2)) {
list.add(10);
}
}场景2:会有并发修改错误
for(int temp : list) {
if(temp == 2) {
list.add(10);
}
}场景3:会有并发修改错误
Iterator<Integer> iterator = list.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()) {
if(iterator.next().equals(2)) {
list.add(10);
}
}场景4:没有并发修改问题
ListIterator<Integer> listIterator = list.listIterator();
while (listIterator.hasNext()) {
if (listIterator.next().equals(2)) {
listIterator.add(10);
}
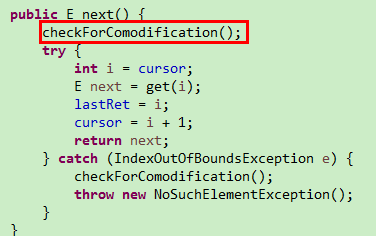
}其实ConcurrentModificationException异常的抛出是由于checkForComodification(AbstractList类中)方法的调用引起的
private void checkForComodification() {
if (this.modCount != l.modCount)
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}而checkForComodification方法的调用发生在Iterator相关api方法中,
在调用list的iterator方法会创建一个Itr对象、
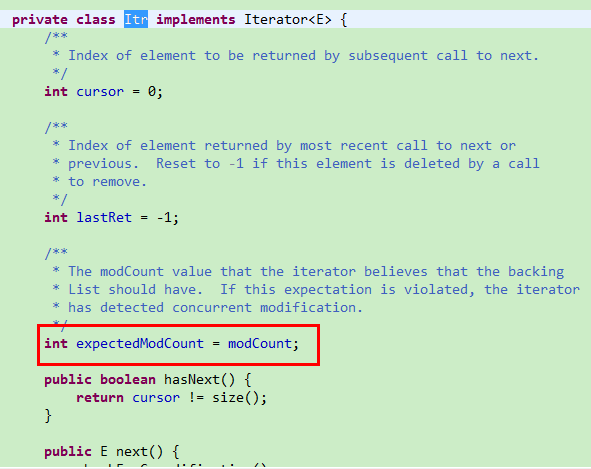
在创建会与AbstractList的modCount赋予相同的值, 而在Itr的next方法中会调用checkForComodification
在场景3中,list.add操作更改modCount的值,所以会有并发修改错误
而场景1中并没有使用iterator相关api,add操作虽然修改了modCount但是不会检查modCount所以没有并发修改错误。
场景4中,ListItr类add方法
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
ArrayList.this.add(i, e);
cursor = i + 1;
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}其中9行:在调用了list.add操作之后,将ListItr中的expectedModCount与AbstractList中的modCount进行了同步,所以在下次调用next也就不会抛出异常了,此时假如以后不调用next或者又重新创建了 ListItr也不会有异常抛出。
最后场景2并没有使用Iterator中的api为什么也抛出了异常了。其实编译器会将for-each循环代码编译为Iterator相关api的调用。
为了便于查看编译后的代码这里添加一个“———-”打印。
List<Integer> list = new ArrayList<Integer>();
list.add(1);
list.add(2);
list.add(3);
System.out.println("------------");
for (int temp : list) {
if (temp == 2) {
list.add(10);
}
}编译后的字节码为:
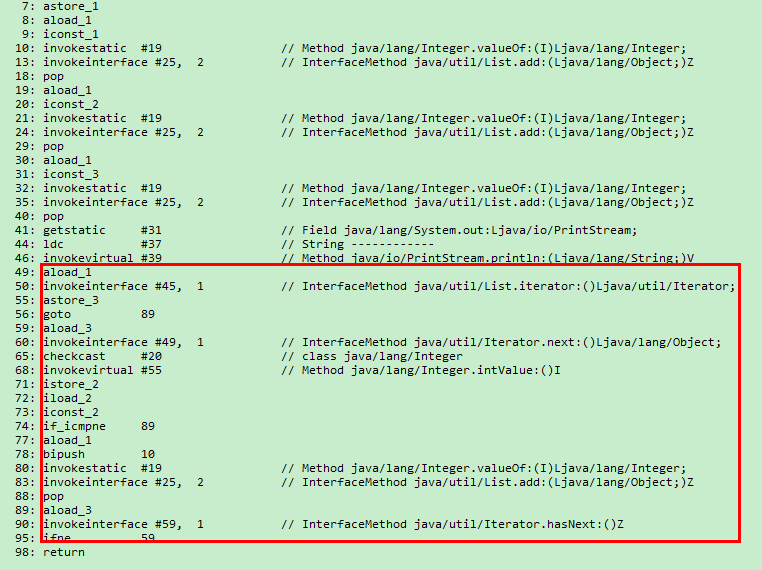
所以场景2和场景3是一样的,也会抛出异常了。






















 650
650

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








